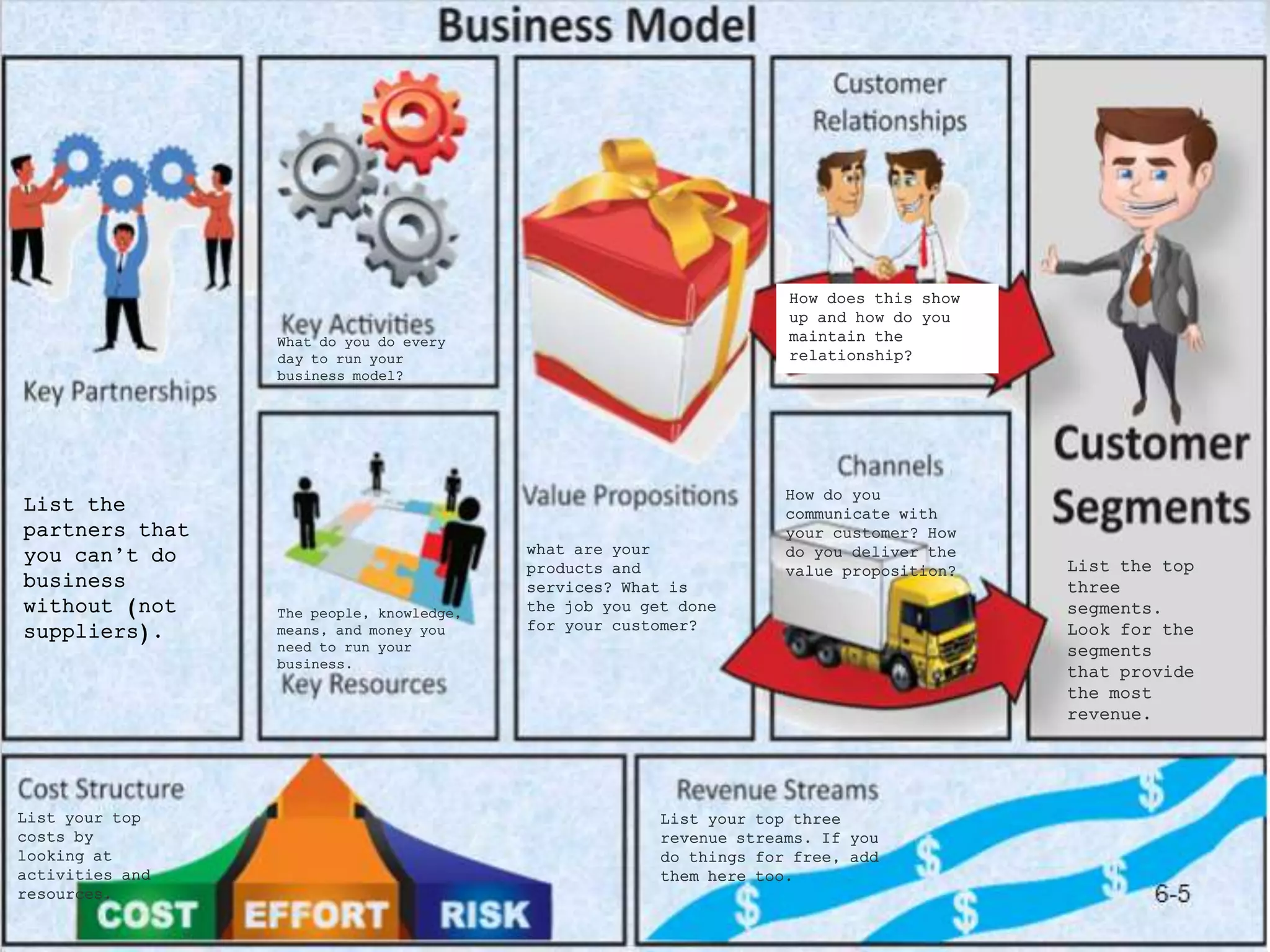
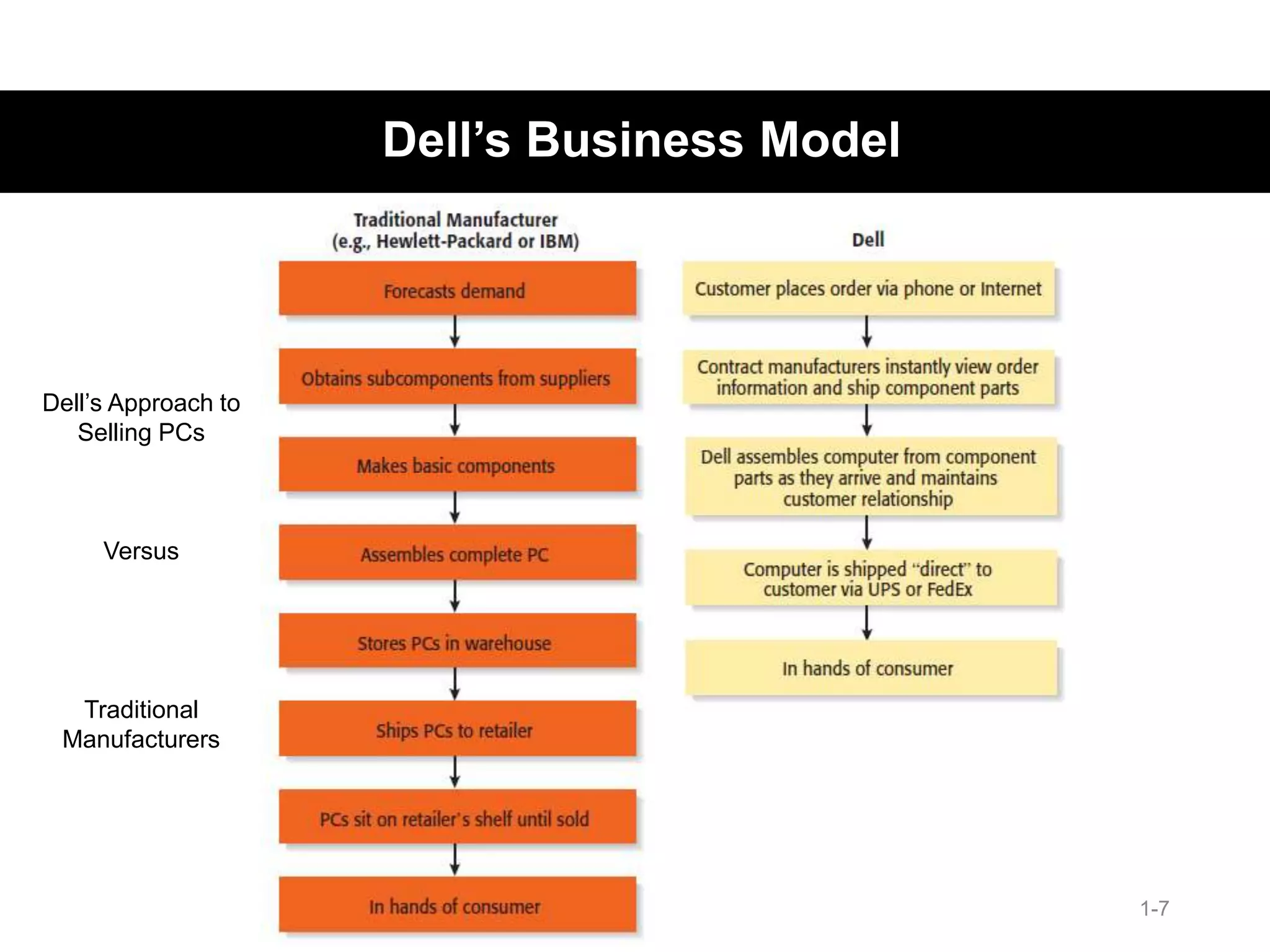
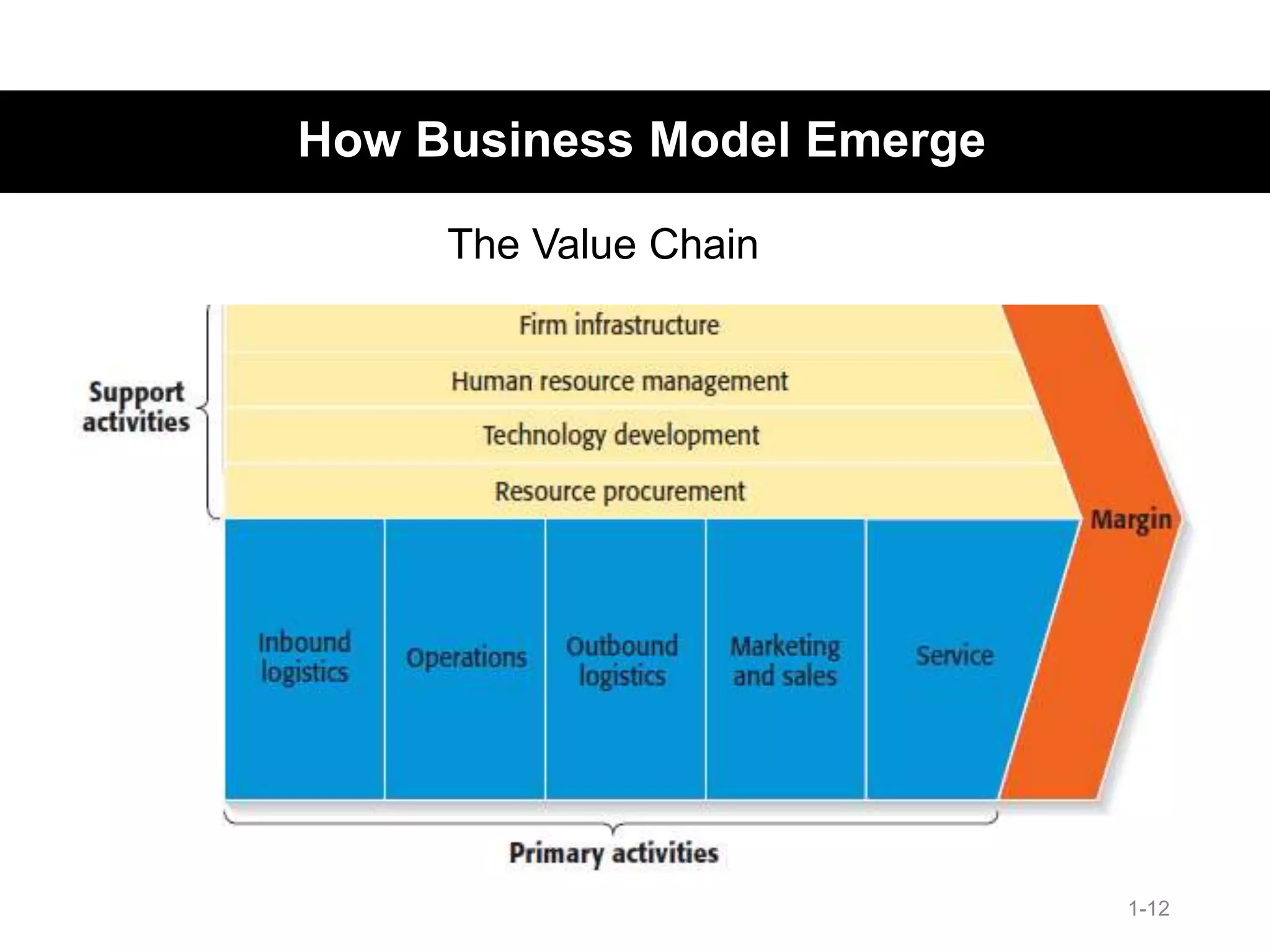
