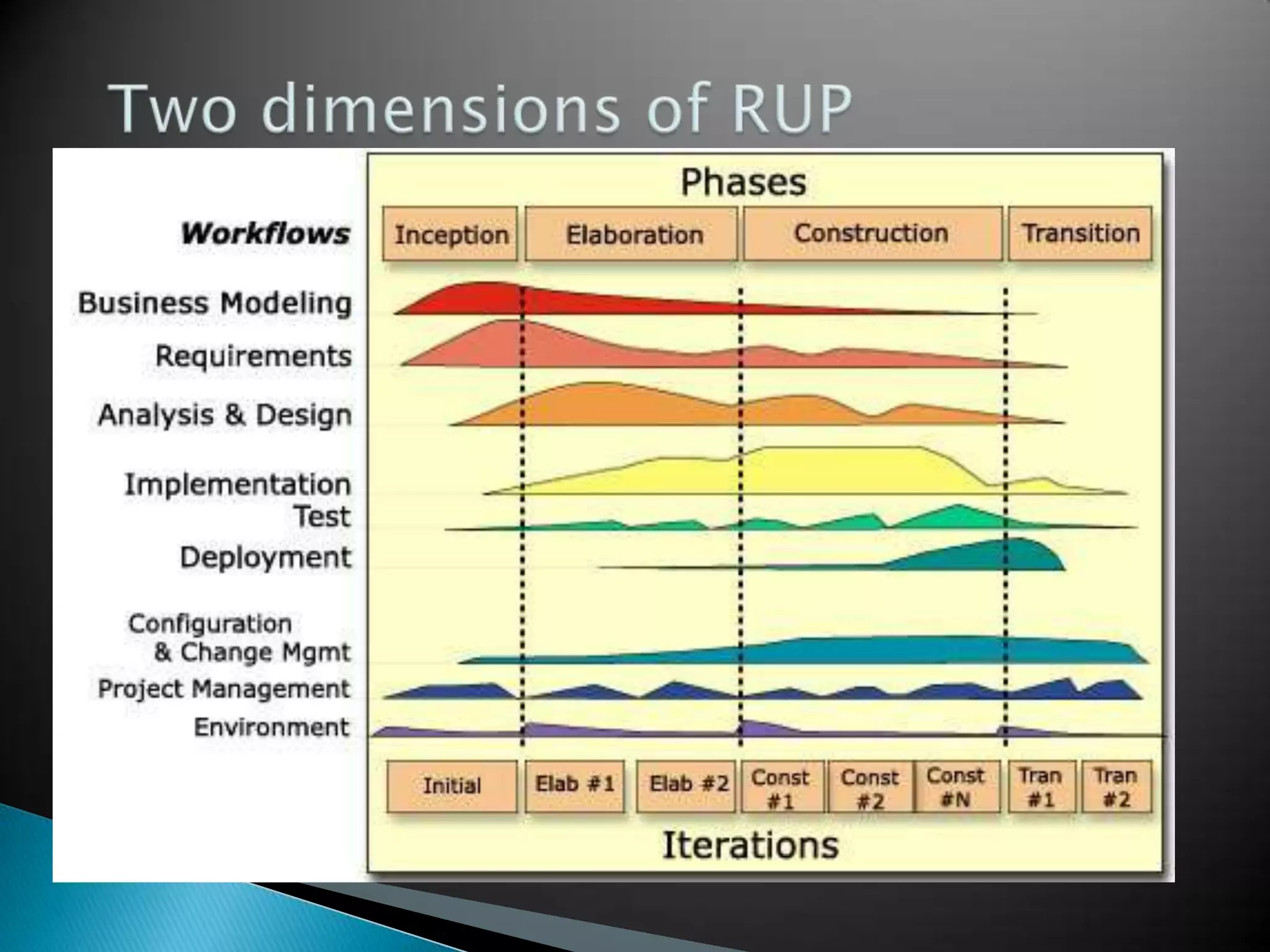
