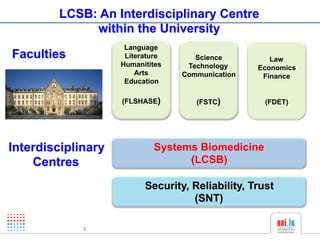
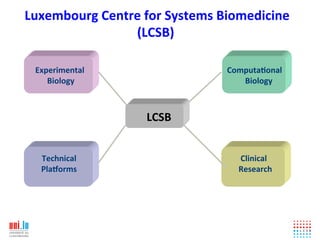
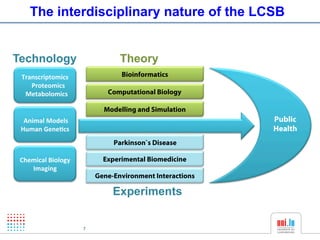
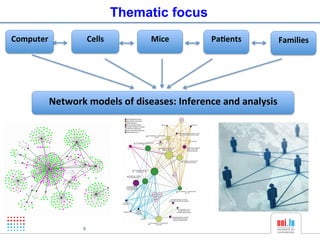
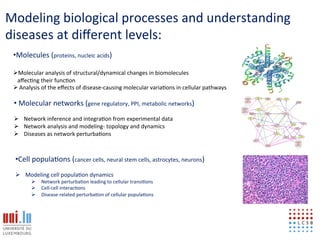
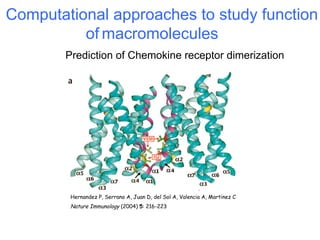
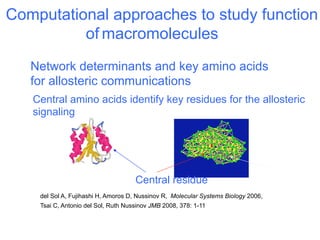
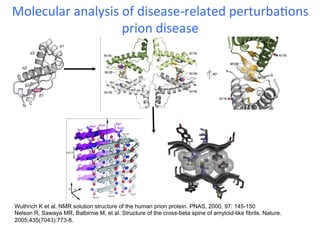
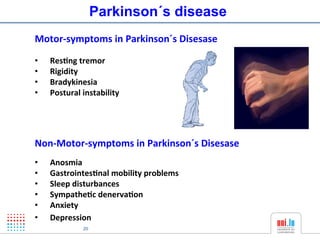
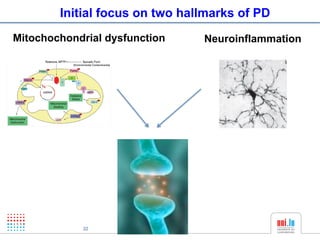
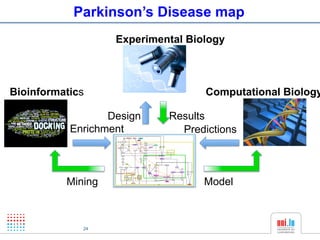
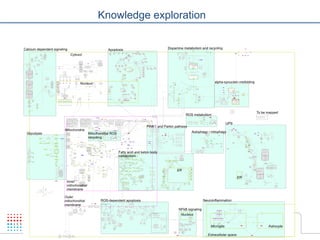
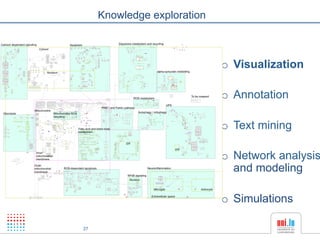
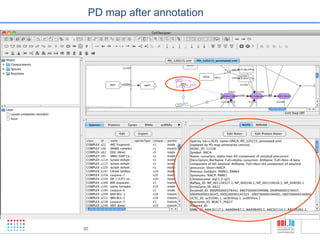
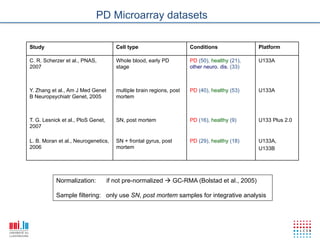
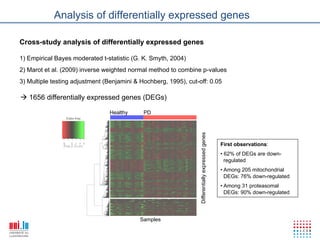
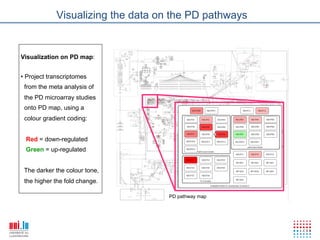
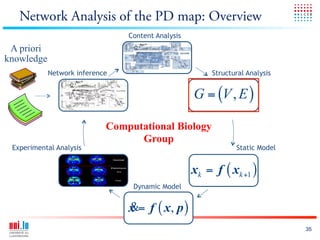
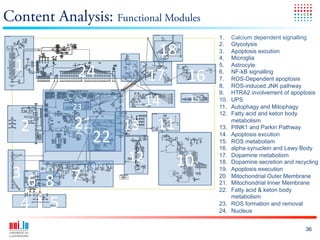
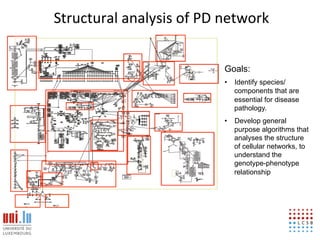
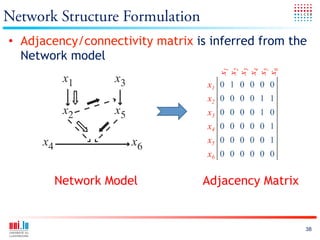
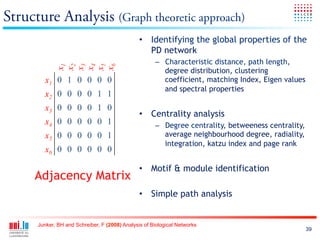
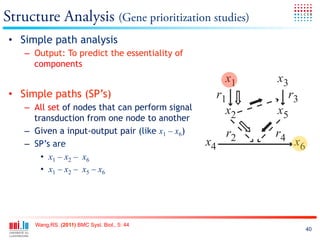
