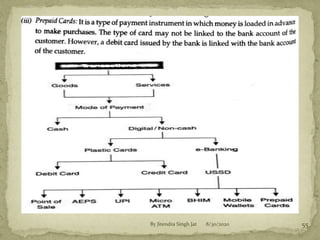
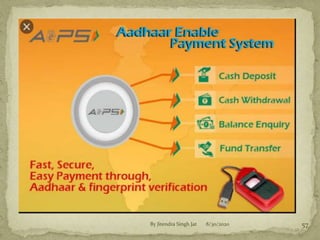
This document outlines several key principles of insurance:
(i) Utmost good faith requires full disclosure by the insured and clarity by the insurer. The insured must disclose all material facts, and failure to do so makes the contract voidable.
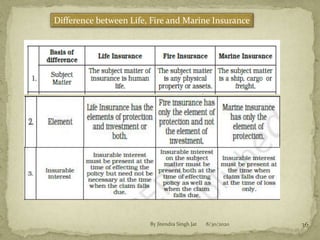
(ii) Insurable interest means the insured will financially suffer if the insured event occurs. For property insurance, this interest must exist when the event happens.
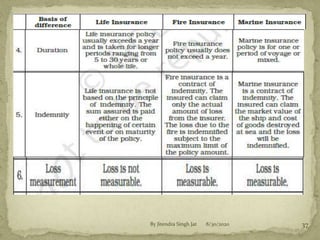
(iii) Indemnity means compensating the insured to the same pre-loss financial position for property insurance losses. It does not apply to life insurance.