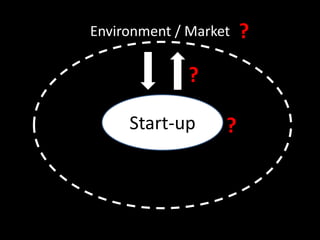
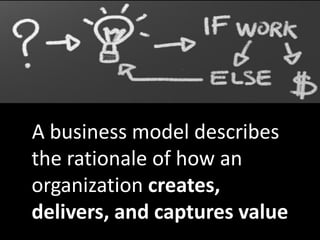
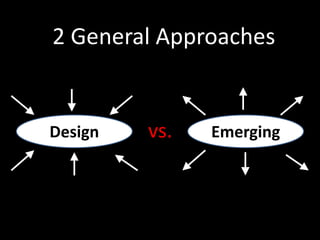
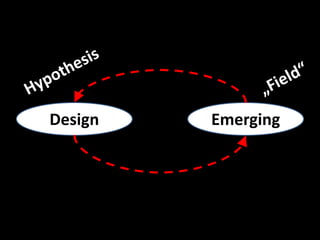
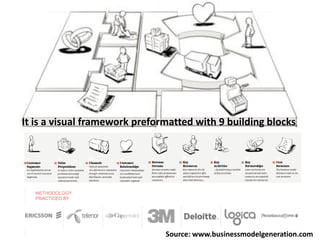
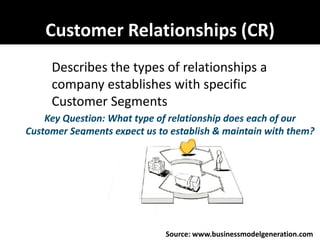
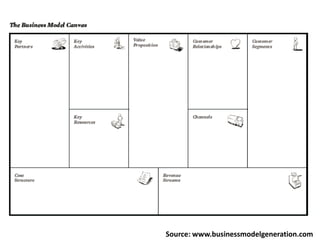
The document provides an overview of business models, including the key components of a business model canvas with 9 building blocks: customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure. It emphasizes that the most important things for startups are to generate cash flows as soon as possible, keep the burn rate low, think but don't overanalyze, and find wrong paths quickly. It also notes that the single most important trait of entrepreneurs is that they take action.