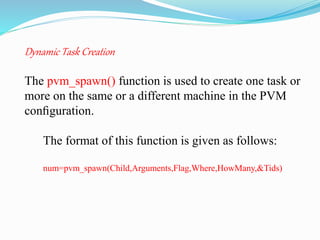
PVM tasks can be started manually or spawned from another task. The initiating task is started manually by running its executable on a host. Additional tasks can be dynamically created using the PVM_spawn() function, where the original task is the parent and newly created tasks are children. PVM_spawn() specifies the machine, executable, number of copies, and arguments for the child tasks. All PVM tasks have a task ID (TID) that can be used to identify senders and receivers in communication. The TID of the current, parent, and daemon tasks can be retrieved using various PVM functions. Dynamic task creation with PVM_spawn() takes parameters like the child executable, arguments, spawn location, and