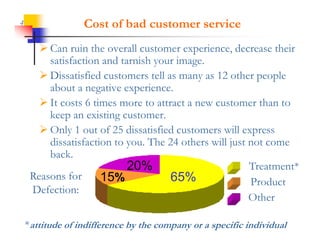
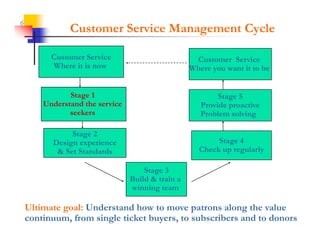
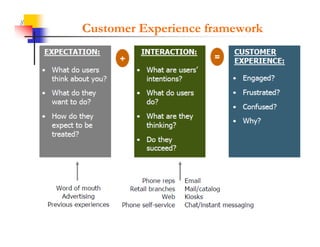
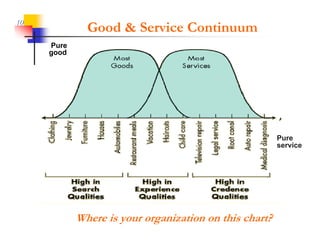
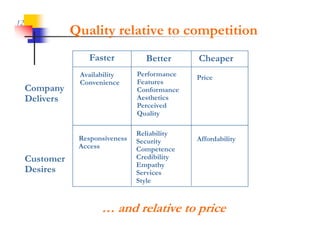
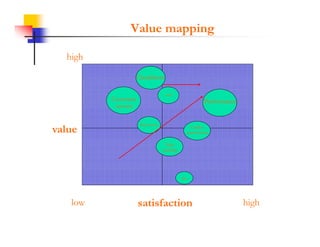
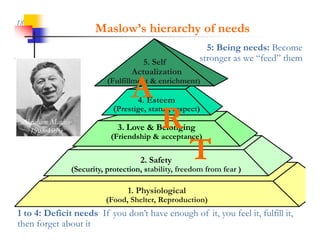
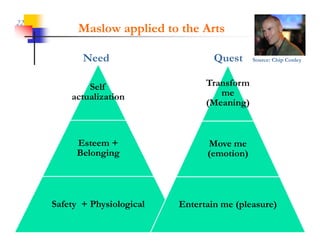
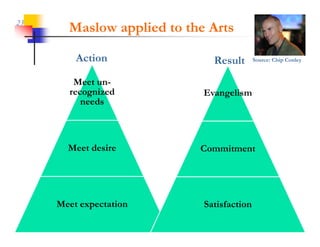
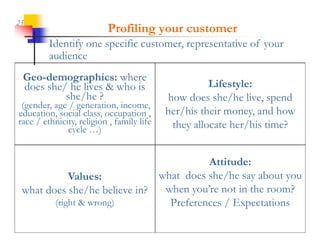
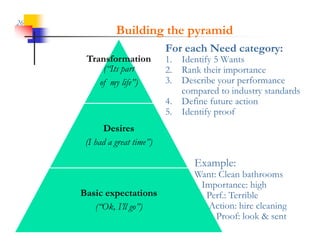
This document discusses improving patron experience at arts organizations. It argues that while the performance or show is important, mediocre customer service can negatively impact perceptions of the experience. Good customer service is controllable through hiring and training friendly staff to ensure queries are promptly answered. In contrast, customer reactions to performances are not fully controllable. The document outlines a customer service management cycle and frameworks for understanding customer needs, wants, and experiences in order to improve satisfaction and loyalty.