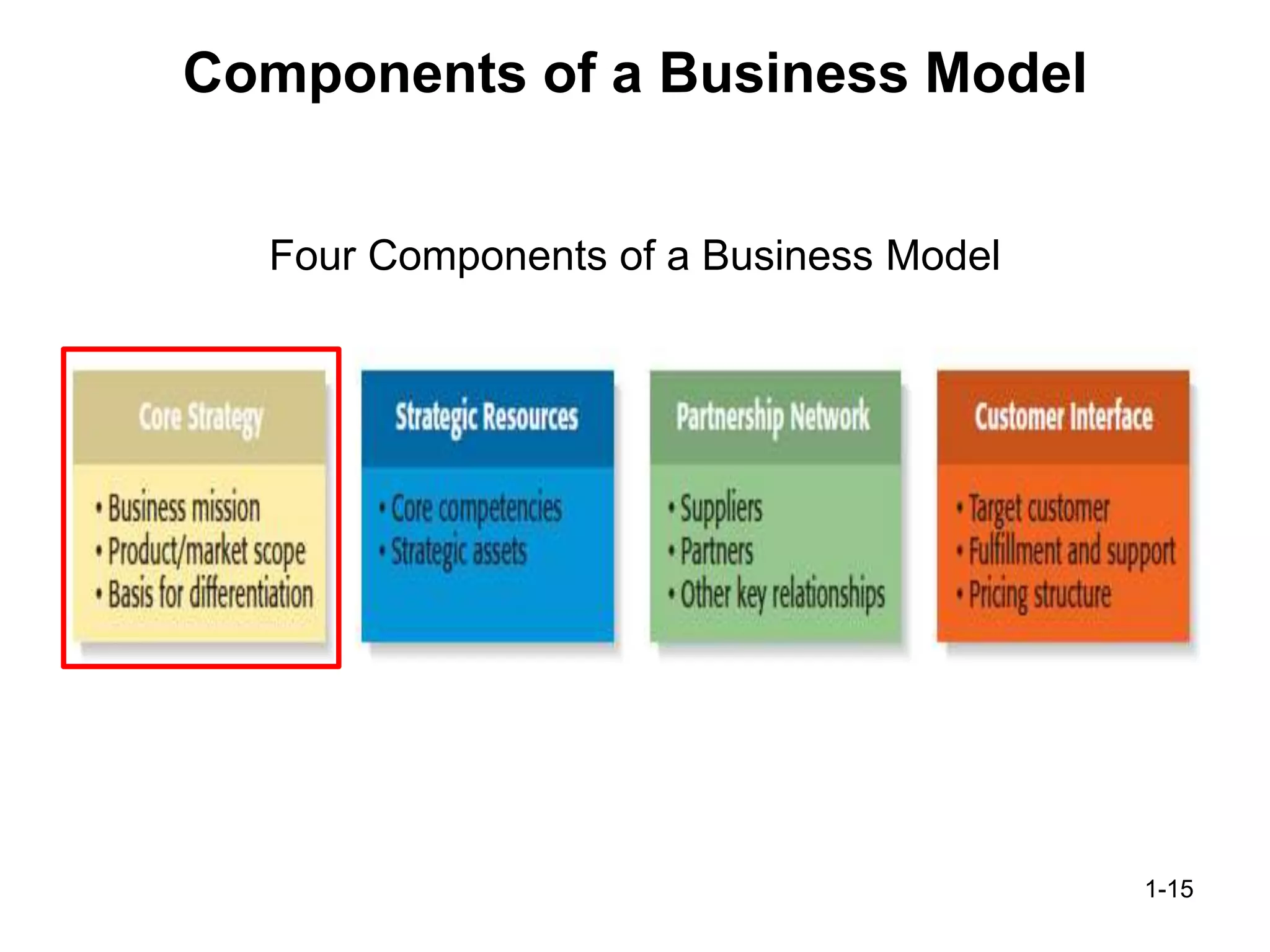
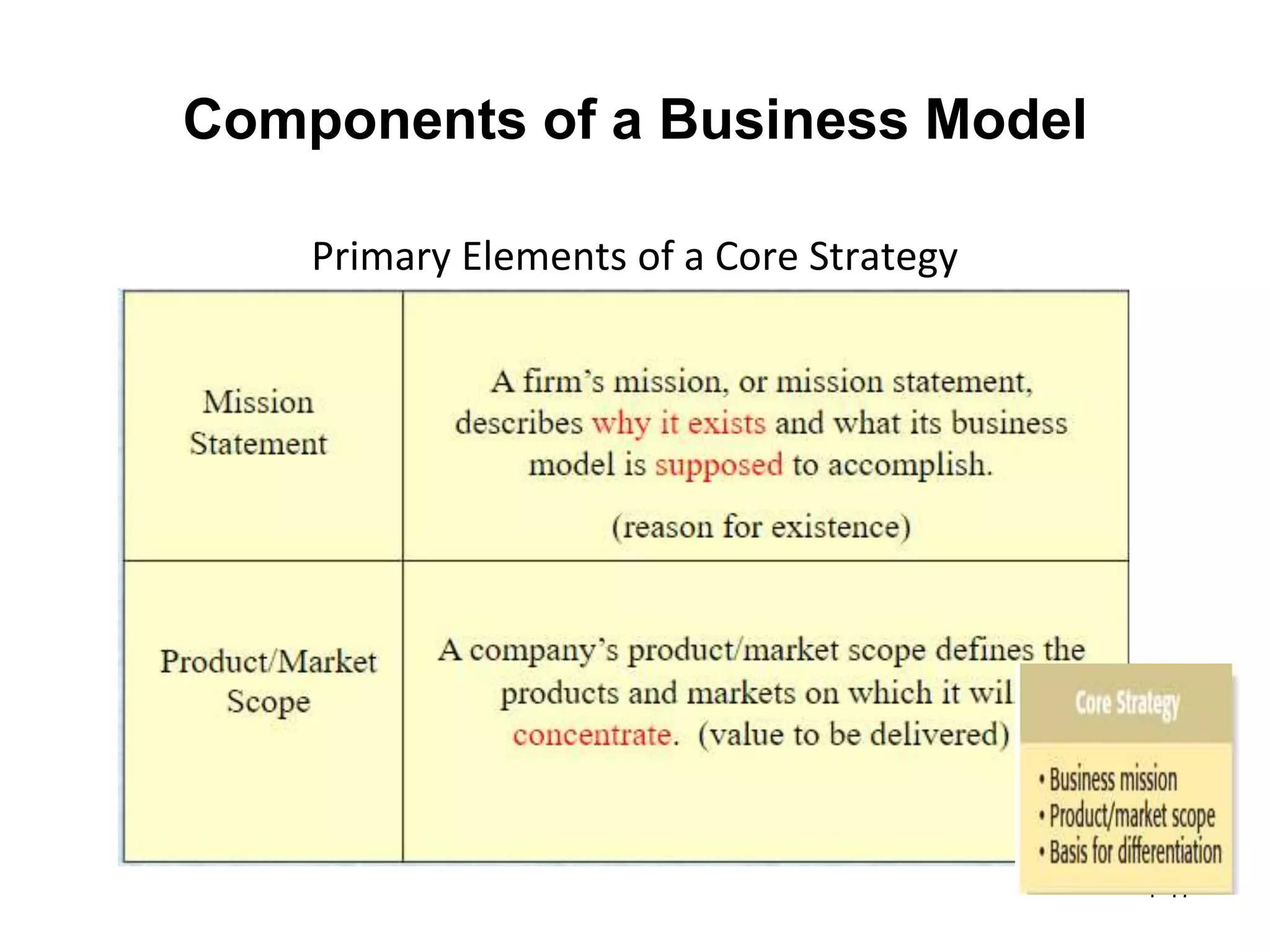
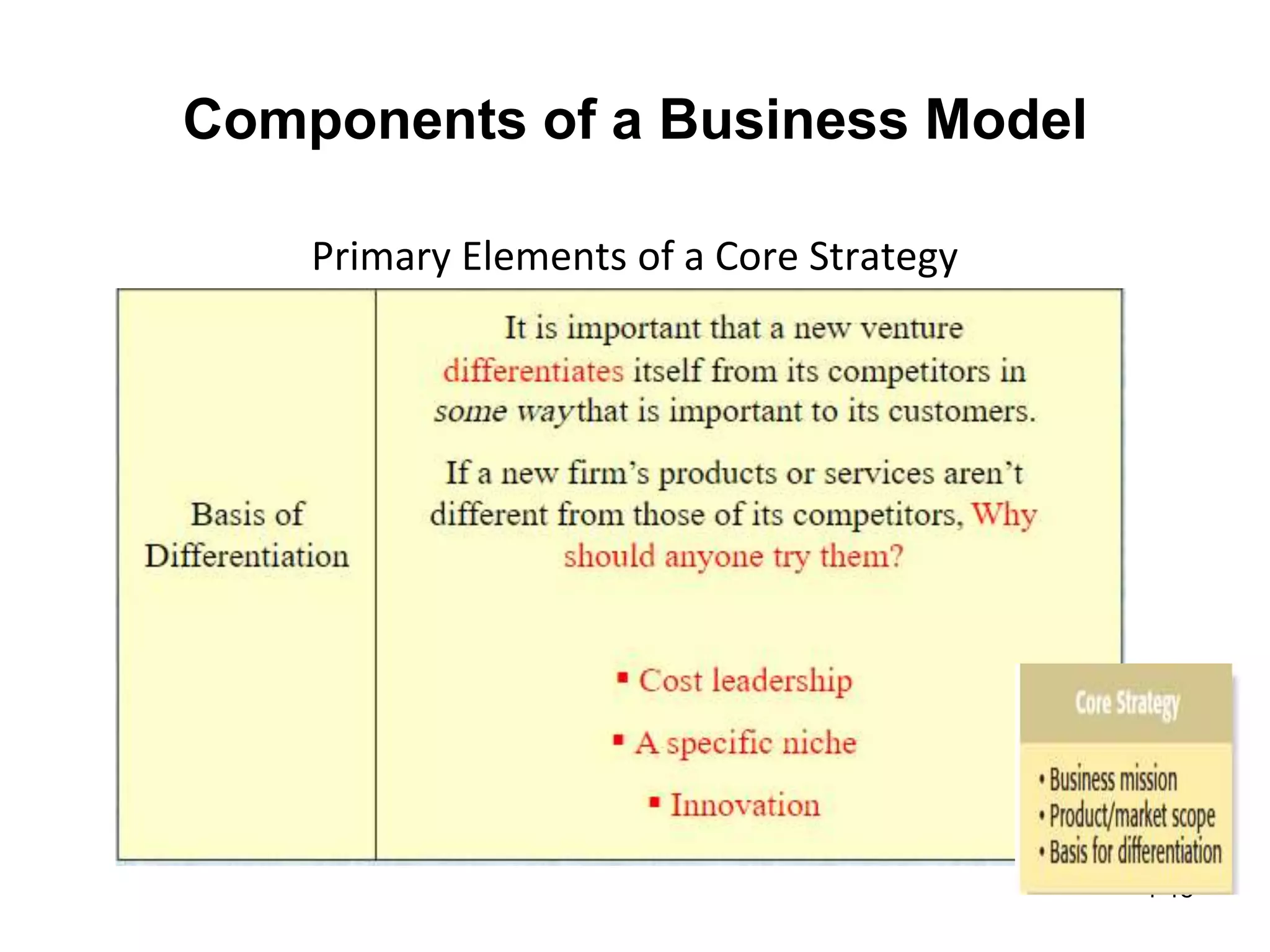
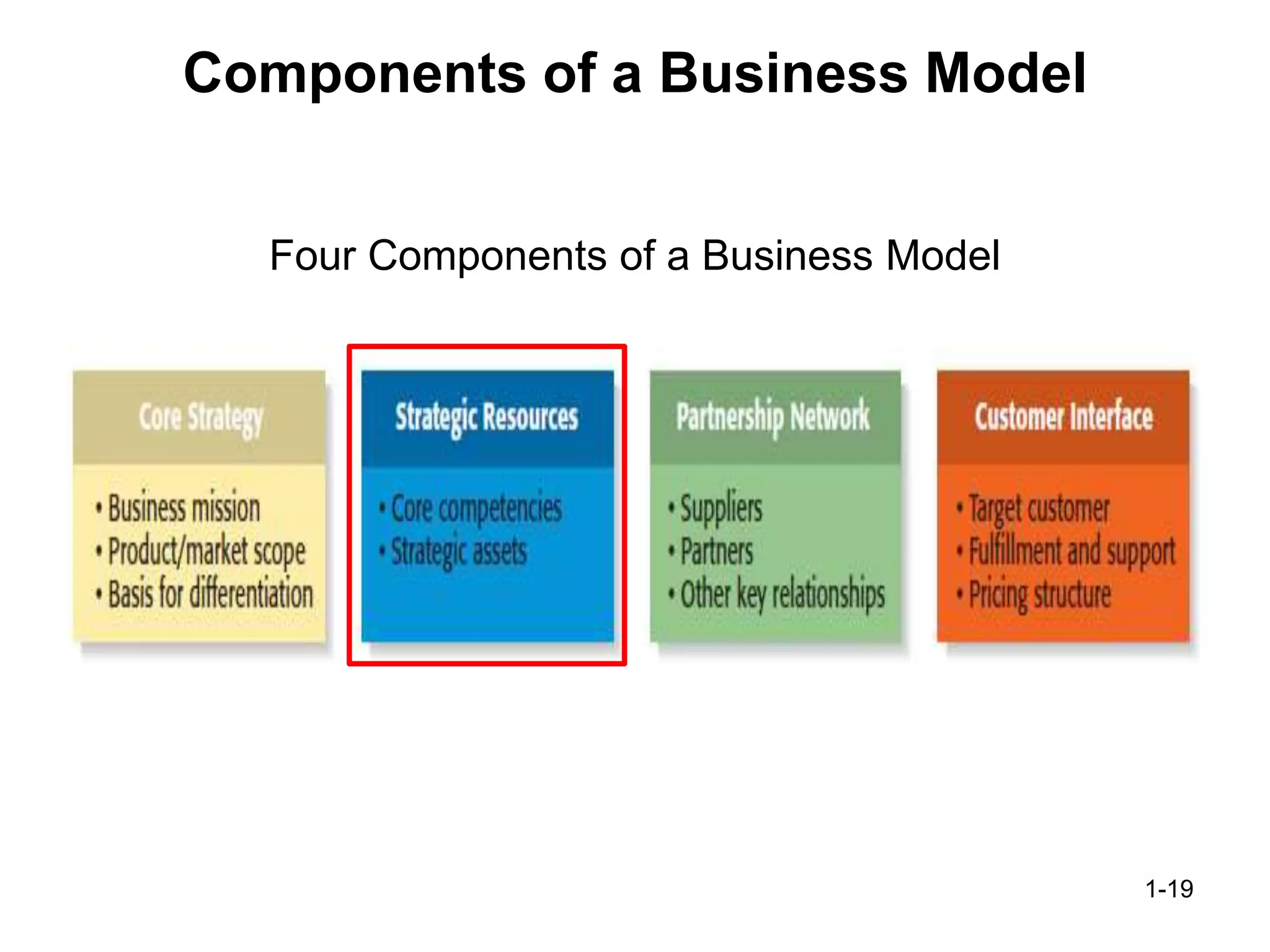
