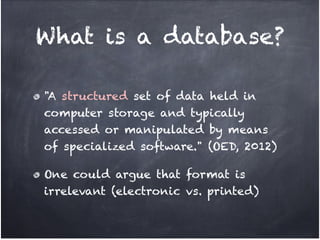
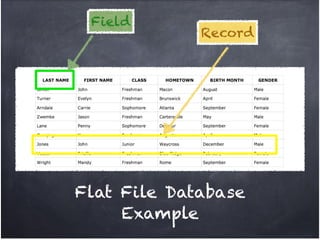
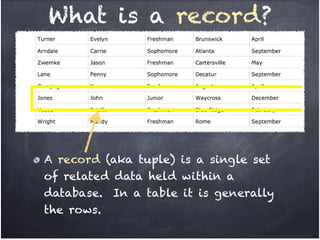
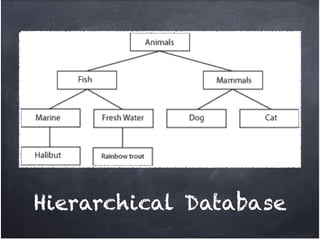
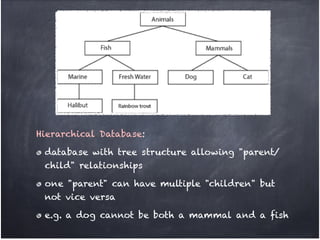
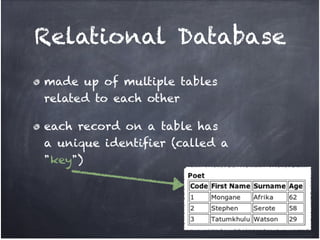
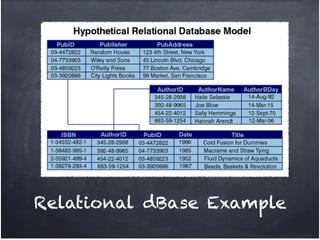
The document discusses database organization and concepts. It begins with an in-class quiz and activity on database organization. It then defines data, information, and databases. The main database types - flat file, hierarchical, and relational - are explained. Key concepts like fields, records, and relationships are defined. Examples of each database type are provided. Finally, the importance of understanding database organization for effective searching is highlighted.