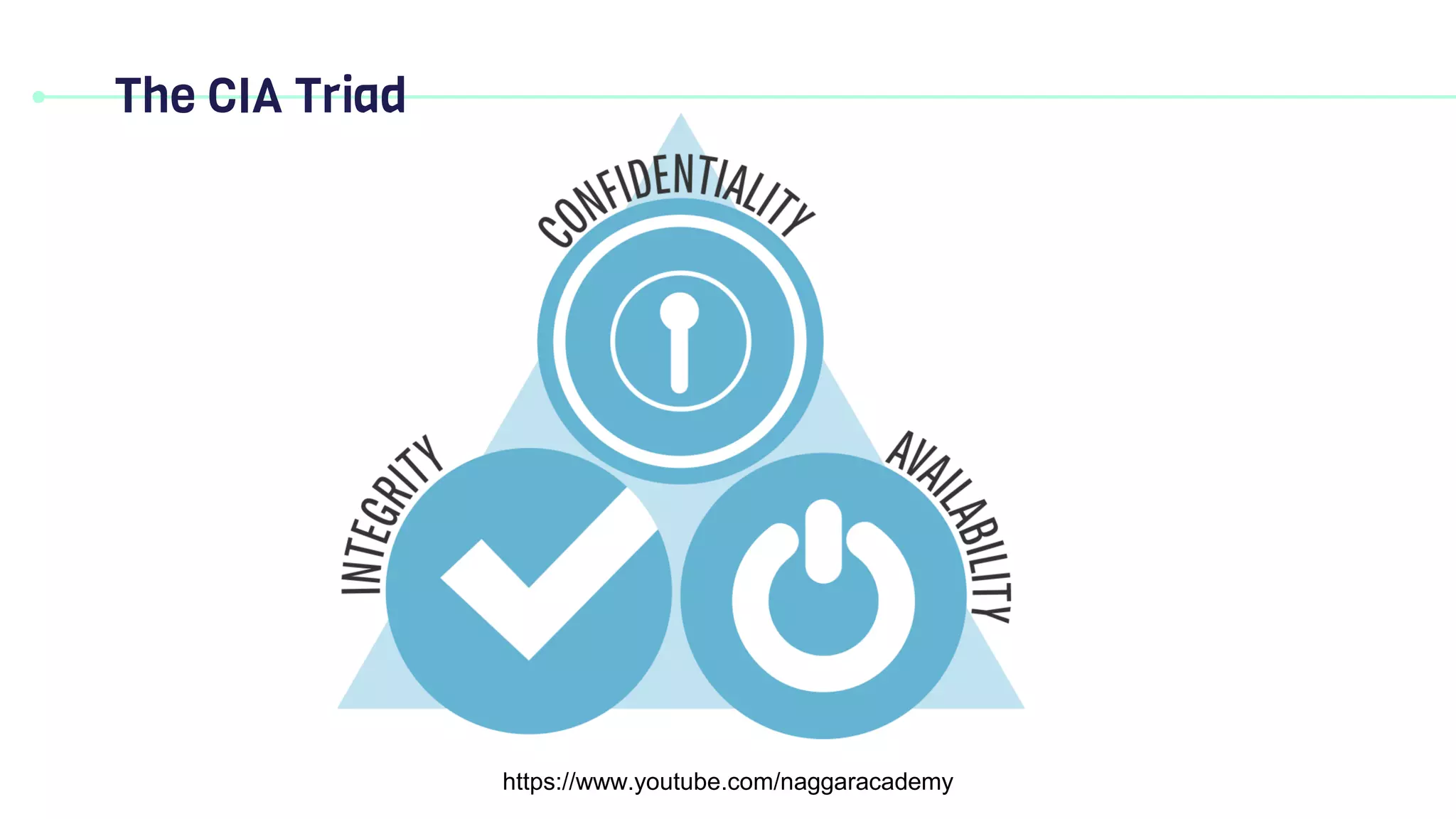
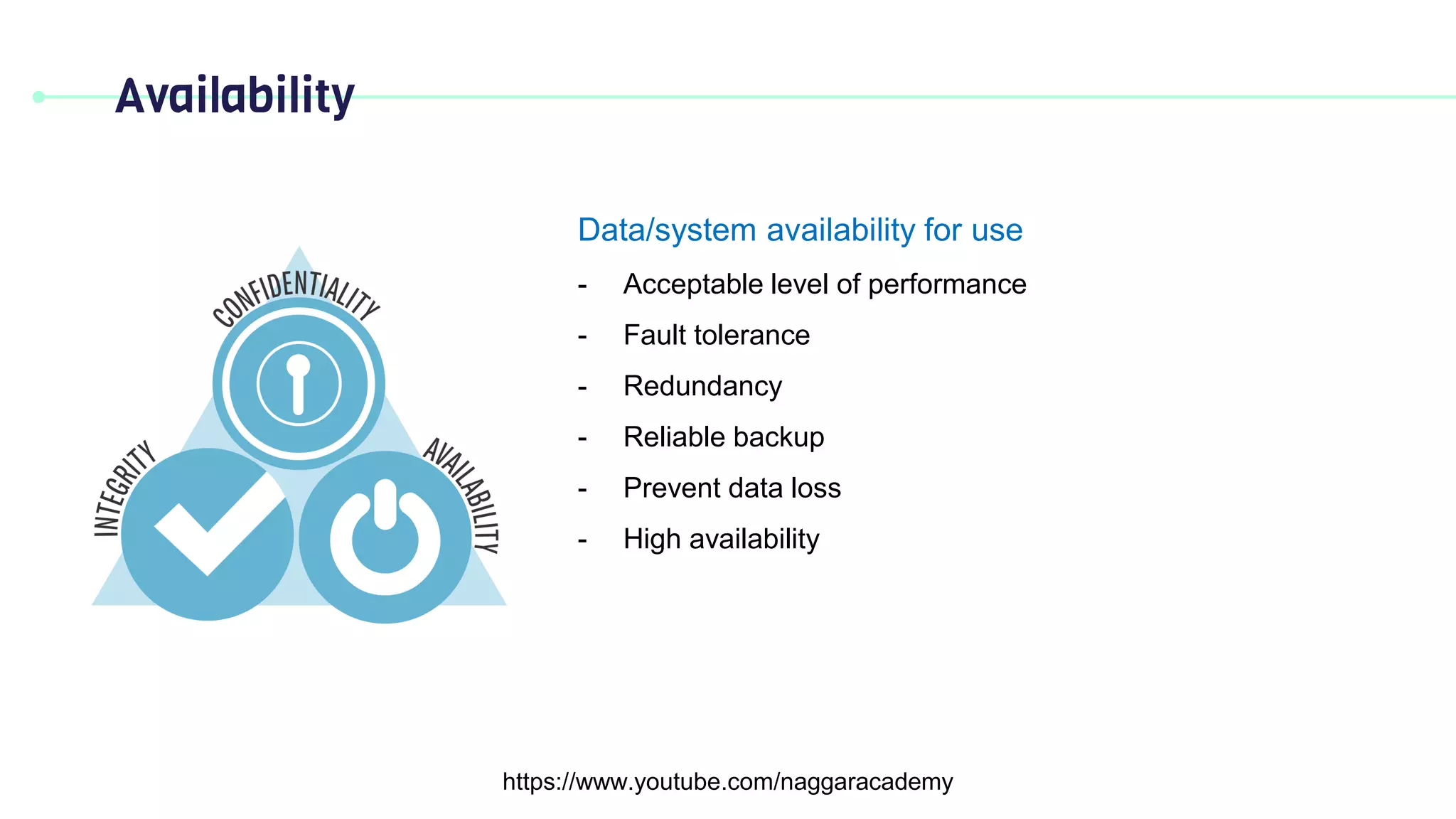
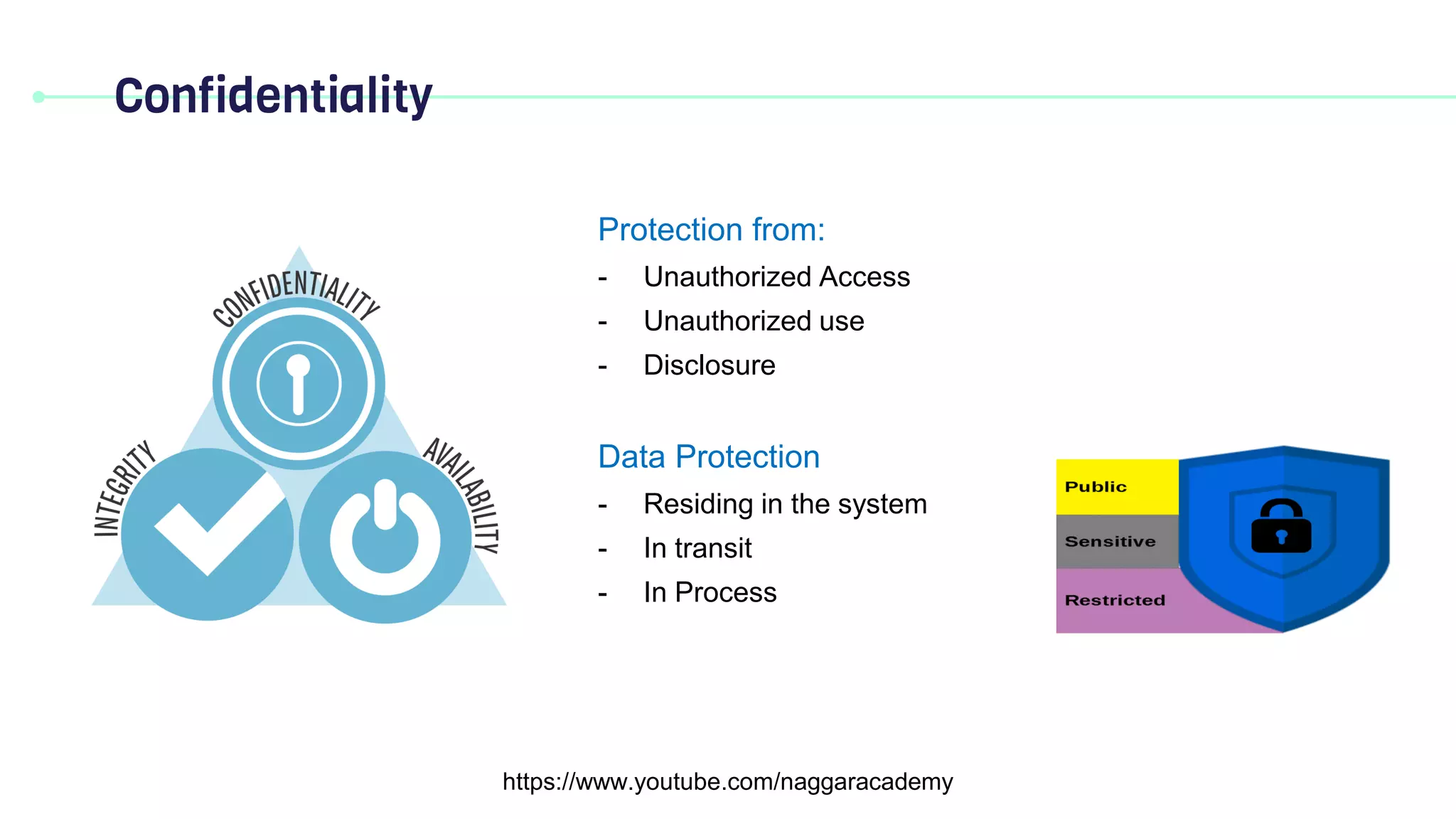