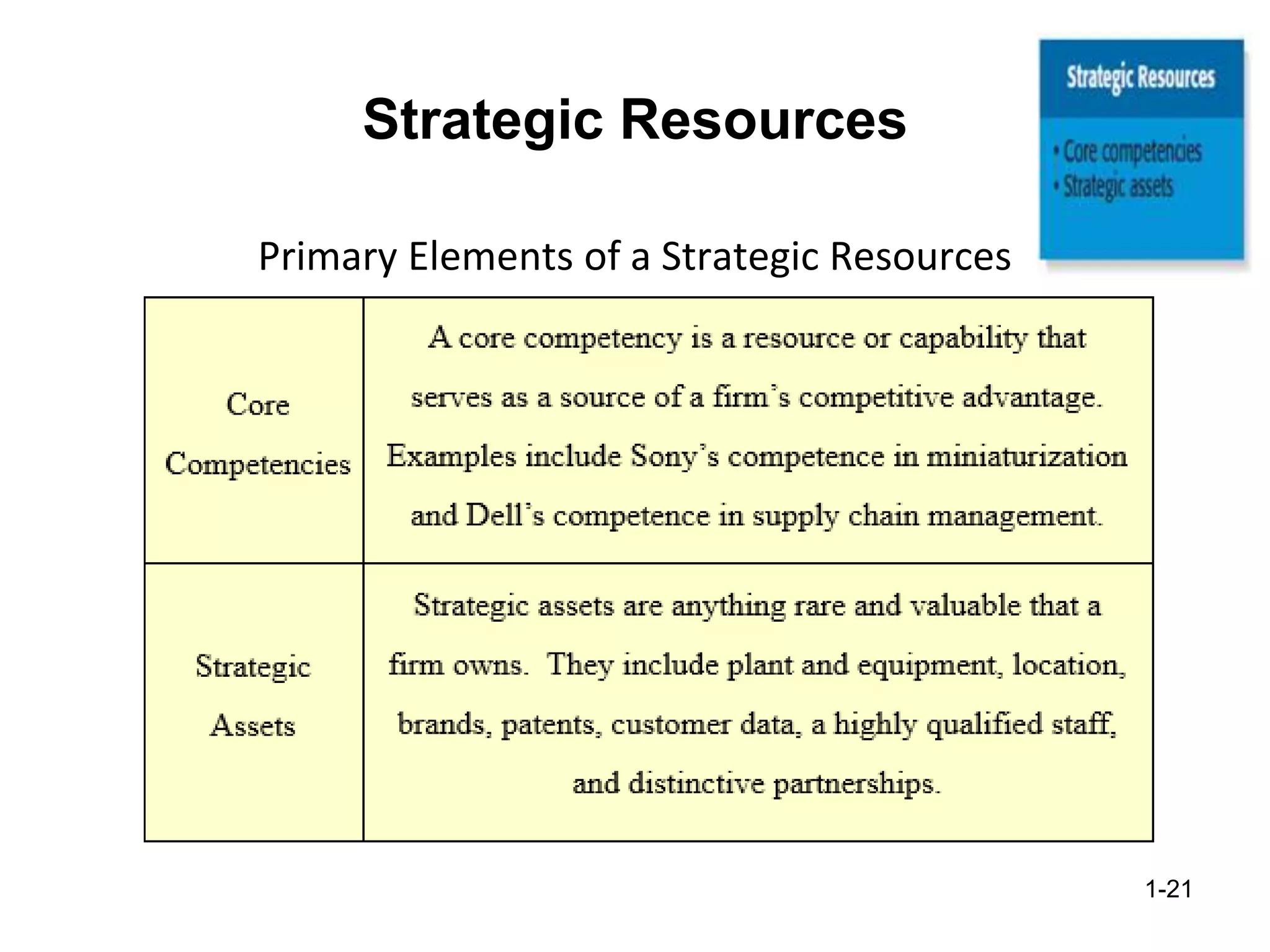
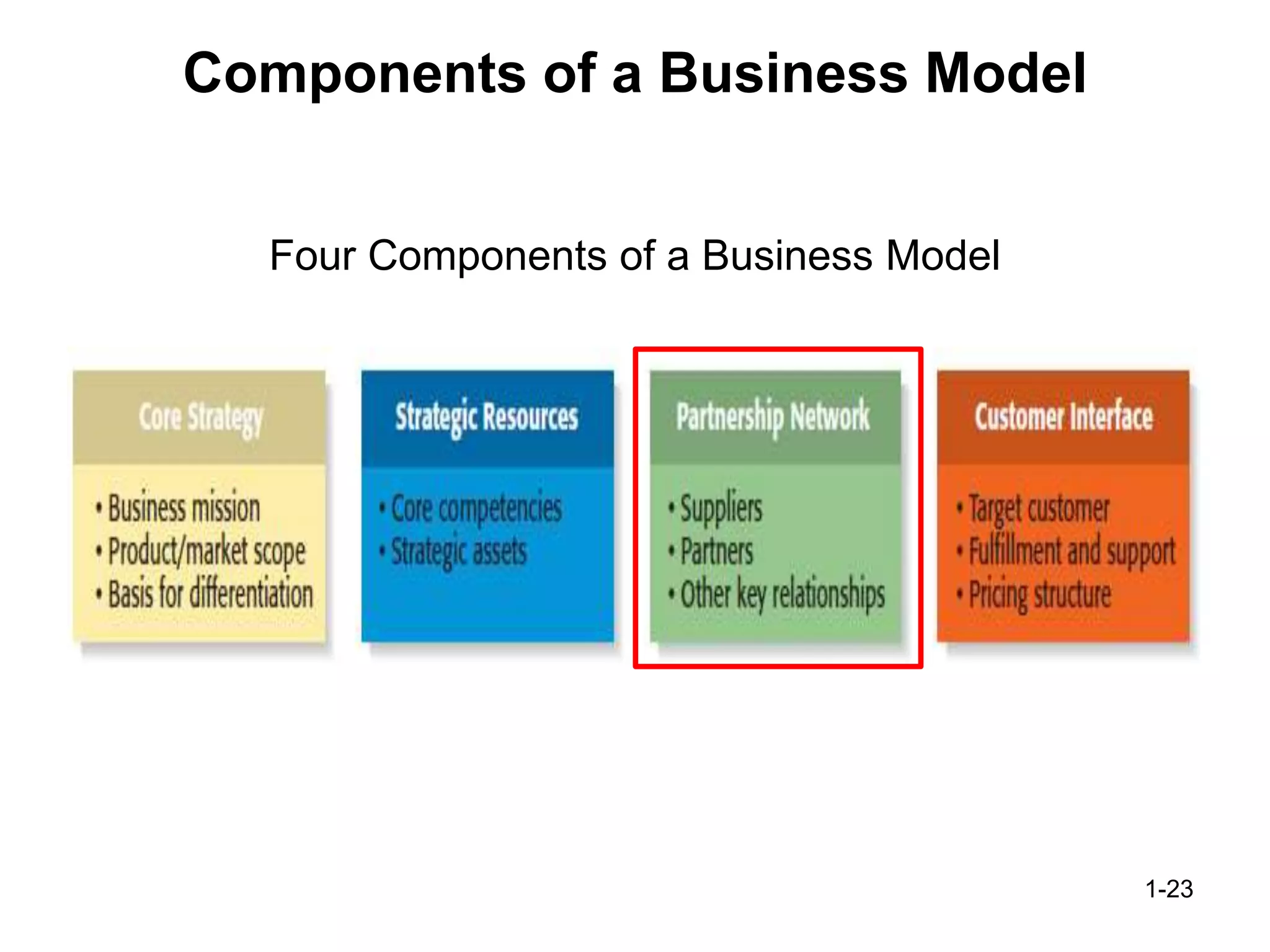
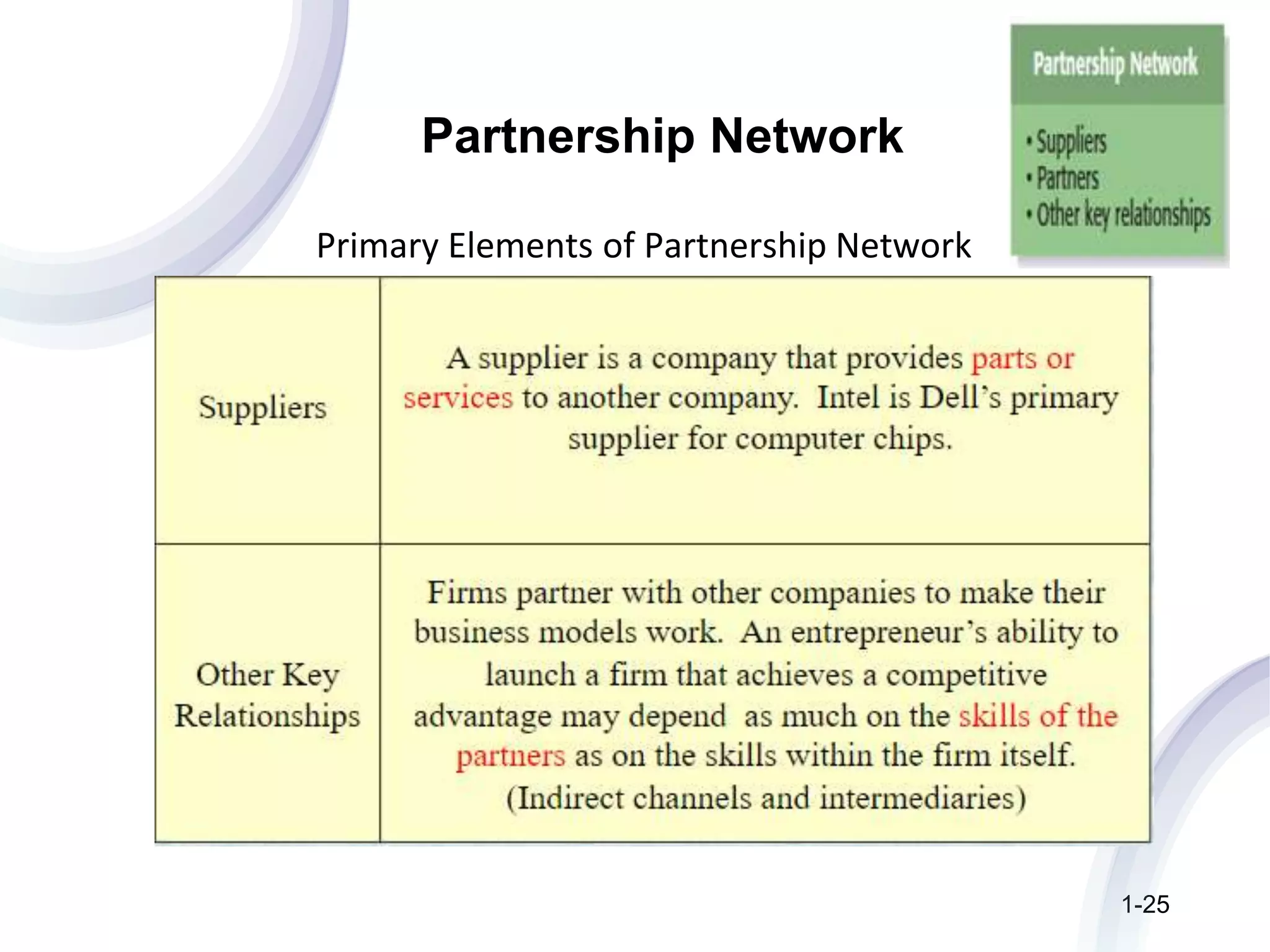
