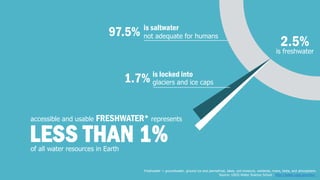
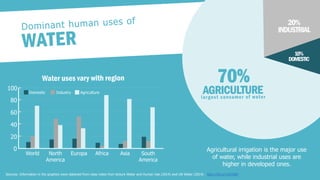
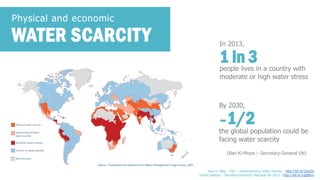
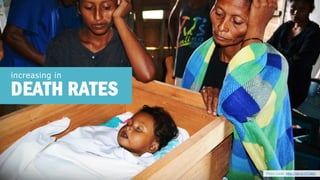
The document discusses the increasing challenge of accessing clean and safe water amidst growing global populations, overconsumption, and pollution. It highlights the importance of water for all life forms and outlines several causes of water scarcity, particularly focusing on the drought situation in São Paulo, Brazil. Additionally, the document proposes various sustainable management and conservation strategies, including responsible usage behaviors and infrastructure investments.