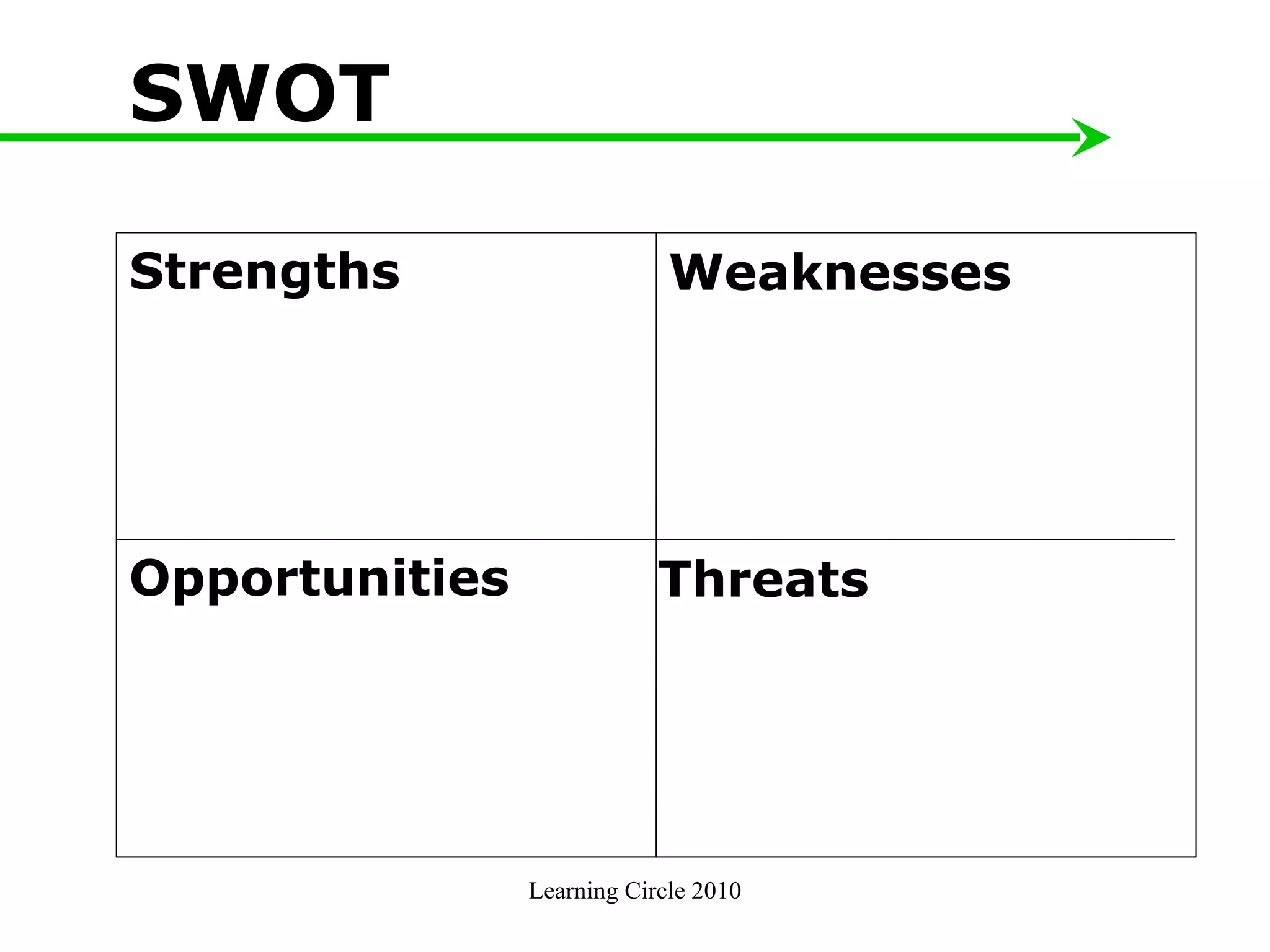
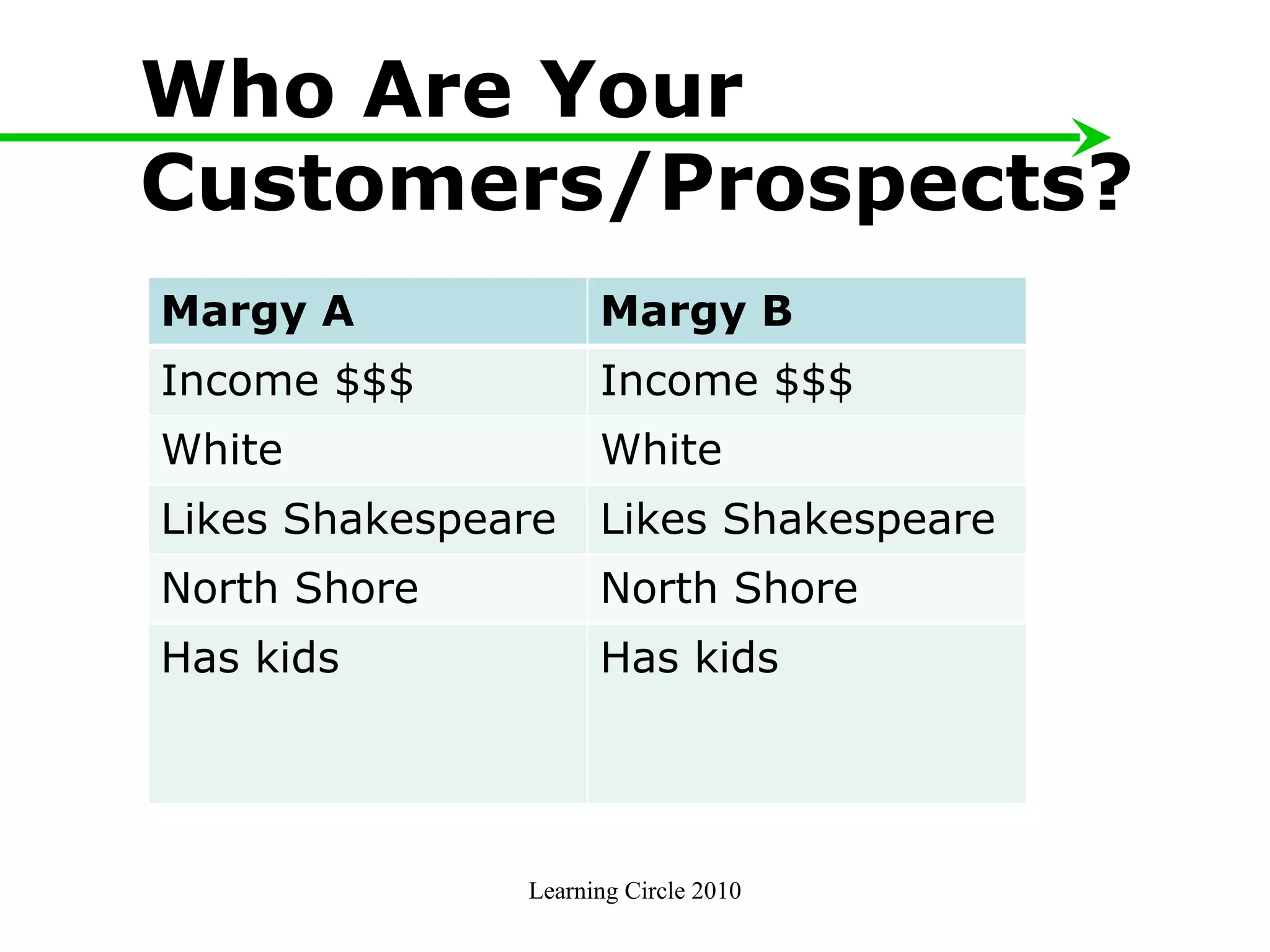
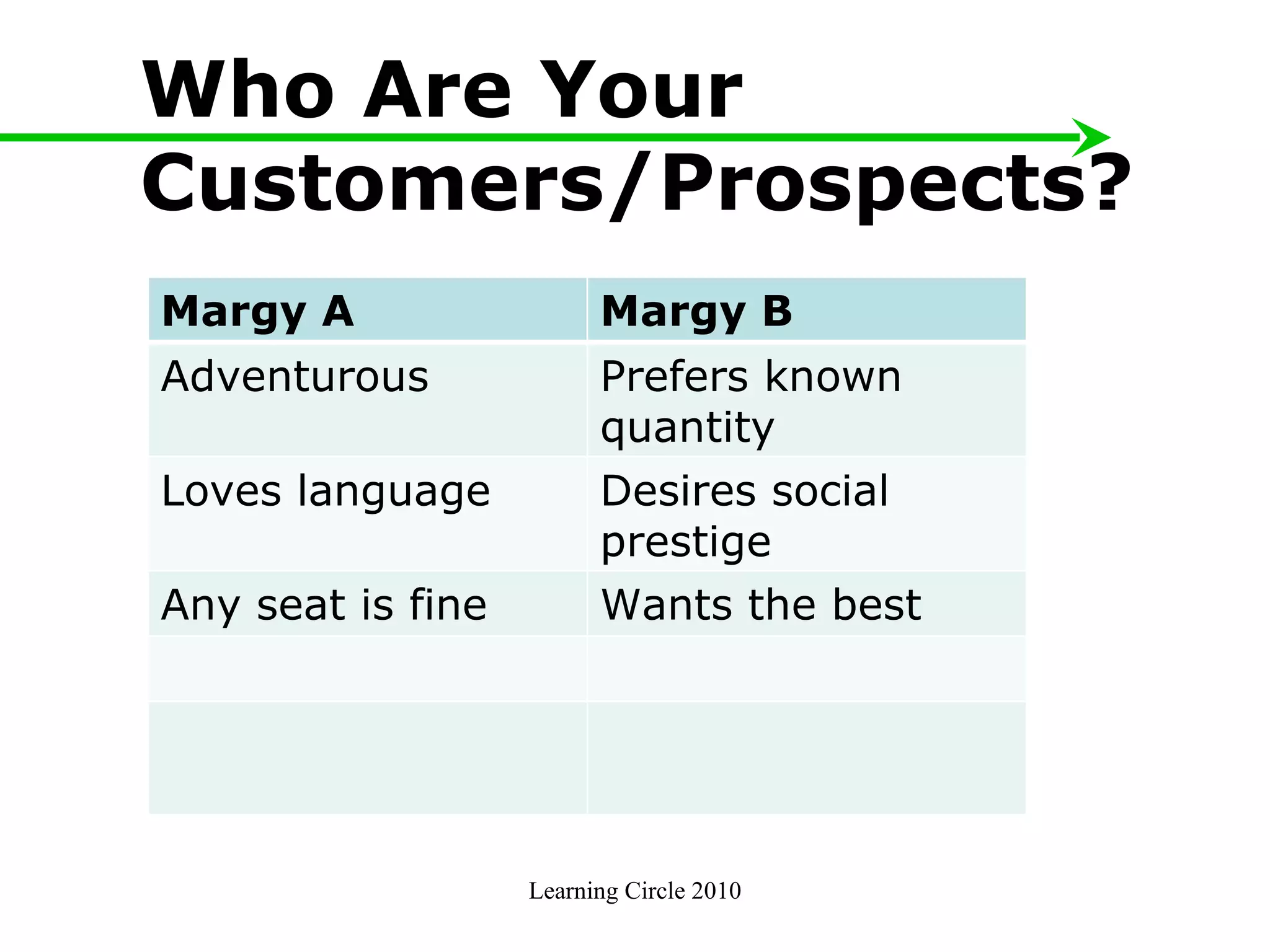
