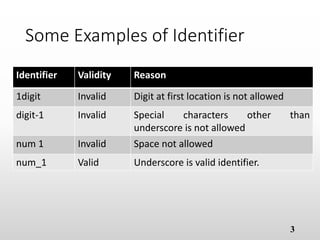
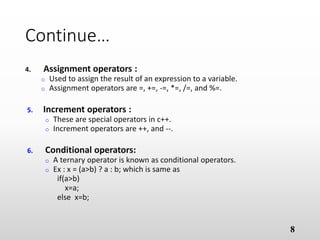
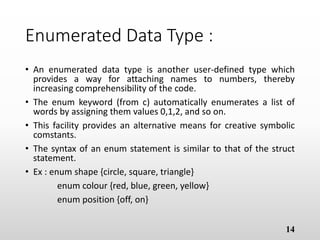
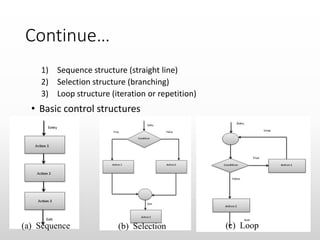
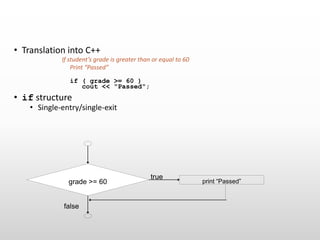
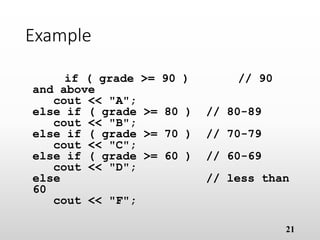
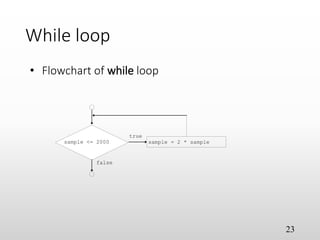
The document provides an overview of basic object-oriented programming concepts, particularly in C and C++, covering identifiers, constants, variables, operators, type casting, enumerated data types, and control structures. It includes rules for naming identifiers, types of constants, variable declaration, various operators (arithmetic, relational, logical), and control structures like loops and selection statements. The content serves as an introductory guide for understanding programming fundamentals and the syntax used in C/C++.