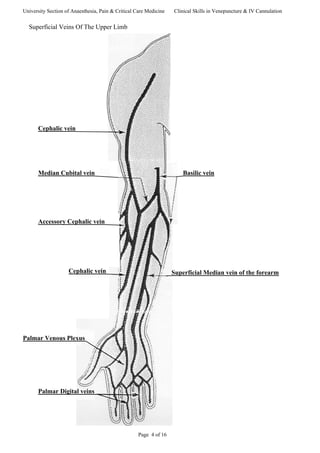
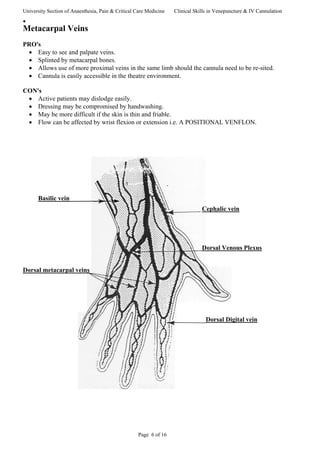
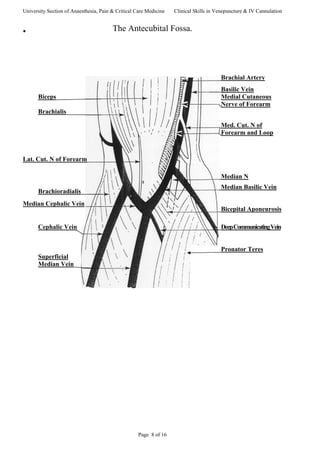
This document provides guidance on venepuncture and intravenous cannulation. It discusses anatomy and vein selection, including superficial veins in the forearm and antecubital fossa. It outlines the procedures for venepuncture and cannulation, including patient assessment, site preparation, equipment, and techniques to minimize pain. Potential complications are also addressed.