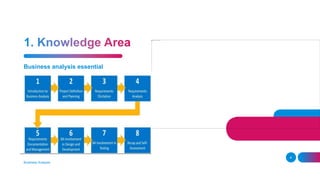
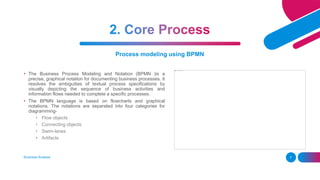
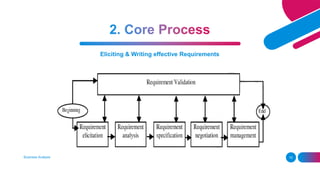
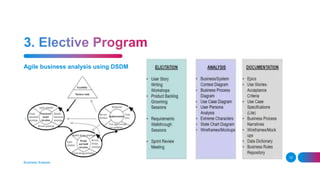
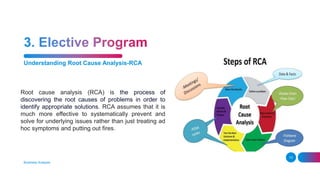
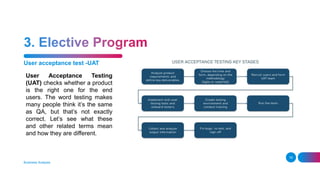
The document outlines the essential and elective programs in business analysis, focusing on strategic analysis, business requirements documentation, process modeling, and effective requirement elicitation. It details methodologies for creating business cases and conducting root cause analysis, along with user training and acceptance testing. Key objectives include understanding stakeholder needs and enhancing operational efficiency within organizations.