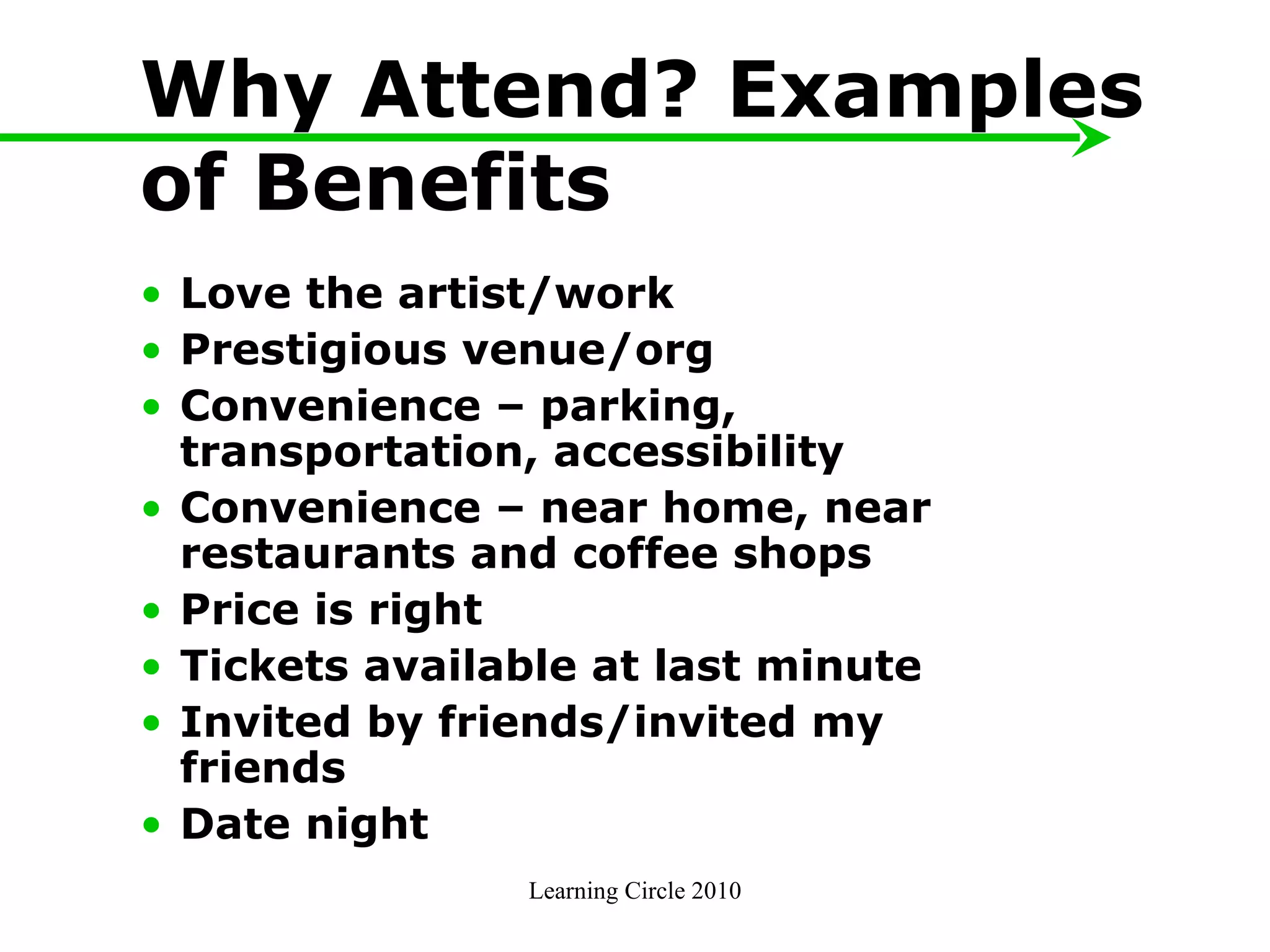
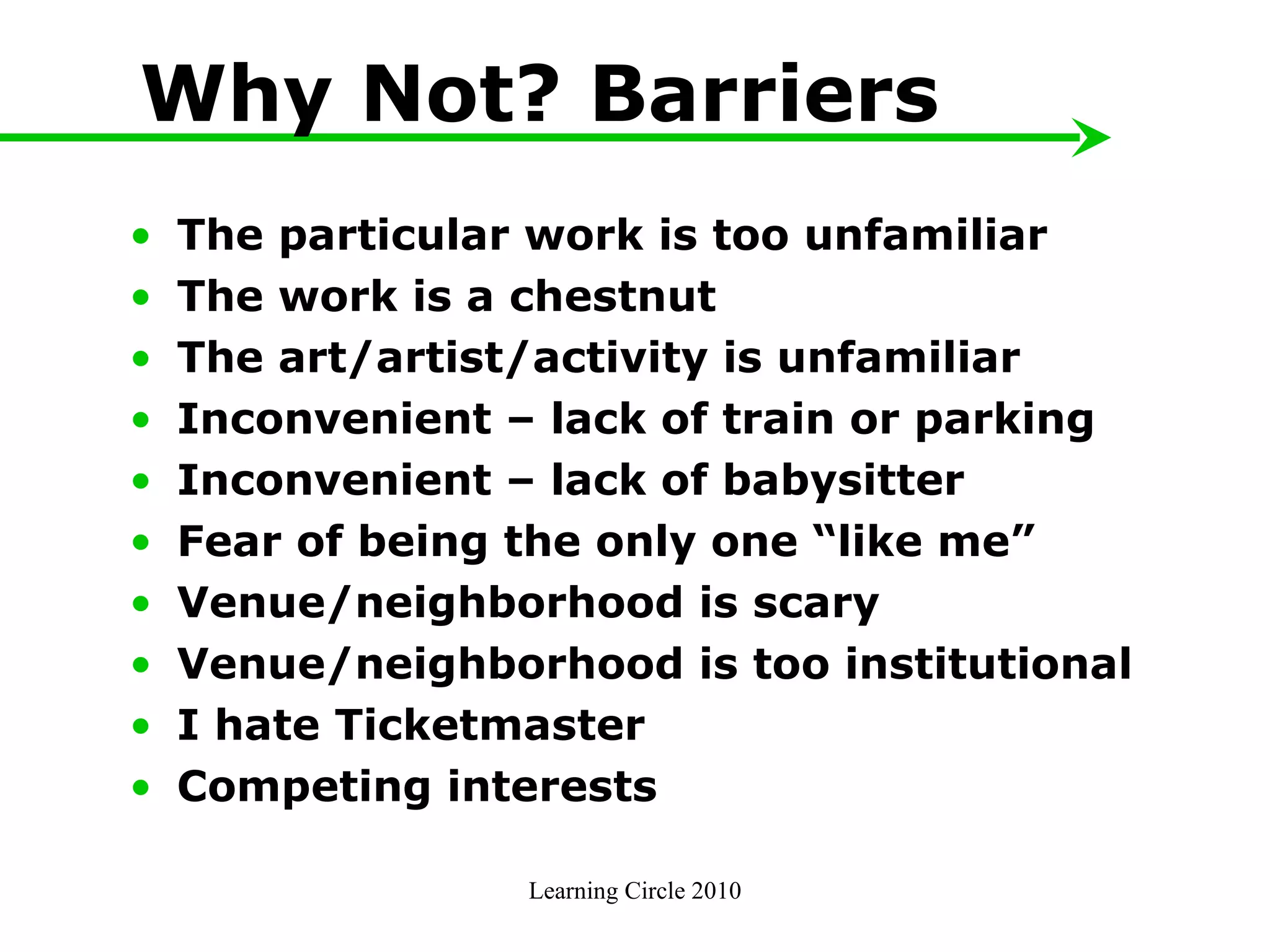