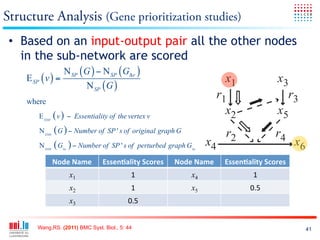
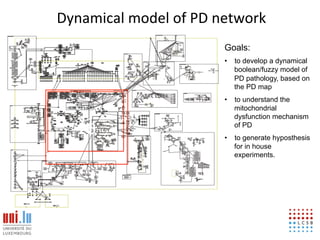
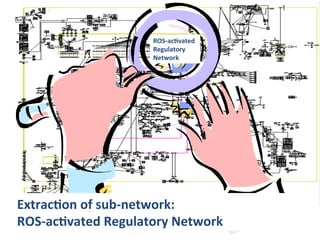
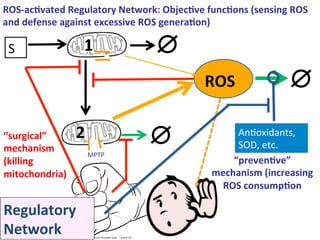
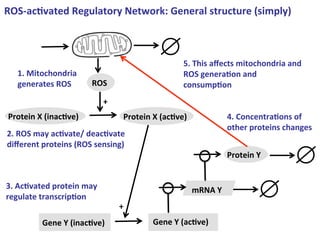
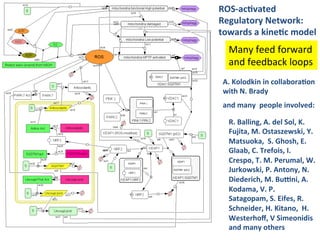
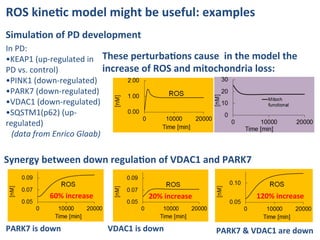
The document discusses a workshop on Systems Biology Graph Notation (SBGN) comprehensive disease maps held at the Luxembourg Centre for Systems Biomedicine (LCSB) in Luxembourg on June 14th, 2012. The workshop was supported by international speakers and aimed to discuss SBGN disease maps. The LCSB is an interdisciplinary research center within the University of Luxembourg focused on experimental and computational biology as well as technical platforms and clinical research related to systems biomedicine. Specific research areas of focus at the LCSB include network models of diseases, computational biology, and Parkinson's disease.