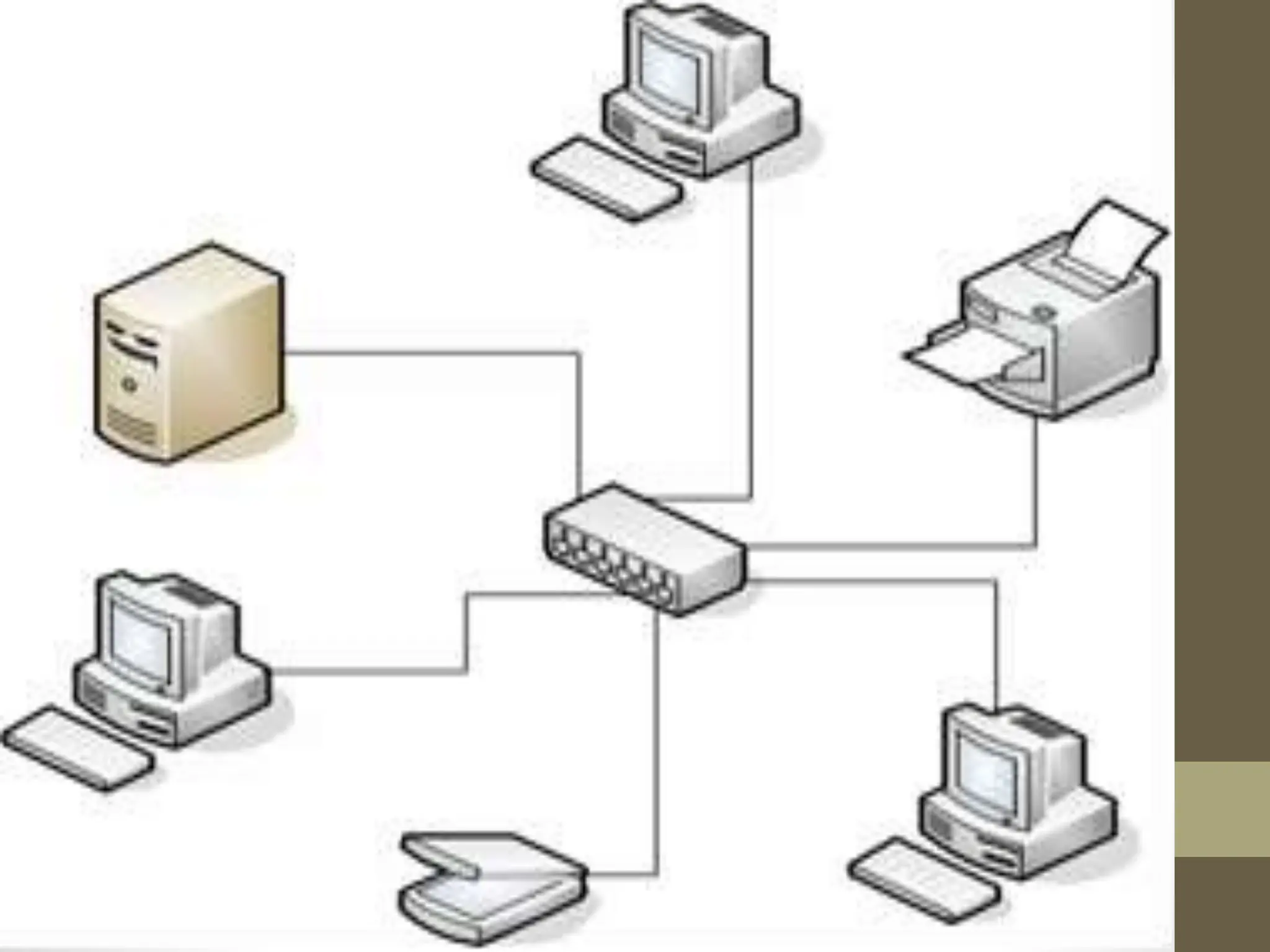
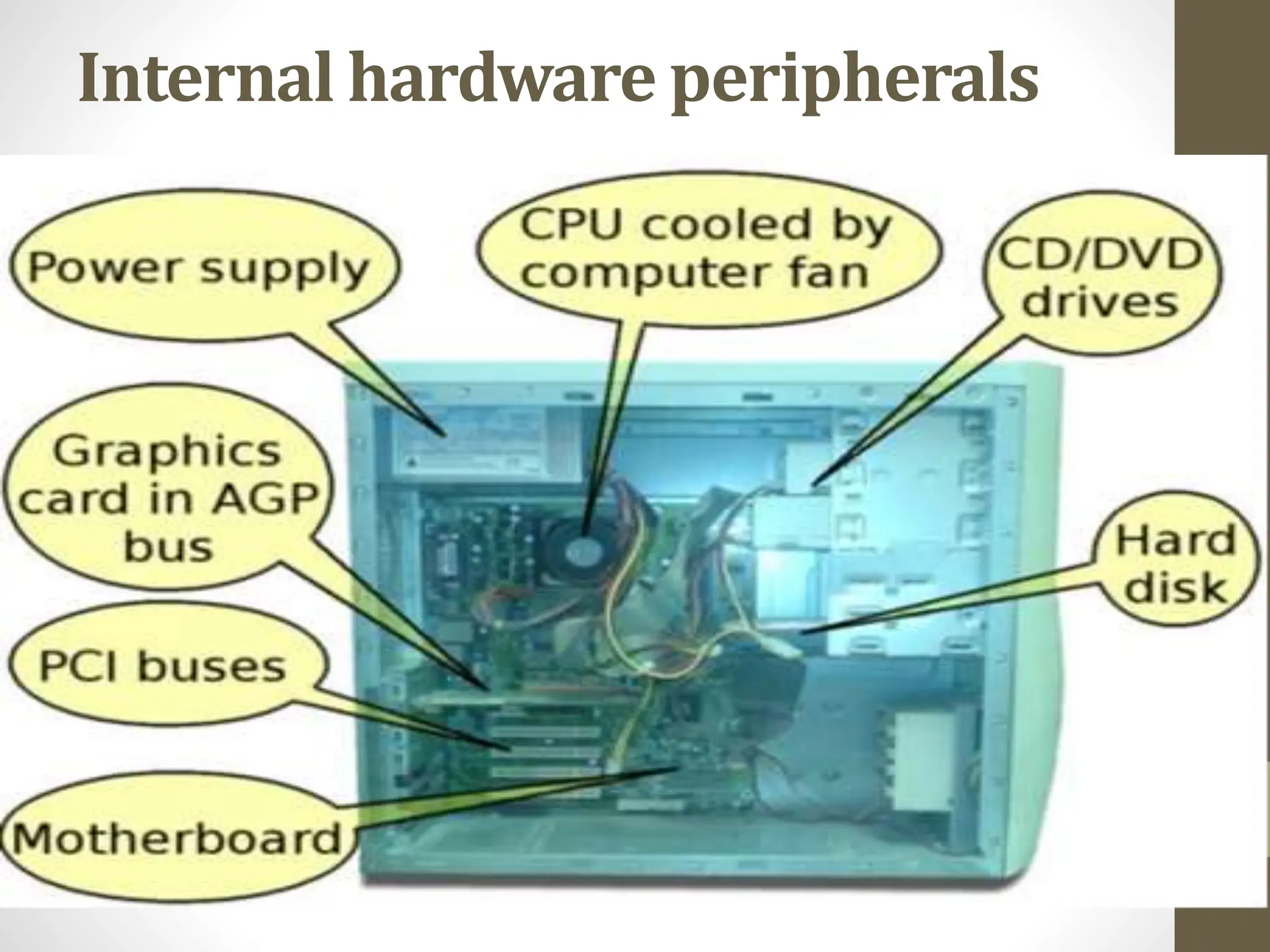
This document provides information about computer hardware components, both internal and external. It discusses the main internal components like the motherboard, CPU, power supply, and storage devices. It also covers external peripherals like monitors, keyboards, printers, and scanners. The document then discusses computer networks, including the advantages of networking computers, types of networks based on coverage area (LAN, MAN, WAN), and types based on configuration (peer-to-peer and server-based networks). Finally, it introduces some specialized servers used in large networks.










![• A hard disk drive (HDD also hard drive or hard disk)[2] is a
non-volatile, random access digital magnetic data storage
device. Today's HDDs operate on high-speed serial interfaces;
i.e., serial ATA (SATA)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carefornetworkandcomputerhardwarel-23-231010083106-e6009fec/75/Care-for-Network-and-Computer-Hardware-L-2-3-pptx-12-2048.jpg)