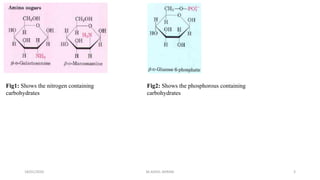
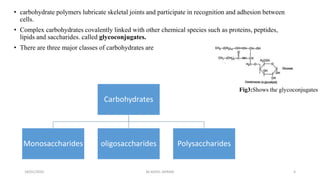
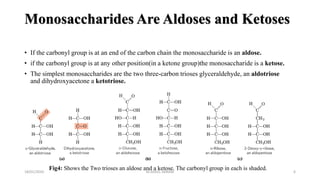
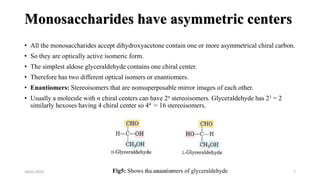
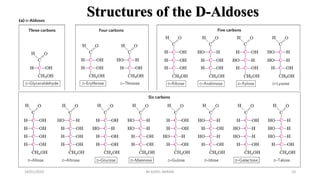
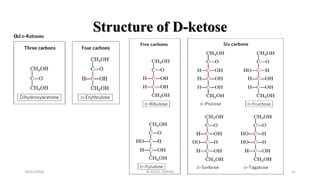
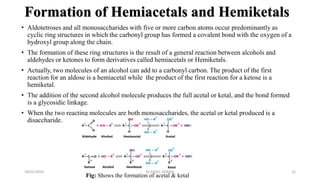
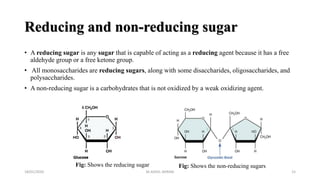
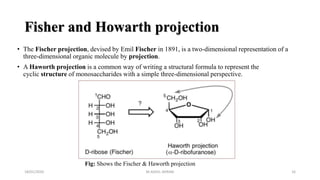
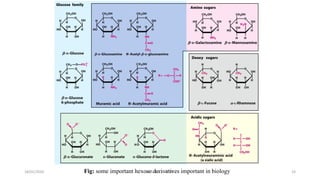
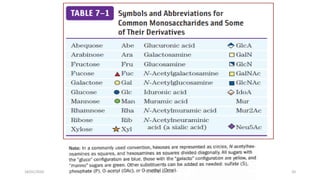
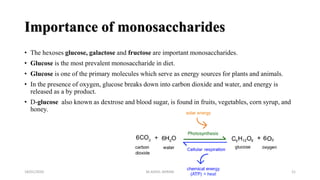
This document discusses monosaccharides, which are the simplest forms of carbohydrates. It defines monosaccharides as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones that cannot be further broken down by hydrolysis. The document outlines the key properties and classifications of monosaccharides, including that they are reducing sugars, contain asymmetric carbons, and often exist as cyclic structures called pyranoses and furanoses. Examples of important monosaccharides are glucose, galactose, and fructose. Glucose is a critical energy source, while mannose and derivatives have biological roles.