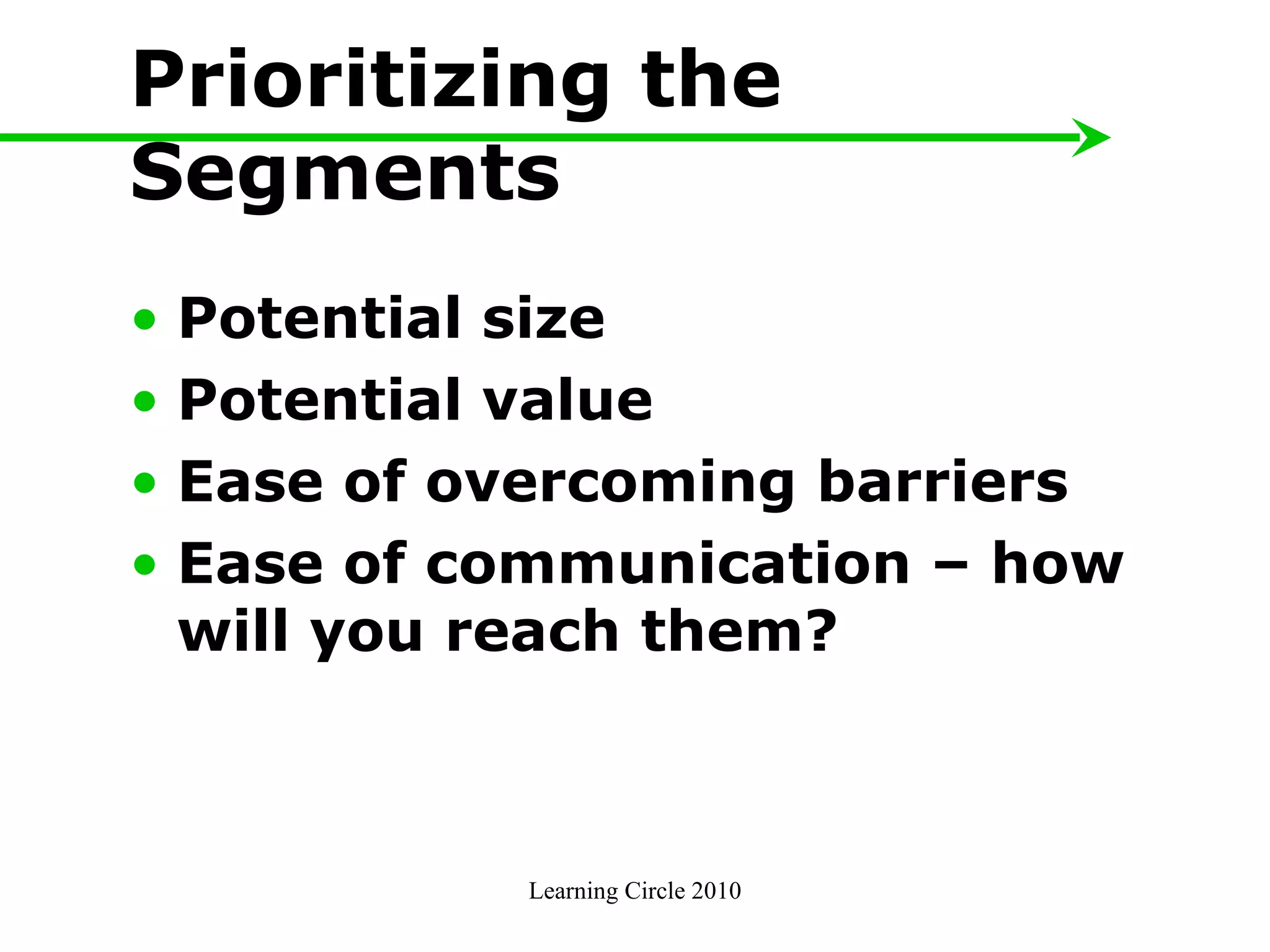
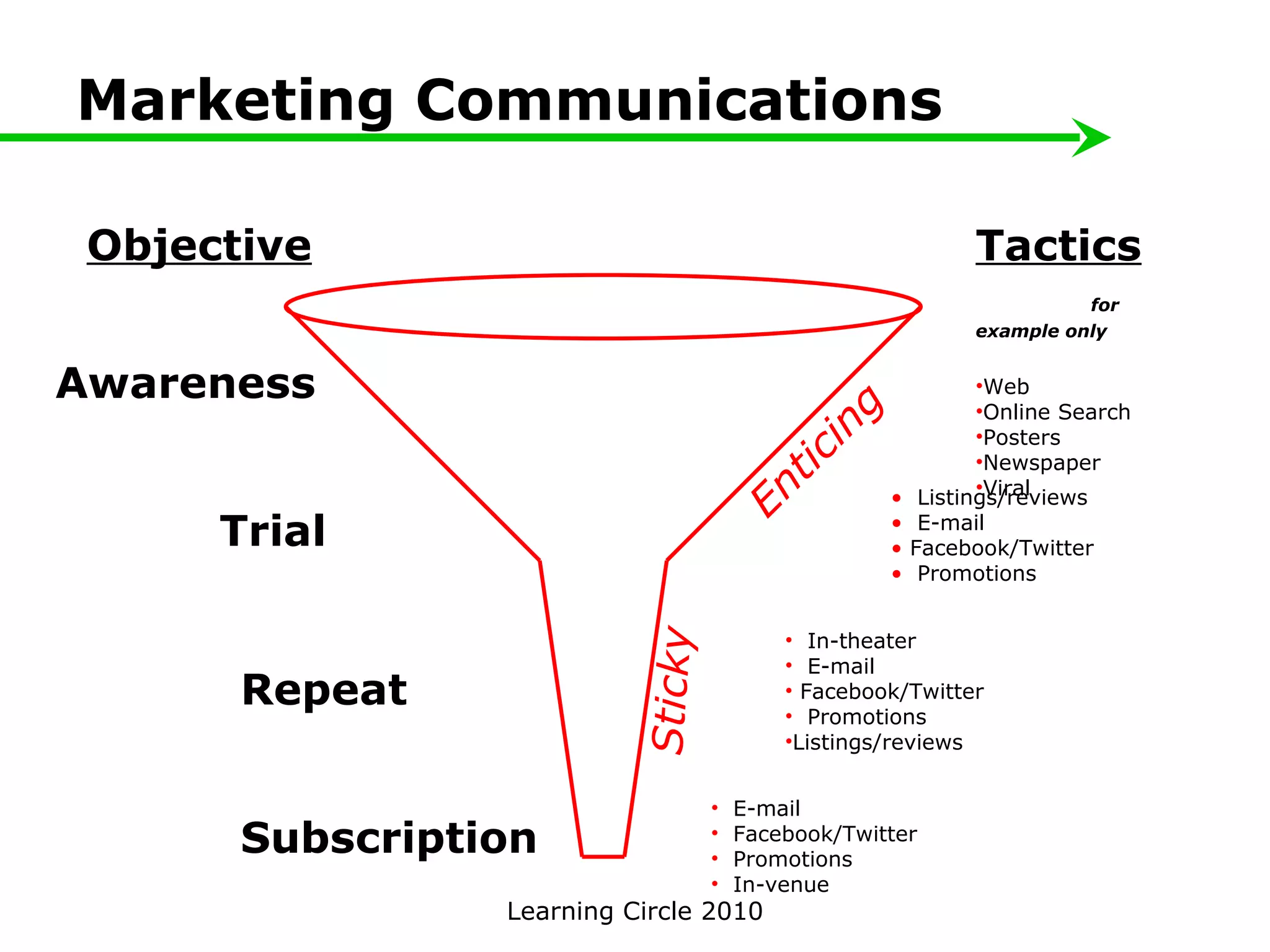
The document provides an overview of developing a marketing plan, including conducting a situation analysis, identifying target customer segments, and creating objectives and strategies. It discusses analyzing the current situation including the mission/vision and SWOT analysis. Key points include identifying customer insights through research, prioritizing target segments, and creating SMARTER objectives and matching marketing strategies and tactics.