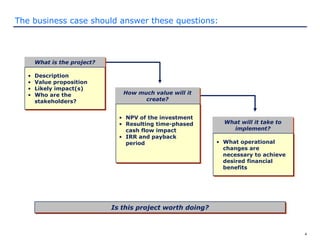
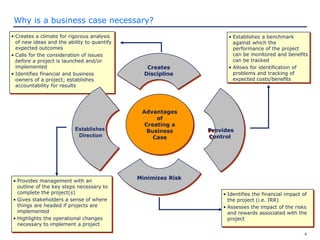
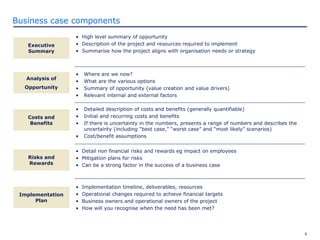
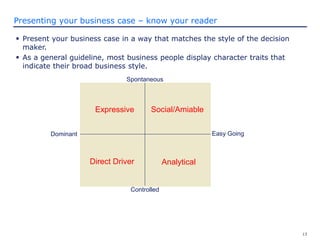
The document discusses how to prepare and present an effective business case. It explains that a business case makes the business reason for a project clear to decision makers and provides information for them to determine if the project should be funded. The document outlines what should be included in a business case such as the project description, costs, benefits, risks, and implementation plan. It also provides guidance on how to present the business case by knowing the audience and tailoring the presentation to their decision making style.