Business Relationship Management (BRM) involves:
- Understanding customer needs and ensuring services meet changing needs over time.
- Establishing constructive relationships between service providers and customers.
- Identifying changes that could impact services and ensuring services deliver value.
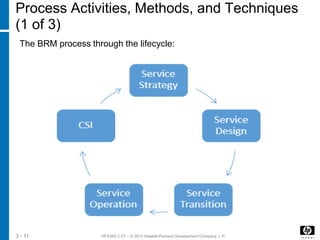
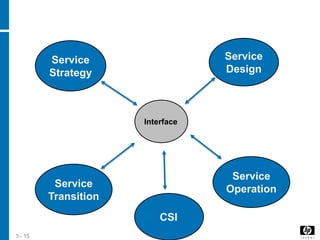
BRM activities occur throughout the service lifecycle. The process is triggered by events like new services or customer issues. BRM interfaces with other processes to share information to improve services and customer satisfaction. Key challenges for BRM include clearly defining services and gaining customer cooperation.