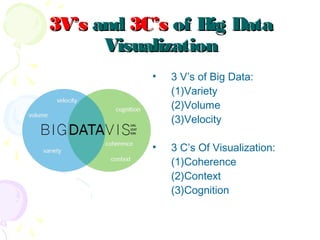
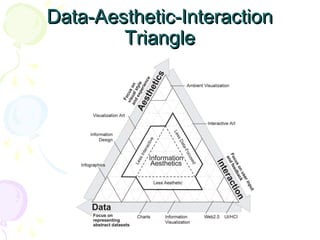
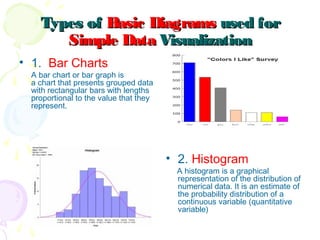
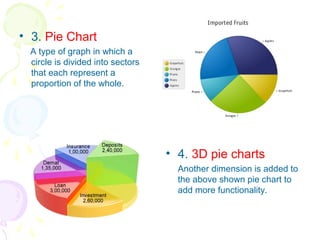
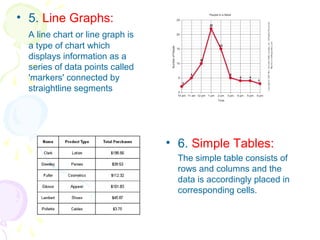
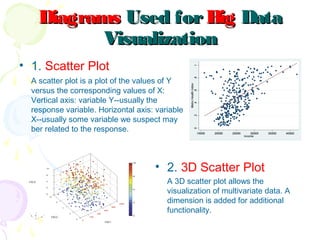
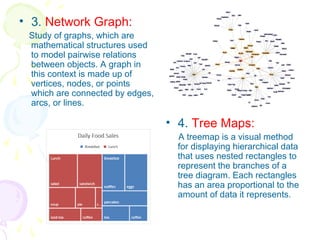
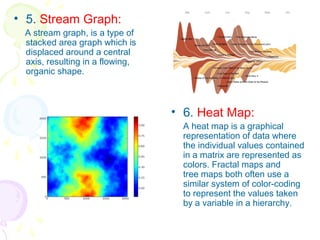
This document discusses visual analytics and big data visualization. It defines big data and explains the need for big data analytics to uncover patterns. Data visualization helps make sense of large datasets and facilitates predictive analysis. Different visualization techniques are described, including charts, graphs, and diagrams suited to simple and big data. Visualization acts as an interface between data storage and users. Characteristics of good visualization and tools for big data visualization are also outlined.









![ReferencesReferences
• [1] S. Y. Kung , “Visualization of Big Data”,
Cognitive Informatics & Cognitive Computing (ICCI*CC)
, pages. 447-449, 6-8 July 2015.
DOI: 10.1109/ICCI-CC.2015.7259428
• [2] I. Herman , G. Melancon ; M. S. Marshall,
“Graph Visualization and navigation” IEEE
Transactions on Visualization and Computer
Graphics (Volume:6 , Issue:1), Pages 24-43,
August 2002.
DOI: 10.1109/2945.841119
• [3] Deepa Gupta, Sameera Siddiqui; “Big data
Implementation and Visualization”, Advances in
Engineering and Technology Research (ICAETR),
2014 International Conference ,
pages-1-10, issue no. 2347-9337, July 2014.
DOI: 10.1109/ICAETR.2014.7012883](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatavisualization-170909074511/85/Visual-Analytics-in-Big-Data-23-320.jpg)
