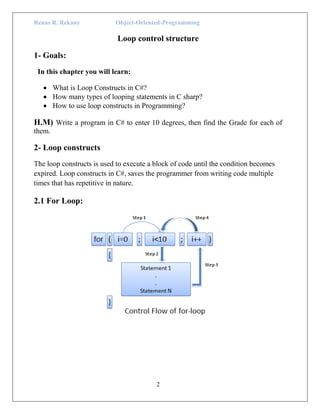
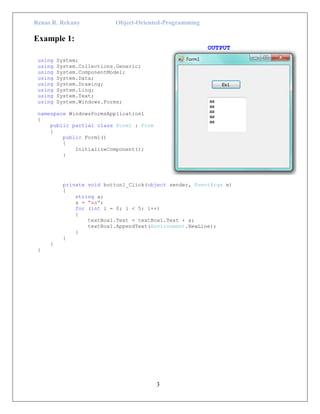
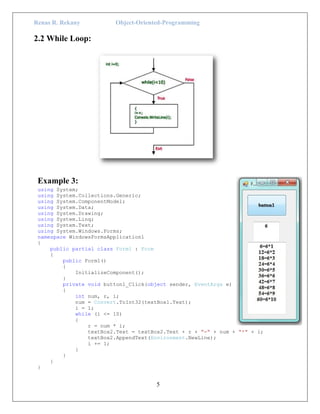
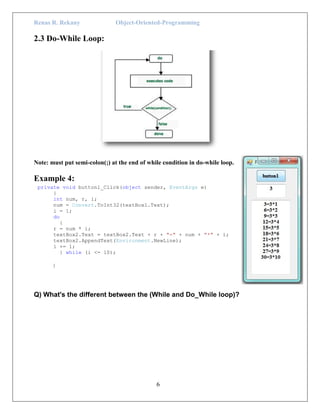
The document discusses loop constructs in C# programming. It covers the main loop types: for, while, and do-while loops. Examples are provided to illustrate each loop, showing how to iterate through code a specified number of times or until a condition is met. The break and continue statements are also explained, with examples showing how break terminates the current loop and continue skips to the next iteration. In summary, the document provides an overview of common loop structures in C# and examples of how to implement for, while, do-while, break, and continue control flows.