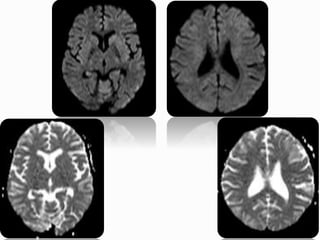
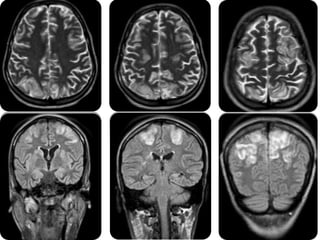
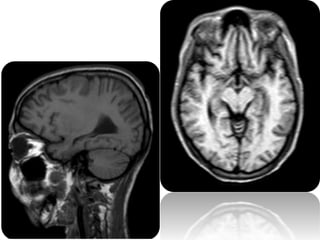
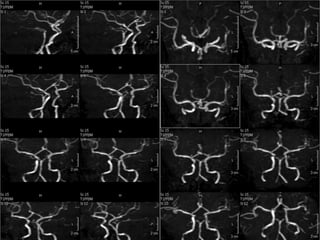
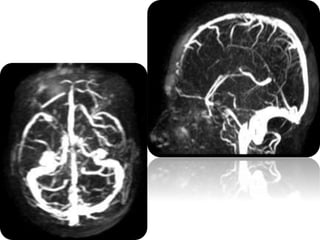
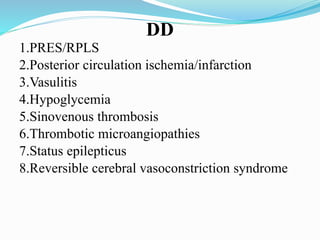
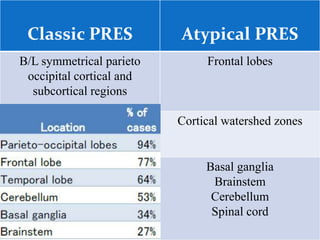
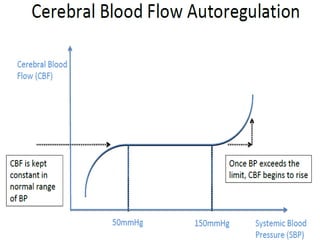
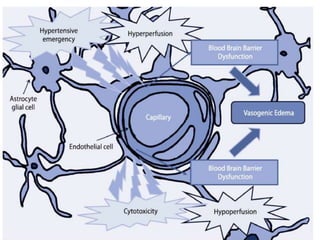
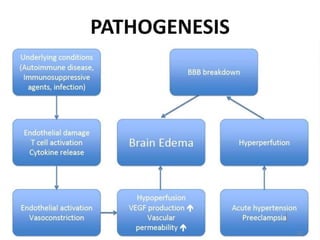
A 21-year-old female patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) on steroids presented with generalized tonic-clonic seizures and altered sensorium. The top differential diagnoses included posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES), posterior circulation ischemia/infarction, vasculitis, hypoglycemia, sinovenous thrombosis, thrombotic microangiopathies, status epilepticus, and reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. The document discusses PRES in more detail, describing its typical parieto-occipital involvement on imaging, various atypical manifestations, pathogenesis related to hypertension and endothelial dysfunction, and common causes like preeclampsia/eclampsia, infection