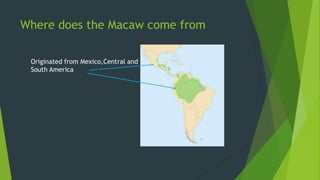
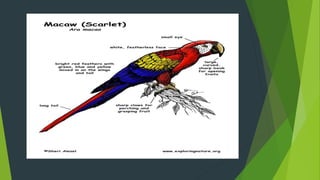
Cage birds such as lovebirds, cockatoos, macaws, and budgies are popular pets that require proper care. Lovebirds are small parrots native to Africa with a lifespan of 10-12 years that come in various colors. Cockatoos are noisy, affectionate birds that require attention and can be prone to health issues like psittacine beak and feather disease if not stimulated. Macaws are large, long-lived parrots from Central and South America that can learn to talk; scarlet and blue-and-gold macaws are two common species. Budgies are small, social parakeets that need a seed-based diet supplemented with fruits and vegetables.