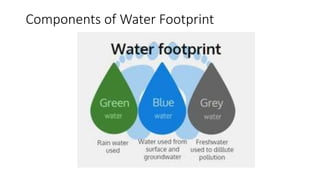
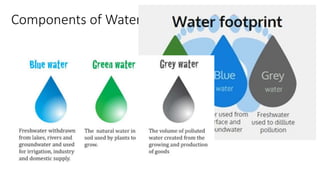
The document discusses the concept of water footprint, which measures the total volume of freshwater used to produce goods and services, highlighting its importance due to the scarcity of freshwater resources. It differentiates between water footprint and virtual water, emphasizing that the former is a multidimensional indicator that also considers the location and timing of water use. Additionally, it introduces the Water Footprint Network, established to promote sustainable and equitable water management globally through shared accounting standards.