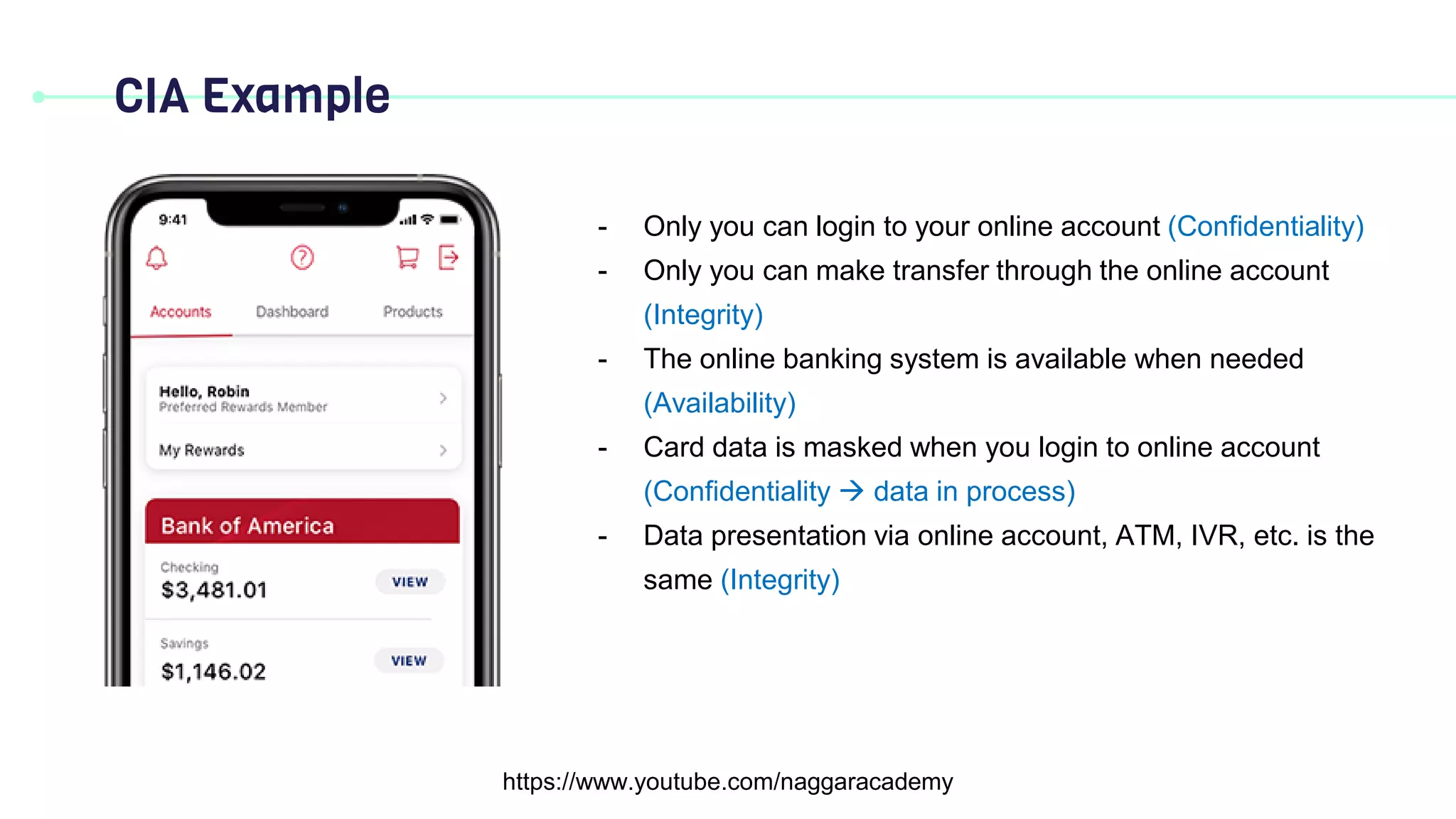
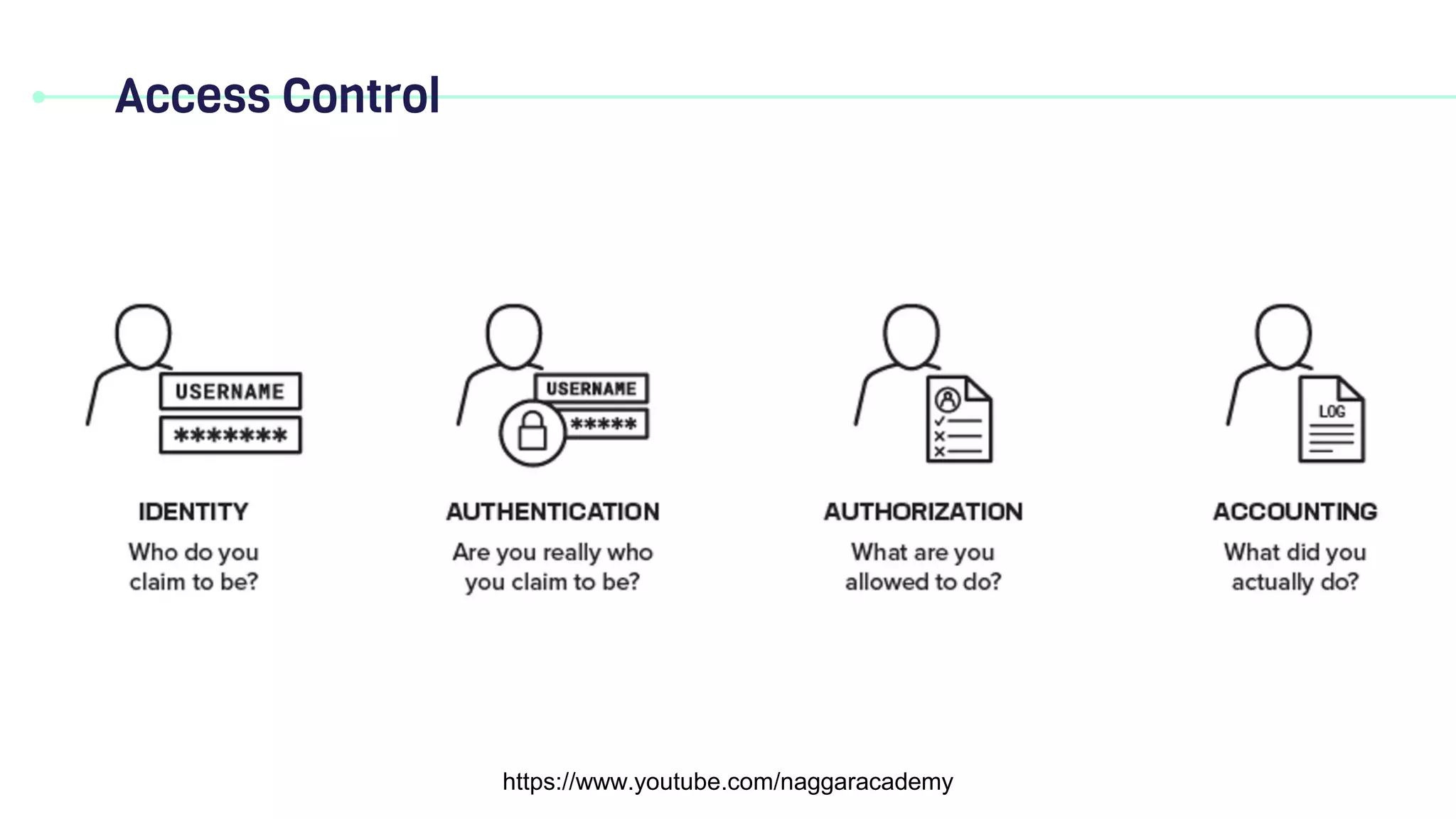
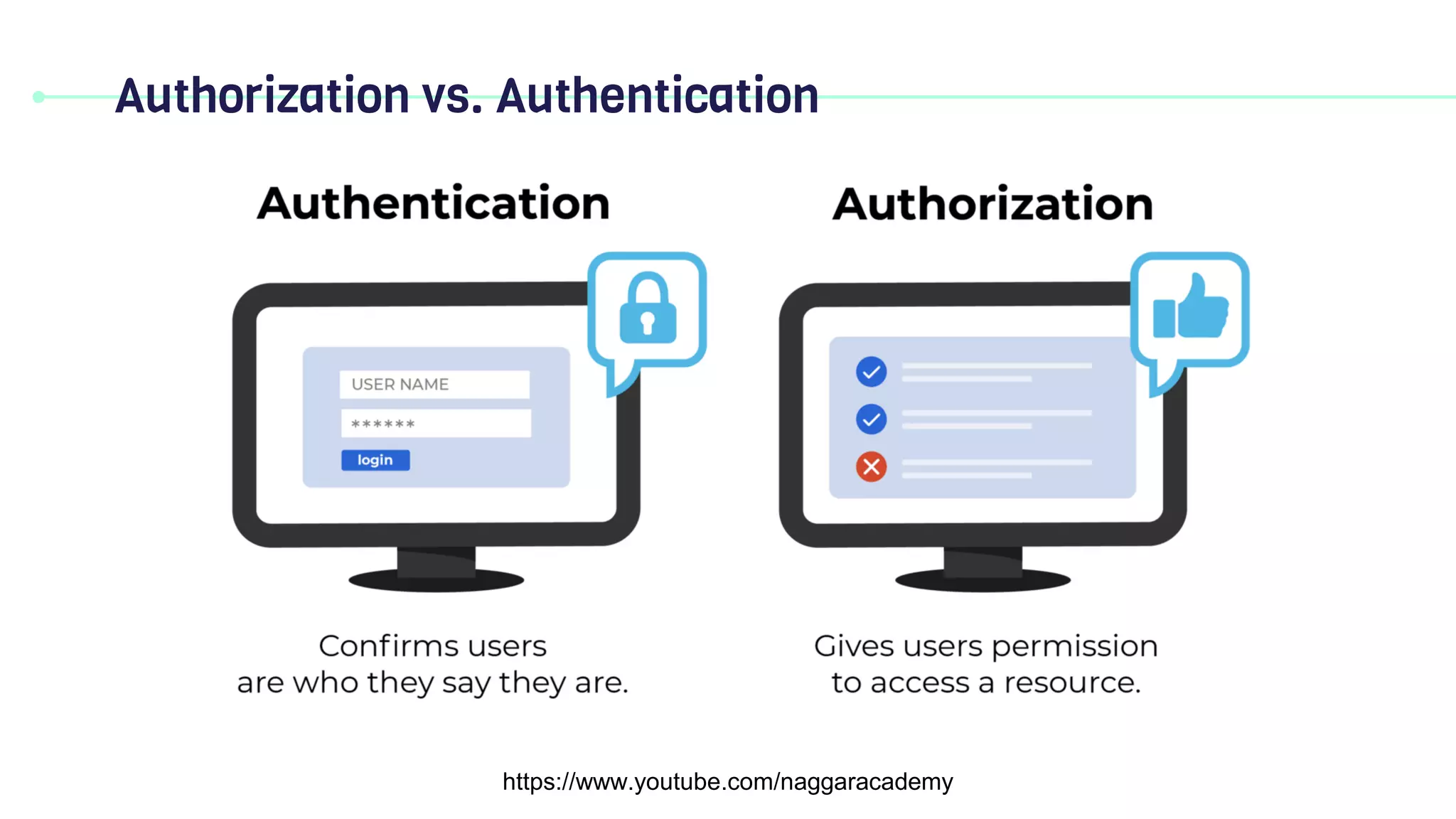
