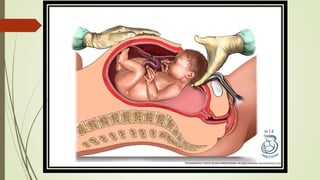
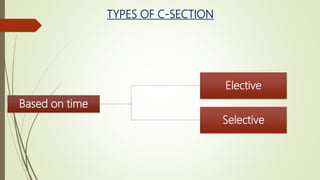
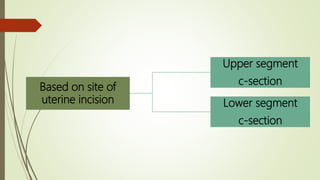
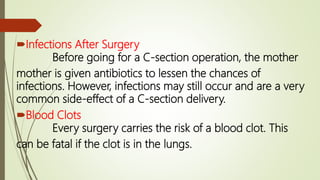
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, is a surgical procedure used to deliver babies through incisions in the mother's abdomen and uterus. It was first performed on mothers who died during childbirth to save the baby. The C-section rate in India has increased from 8.5% in 2005-06 to around 17.2% in 2015-16. Indications for C-section include fetal distress, breech positioning, and medical risks in the mother like hypertension or previous C-section. While reducing some risks to mother and baby, C-sections also carry risks of infection, bleeding, pain, and complications in future pregnancies.