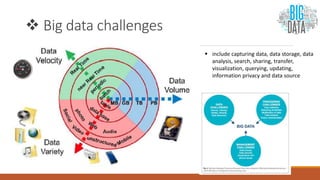
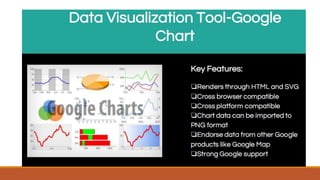
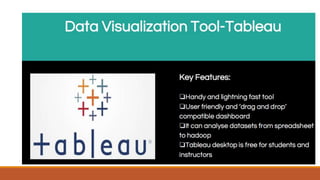
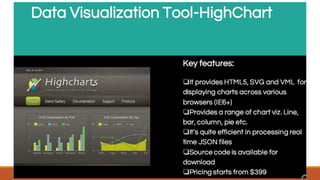
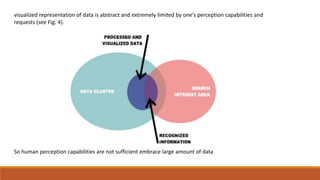
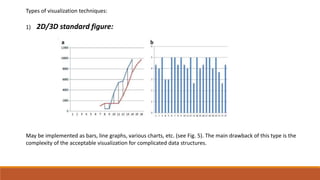
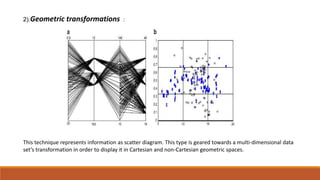
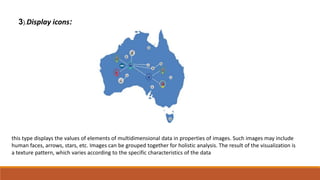
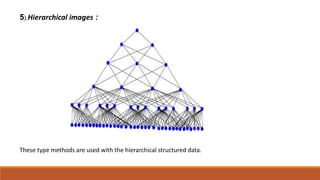
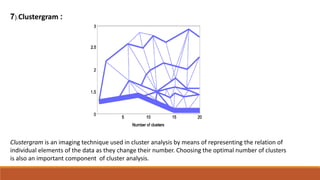
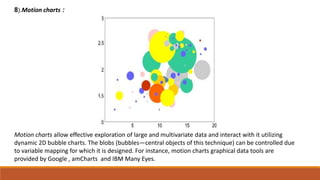
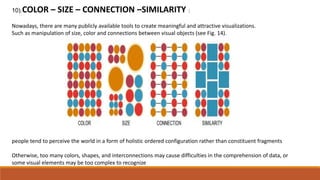
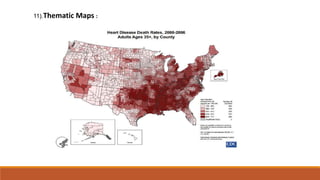
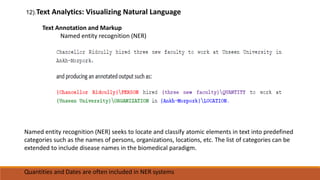
Big data involves analyzing large and complex datasets that cannot be processed by traditional methods. It faces challenges including data volume, variety, velocity, and veracity. Data visualization helps address these challenges by making patterns in the data easier to see. It allows faster understanding of data and trends. Effective visualization techniques depend on the type of data, and may include standard charts, geometric transformations, icons, pixels, hierarchies, tags, clusters, motion charts, dashboards, color/size/connections, maps, and text analysis.