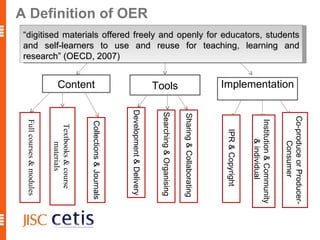
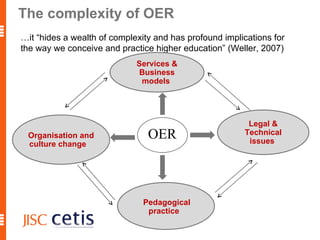
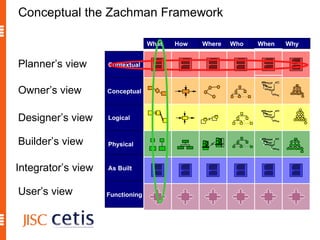
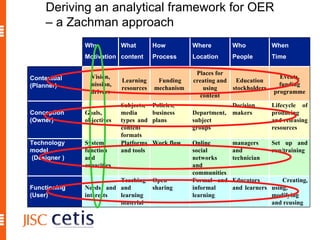
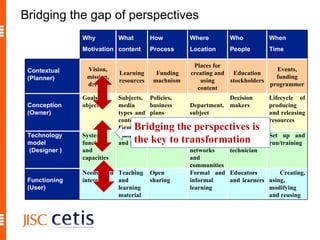
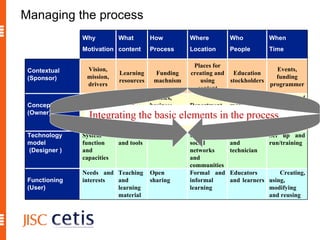
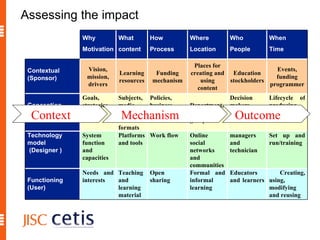
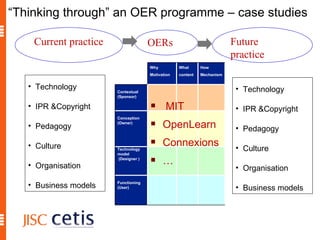
The document proposes a framework for understanding and evaluating the impact of open educational resources (OER) based on the Zachman Framework. It defines OER and provides examples of OER programs. It then adapts the Zachman Framework's six perspectives to the context of OER, covering motivation, content, processes, locations, people, and time. This adapted framework can be used to assess OER programs and impact by considering the perspectives of planners, owners, designers, and users.