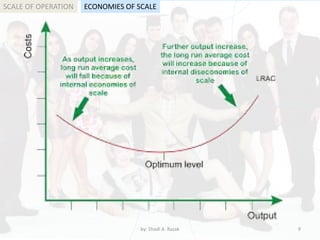
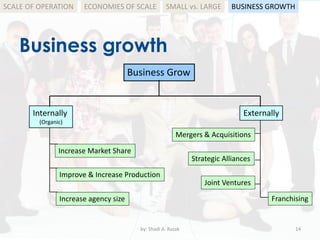
The document outlines the concept of scale of operation in business, emphasizing the benefits of economies of scale and the challenges of diseconomies of scale. It differentiates between internal and external growth strategies, detailing how businesses can achieve growth through organic methods, mergers, and acquisitions. Furthermore, it compares small and large organizations, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages in terms of management, flexibility, and access to resources.