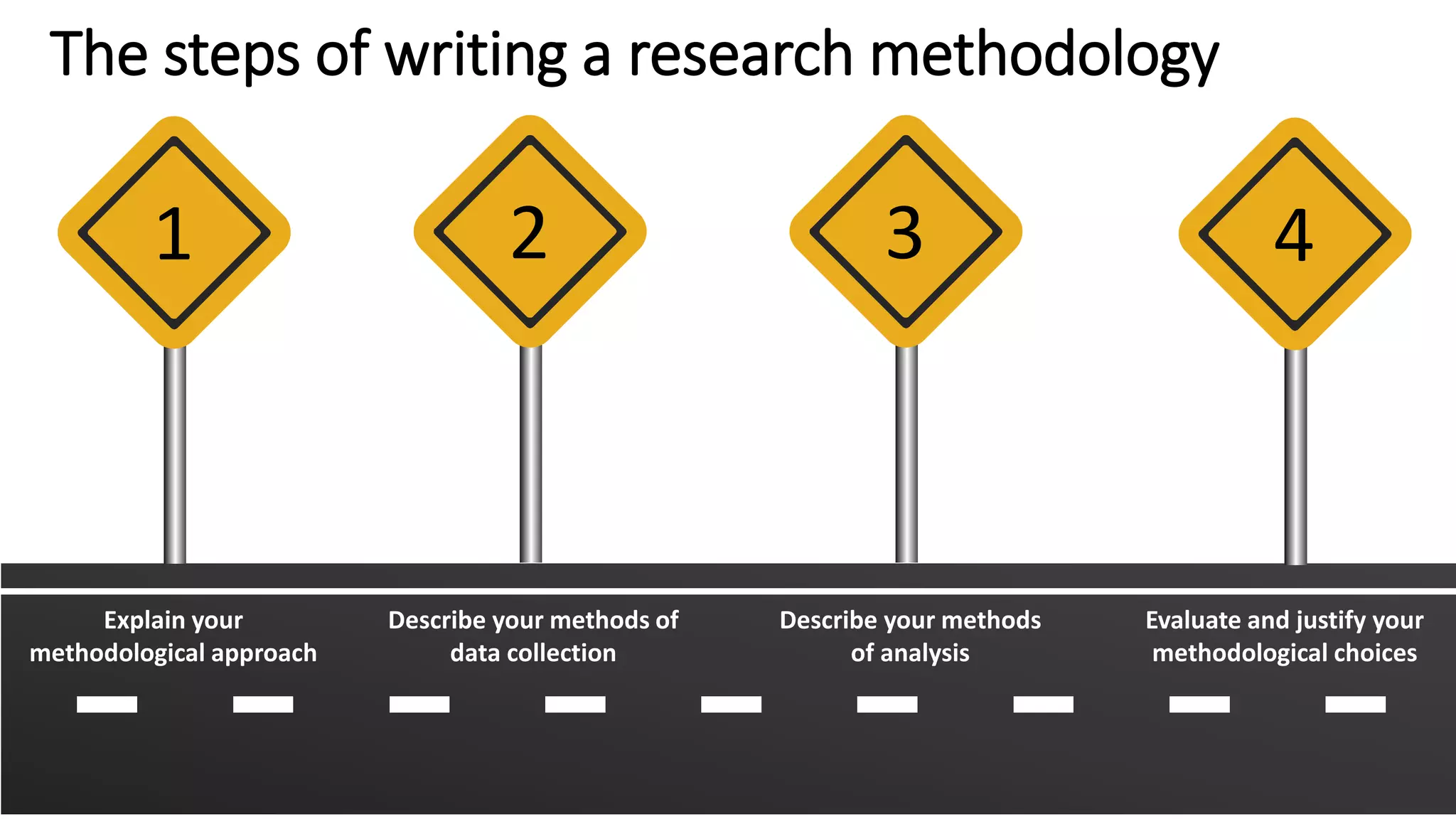
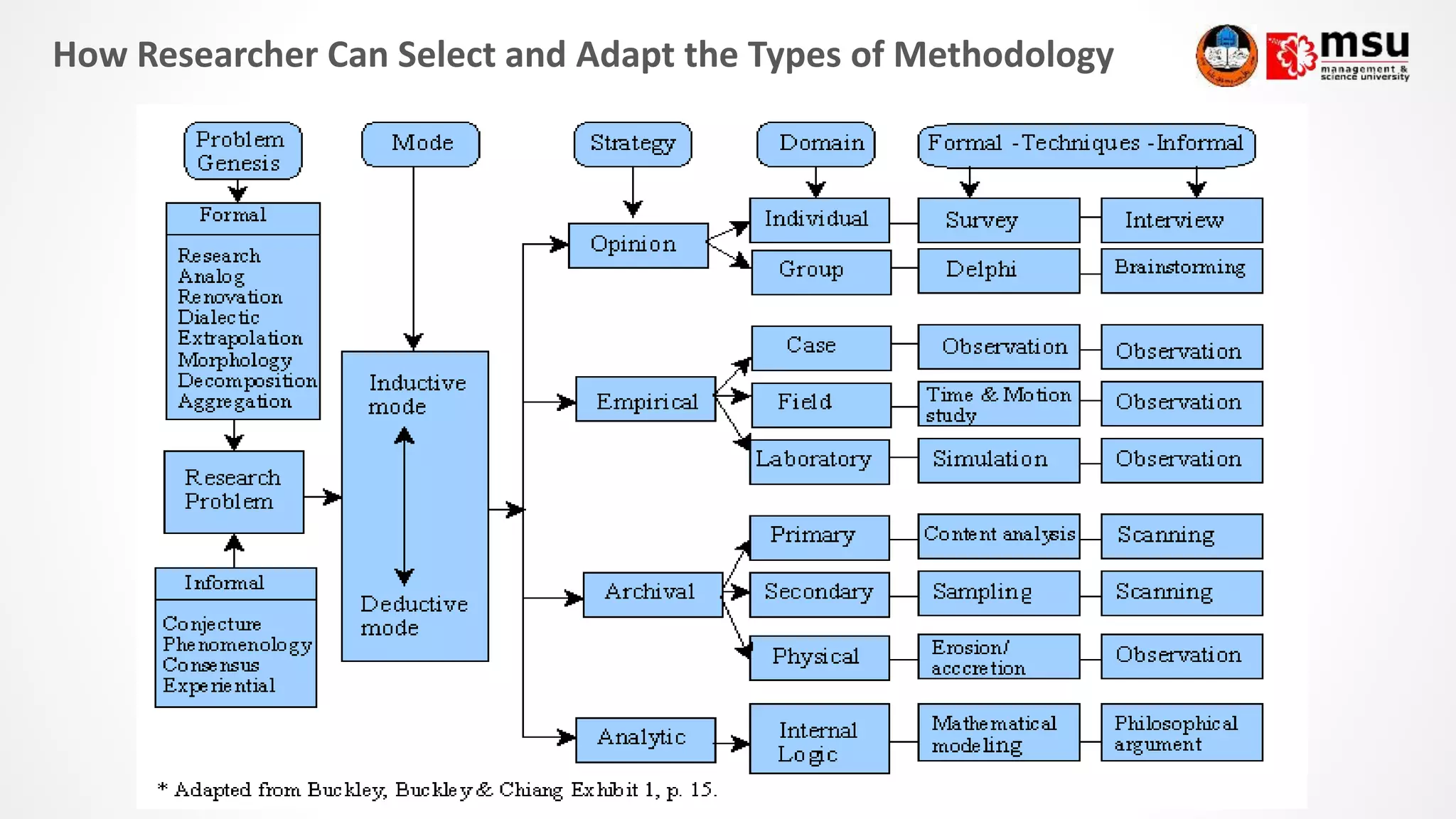
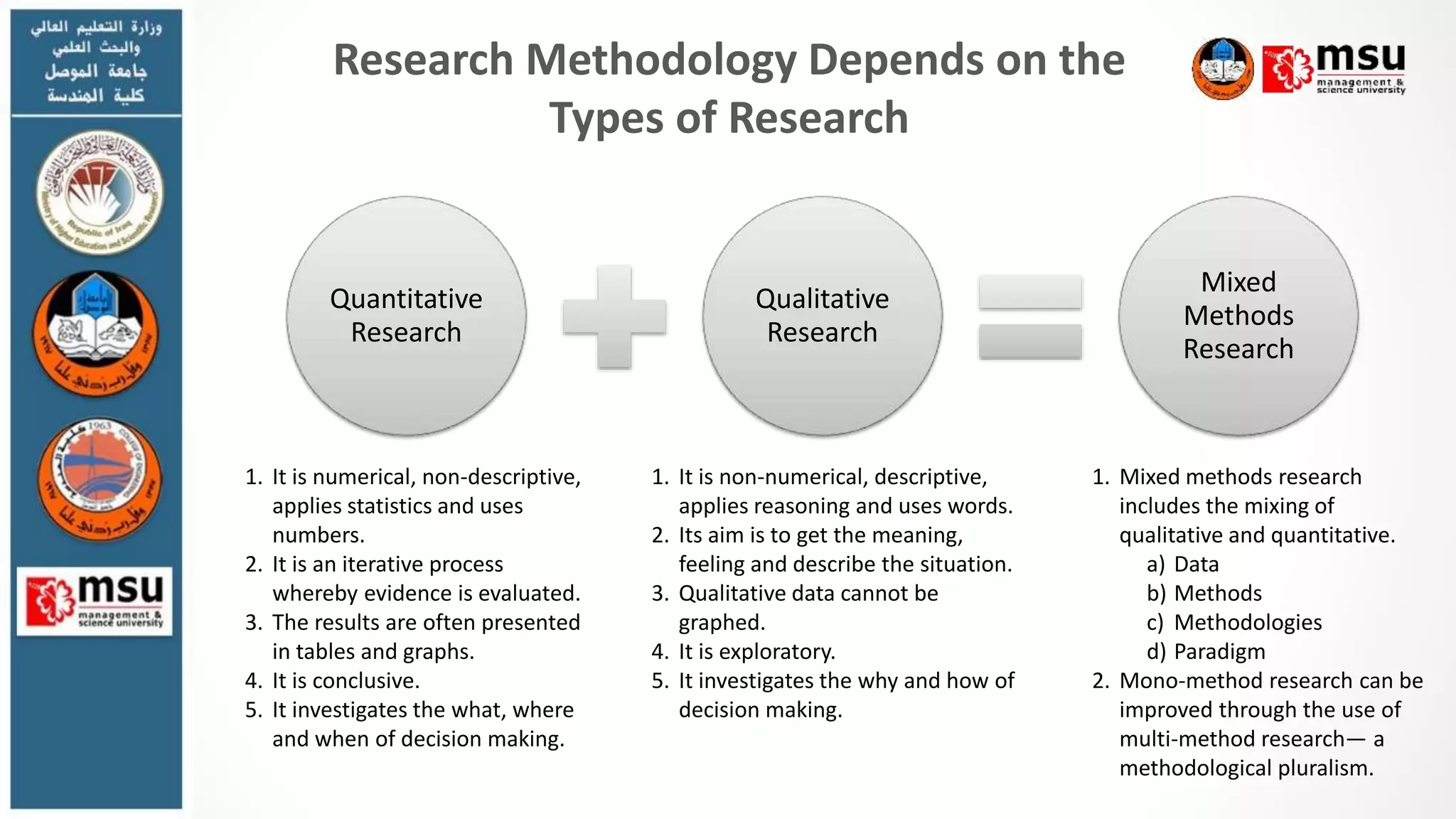
The document discusses research methodology and provides guidance on writing the methodology section of a thesis or research paper. It explains that the methodology section outlines the methods used to conduct the research, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of the results. It provides tips for writing each part of the methodology section, including explaining the methodological approach, describing data collection and analysis methods, and justifying the methodological choices. The document also discusses different research methodologies for quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research.