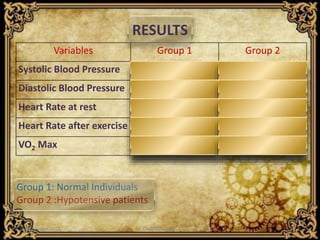
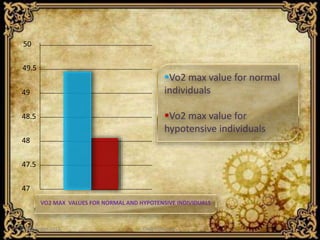
This study compared the aerobic capacity, as measured by VO2 Max values, of normal females versus hypotensive females. Seventy females participated in the study, with VO2 Max values indirectly assessed using the Queen's College step test. The results showed VO2 Max values were significantly lower in hypotensive females compared to normal females, indicating lower cardiorespiratory fitness. The lower arterial pressure in hypotensive females likely limits oxygen perfusion to exercising muscles, resulting in their lower VO2 Max values. Further research with larger populations is needed, but this study suggests hypotension should receive attention regarding fitness levels.