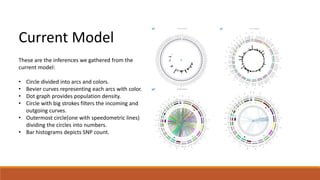
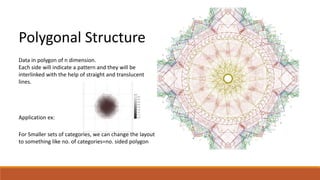
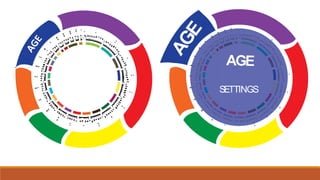
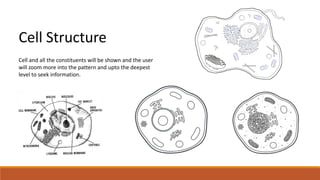
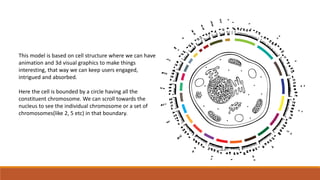
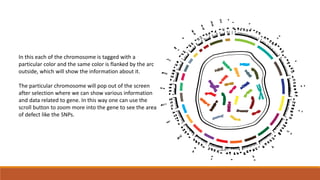
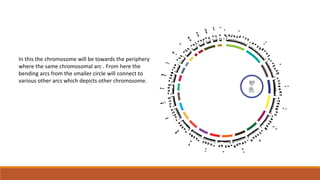
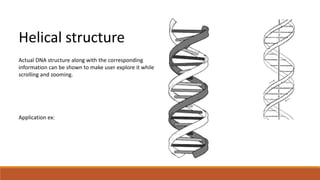
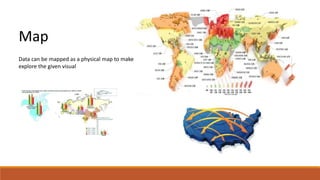
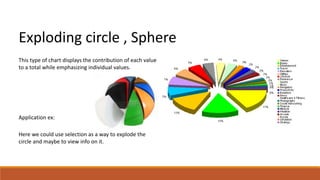
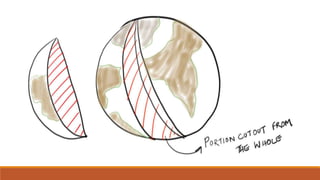
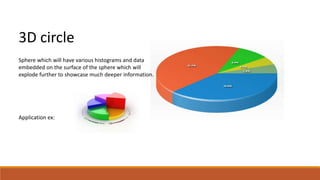
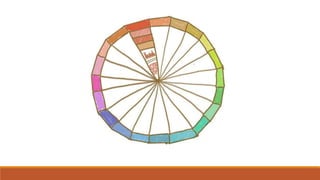
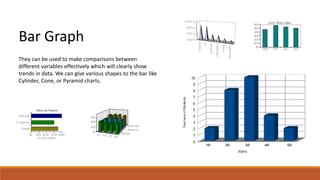
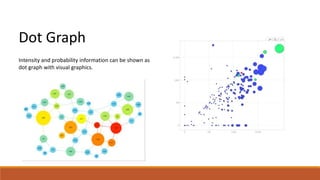
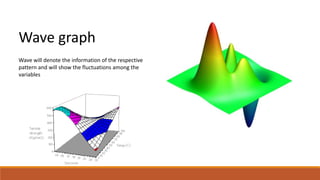
The document discusses potential approaches to visualizing large and complex genomic data sets. It describes some common challenges with analyzing big data in healthcare. Several existing and proposed visualization models are outlined, including representing data in polygons, n-dimensional illustrations, cell structures, helical structures, maps, exploding circles, 3D spheres, universe models, bar graphs, dot graphs, wave graphs, line graphs, and heat maps. The goal is to develop interactive visualizations that make complex genomic data more understandable and useful for researchers, medical practitioners, and patients.