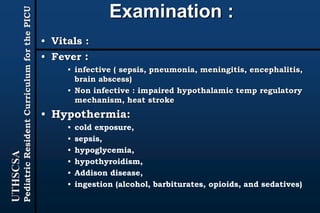
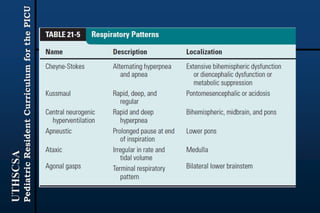
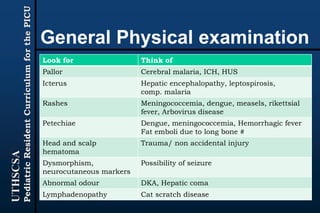
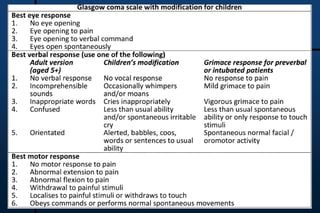
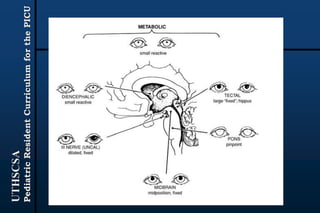
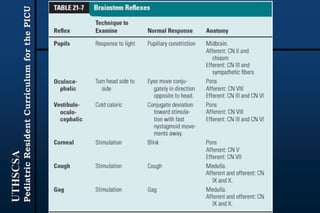
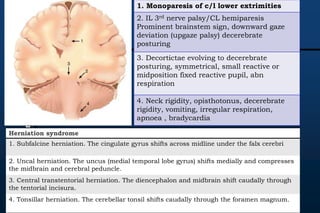
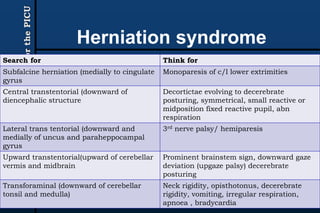
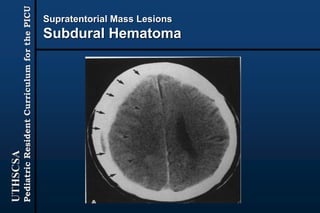
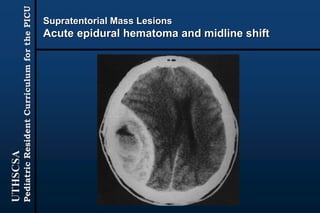
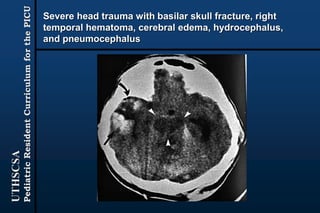
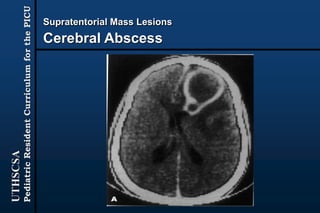
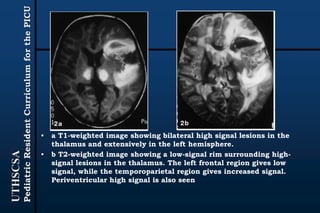
The document provides guidance for pediatric residents on evaluating and managing comatose children. It outlines the primary objectives of stabilizing the patient by addressing airway, breathing and circulation. Causes of coma are categorized as those with focal neurological signs, those without focal signs but with meningeal irritation, and those without either. A thorough history, physical exam including Glasgow Coma Scale, and neurological assessment are recommended to identify potential causes and guide management and treatment. Specific etiologies like infections, metabolic disturbances, trauma and others are discussed. Ongoing monitoring for changes is also advised.