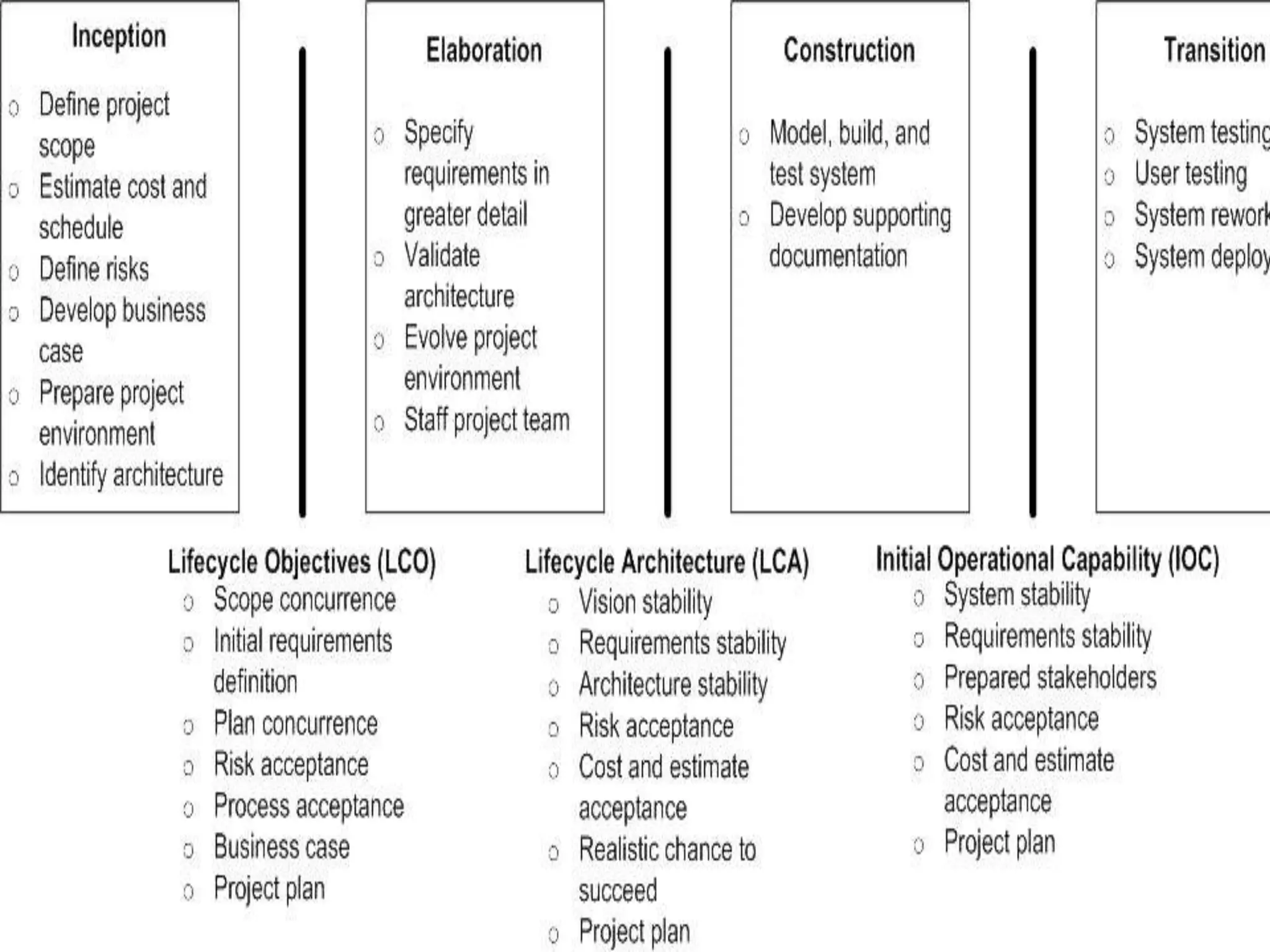
