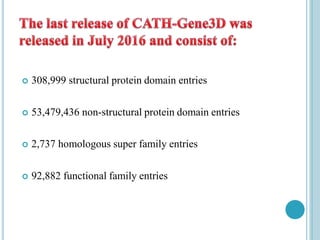
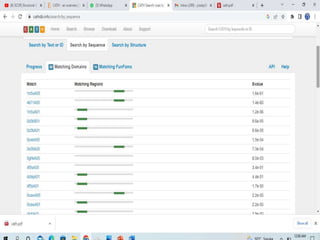
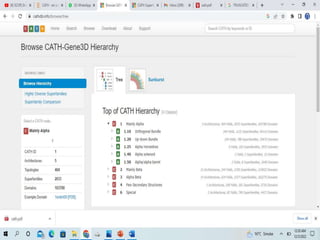
The CATH database provides information on the evolutionary relationships of protein domains. It was created in the 1990s by Professor Christine Orengo and classifies protein domains into categories based on their secondary structure, topology, and homology. The CATH database contains over 300,000 structural protein domain entries that are classified and organized based on analyses of their structures deposited in the Protein Data Bank.