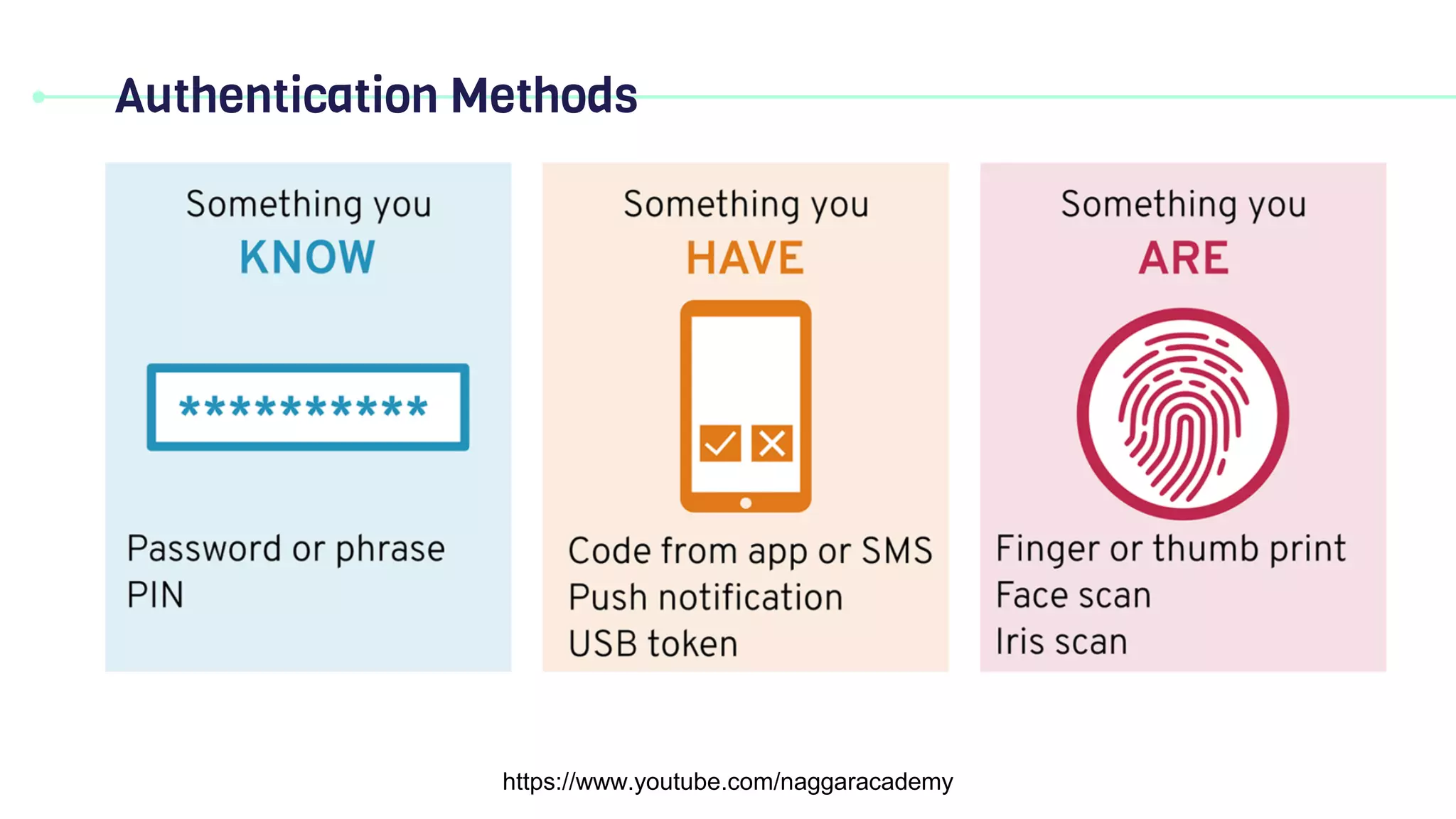
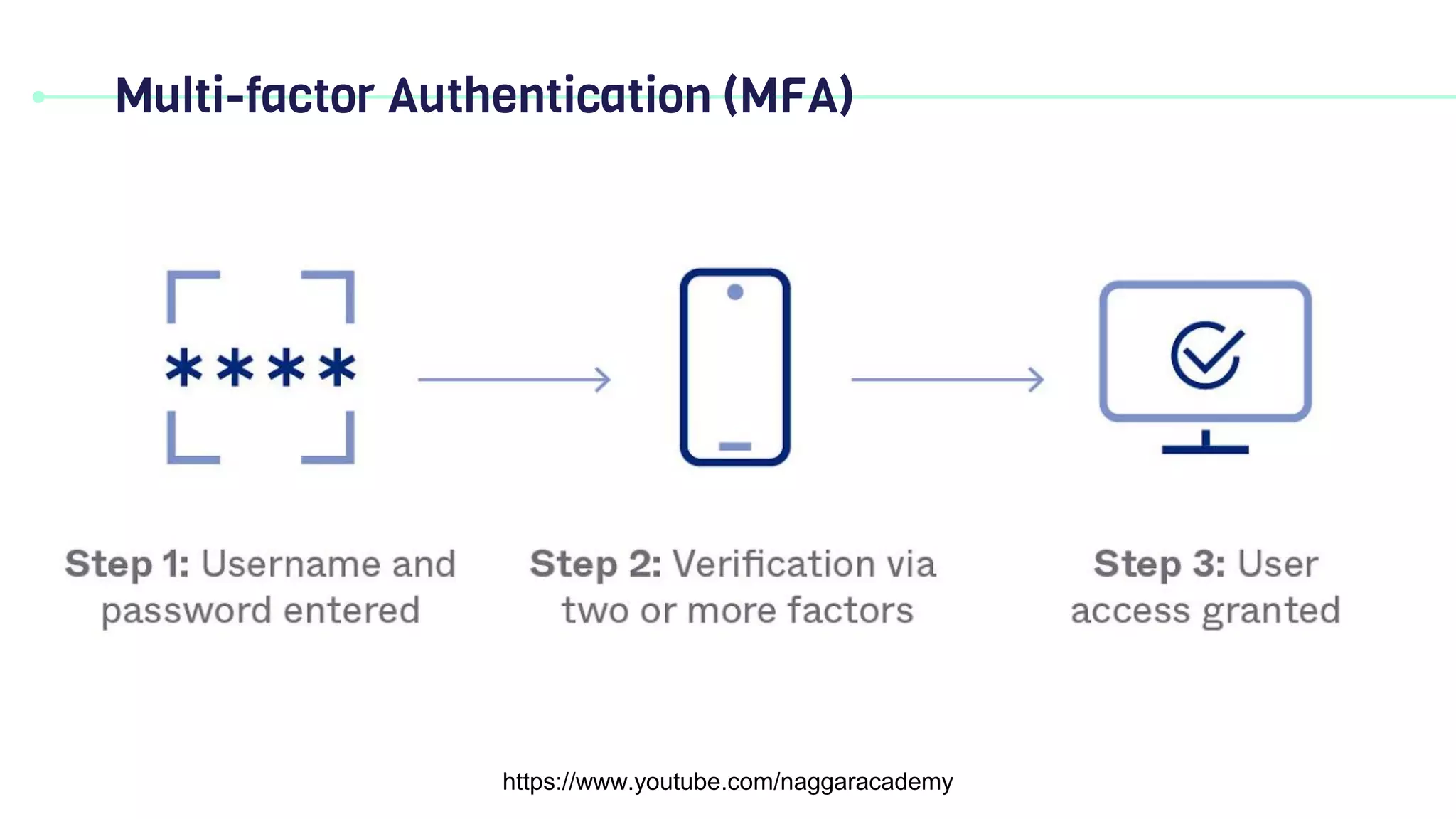
This document discusses key security principles including concepts of information security, risk management, security controls, ethics, and governance. It specifically focuses on the CIA triad of security - confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Confidentiality ensures data is accessible only by authorized users, integrity means data remains accurate and unaltered, and availability means the system and data are accessible when needed. Access control, authentication, authorization, and multi-factor authentication are discussed as methods to achieve the CIA principles. Non-repudiation is also summarized as proving the authenticity and integrity of messages.