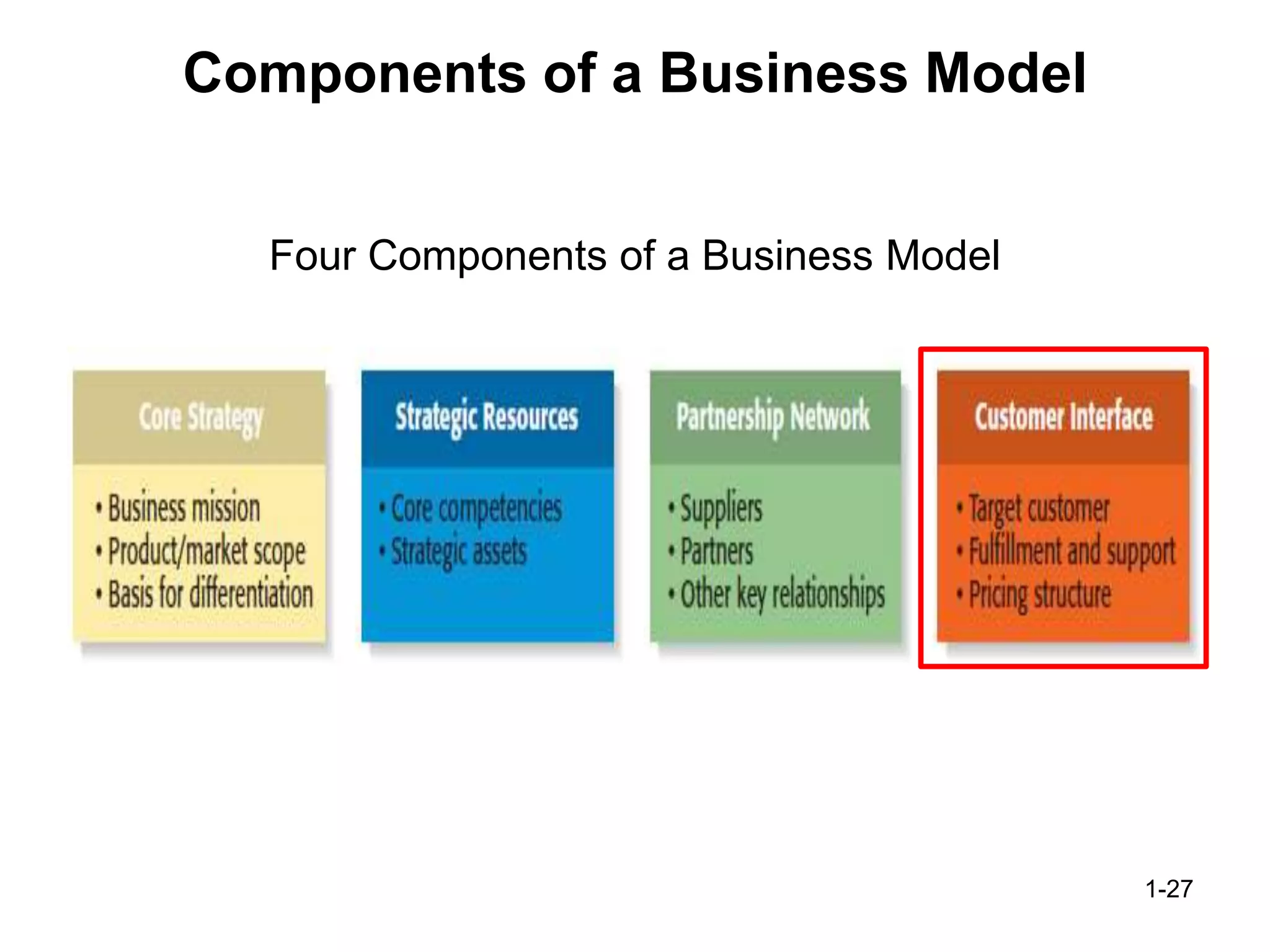
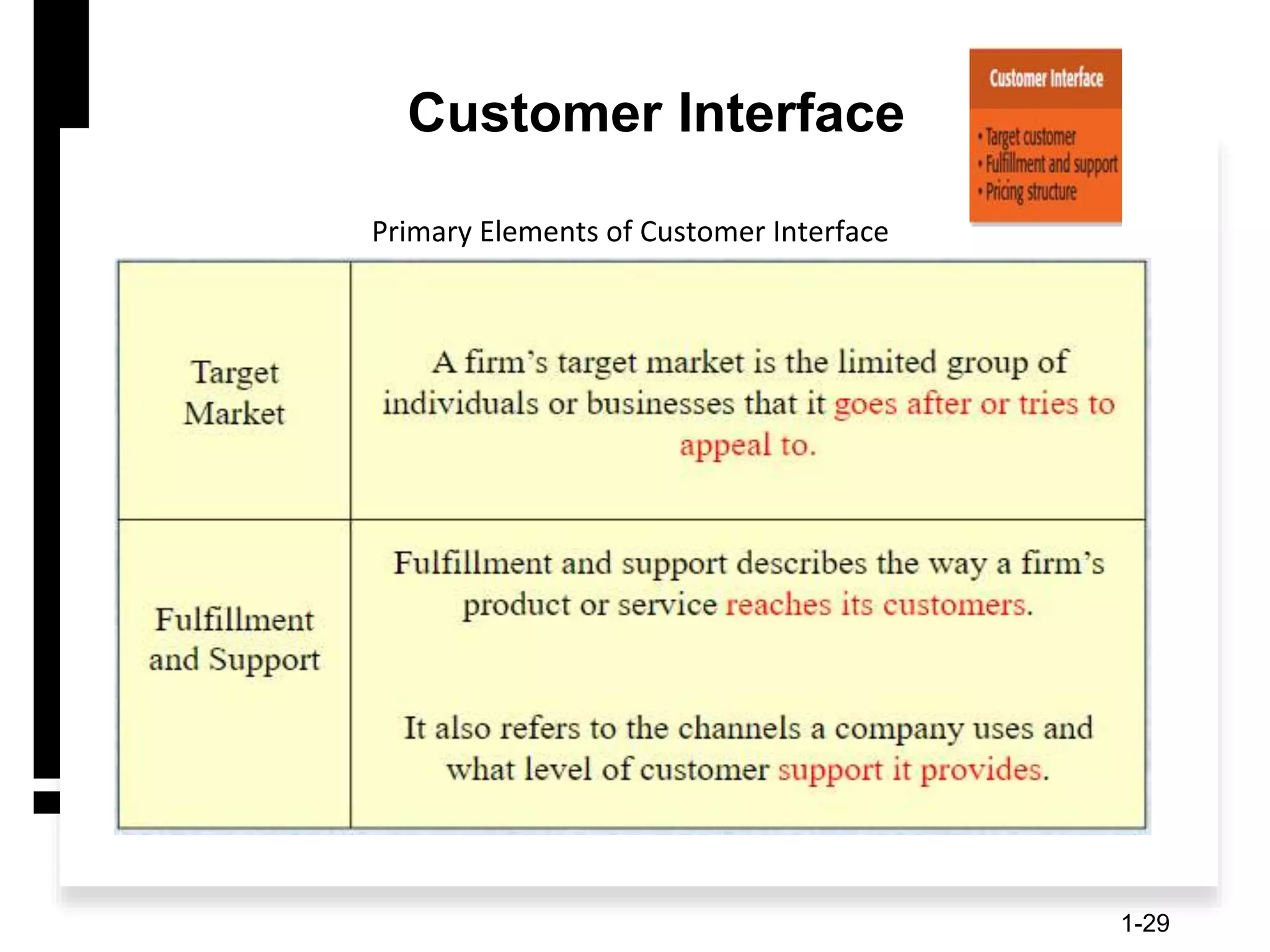
The document discusses the components and importance of developing an effective business model. It describes a business model as a firm's plan for how it competes, uses resources, structures relationships, interfaces with customers, and creates value. An effective business model has four key components: core strategy, strategic resources, partnership network, and customer interface. Developing a clear business model is important because it serves as an ongoing feasibility analysis, focuses attention on how elements fit together, and explains why network participants are willing to work with the company.