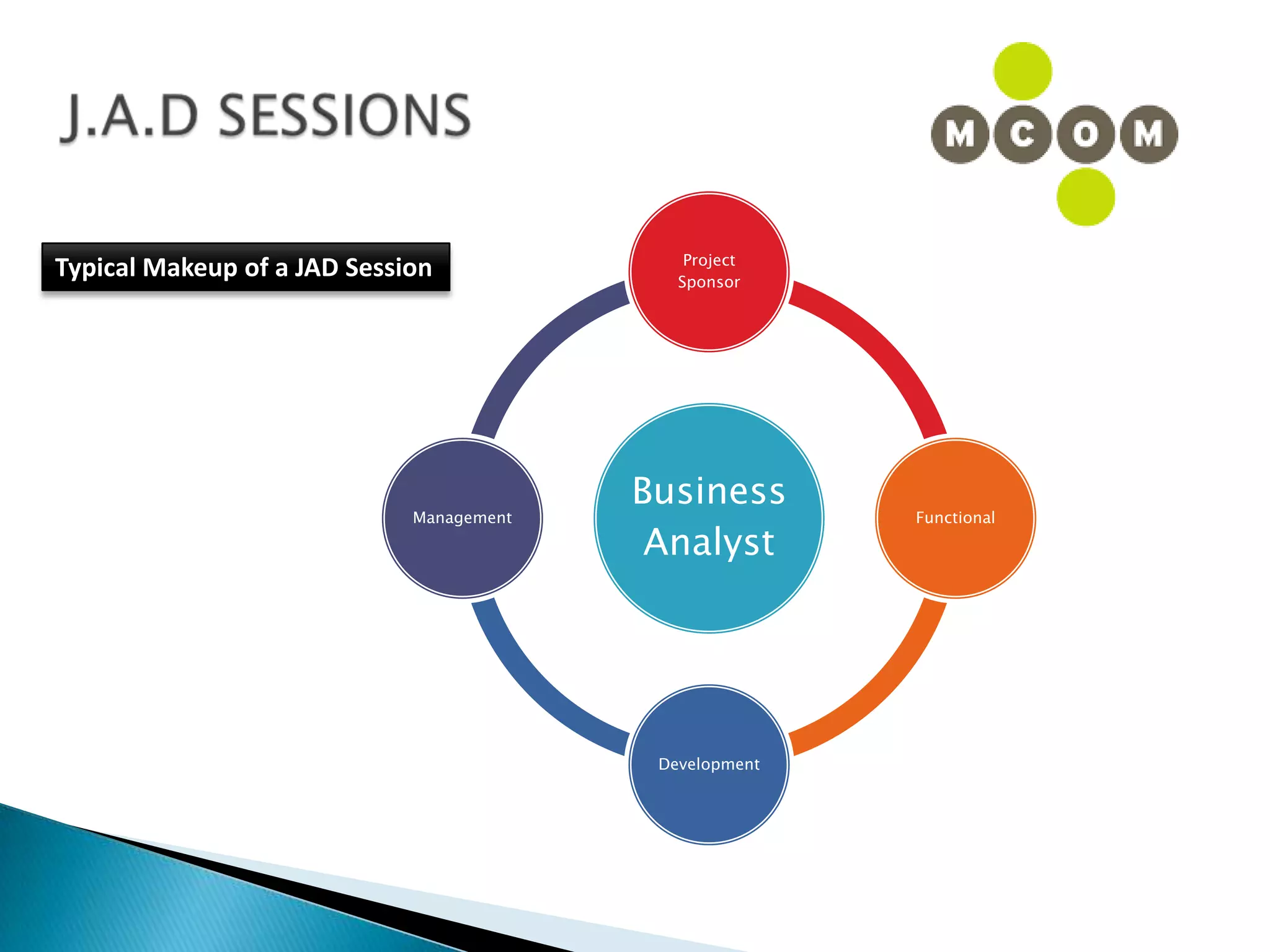
