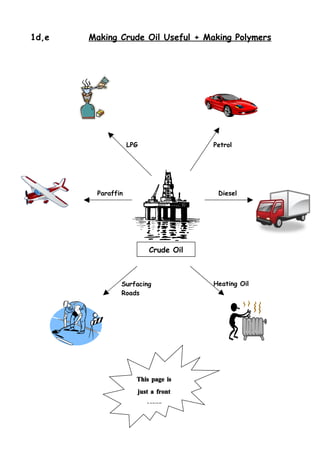
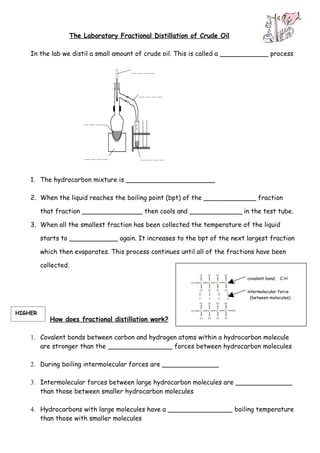
1. Crude oil is separated into fractions of different hydrocarbons by fractional distillation based on varying boiling points.
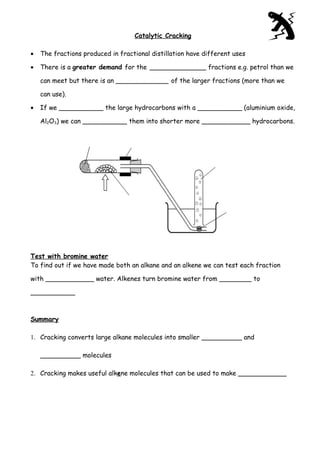
2. Larger hydrocarbon fractions can be cracked into smaller, more useful fractions like gasoline and diesel through catalytic cracking.
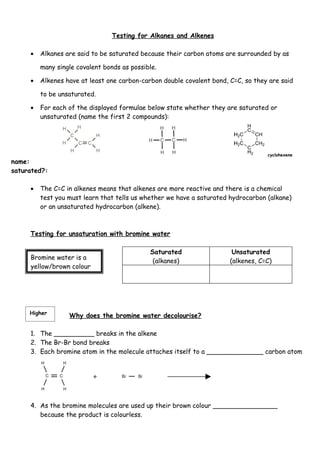
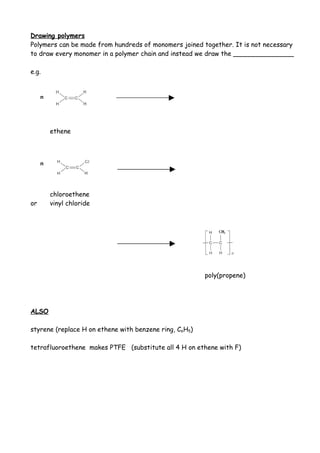
3. Unsaturated hydrocarbon monomers like ethene and styrene can undergo addition polymerization to form saturated polymers like polyethylene and polystyrene through a repeating process of carbon-carbon double bonds breaking and reforming.