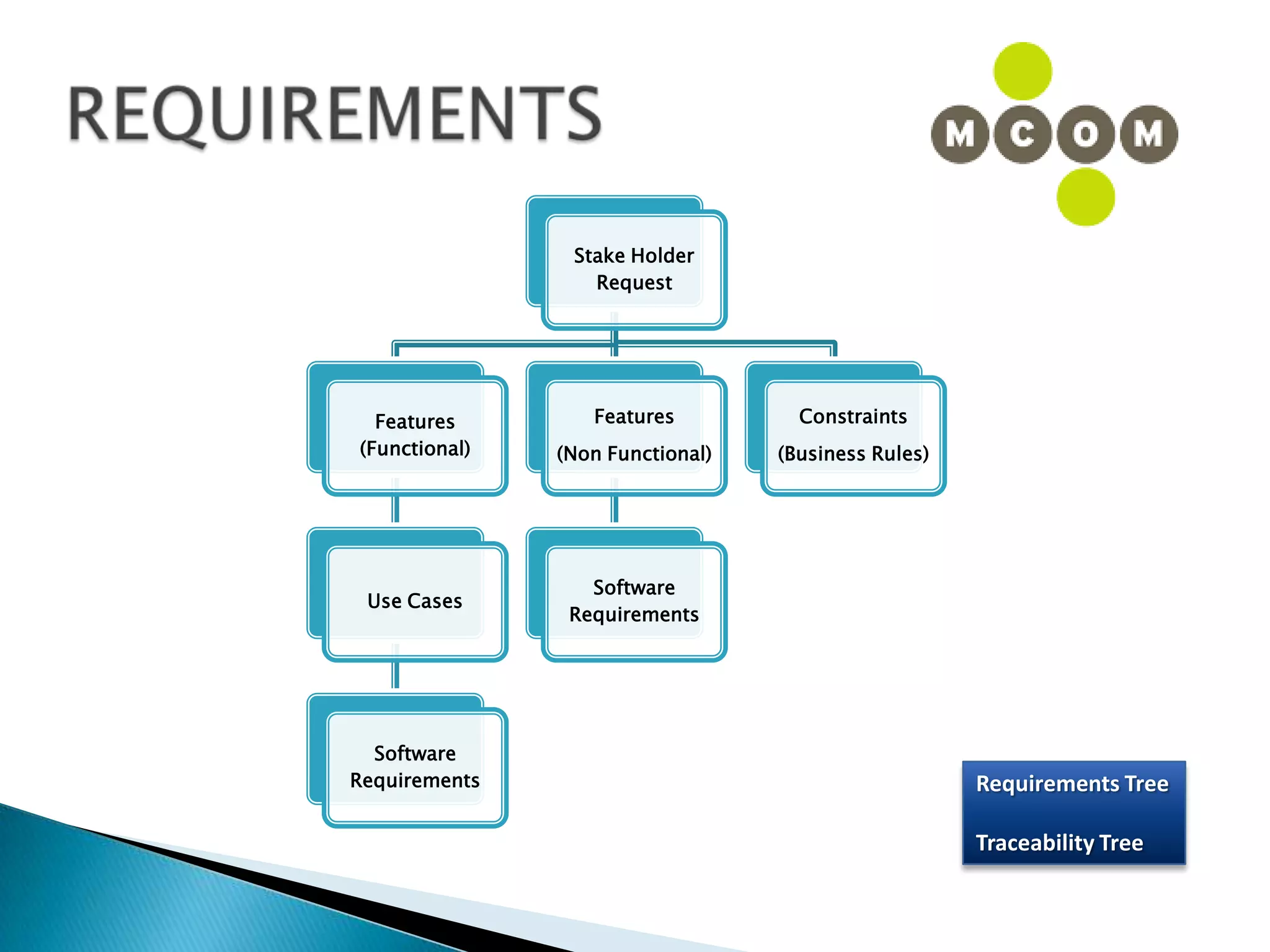
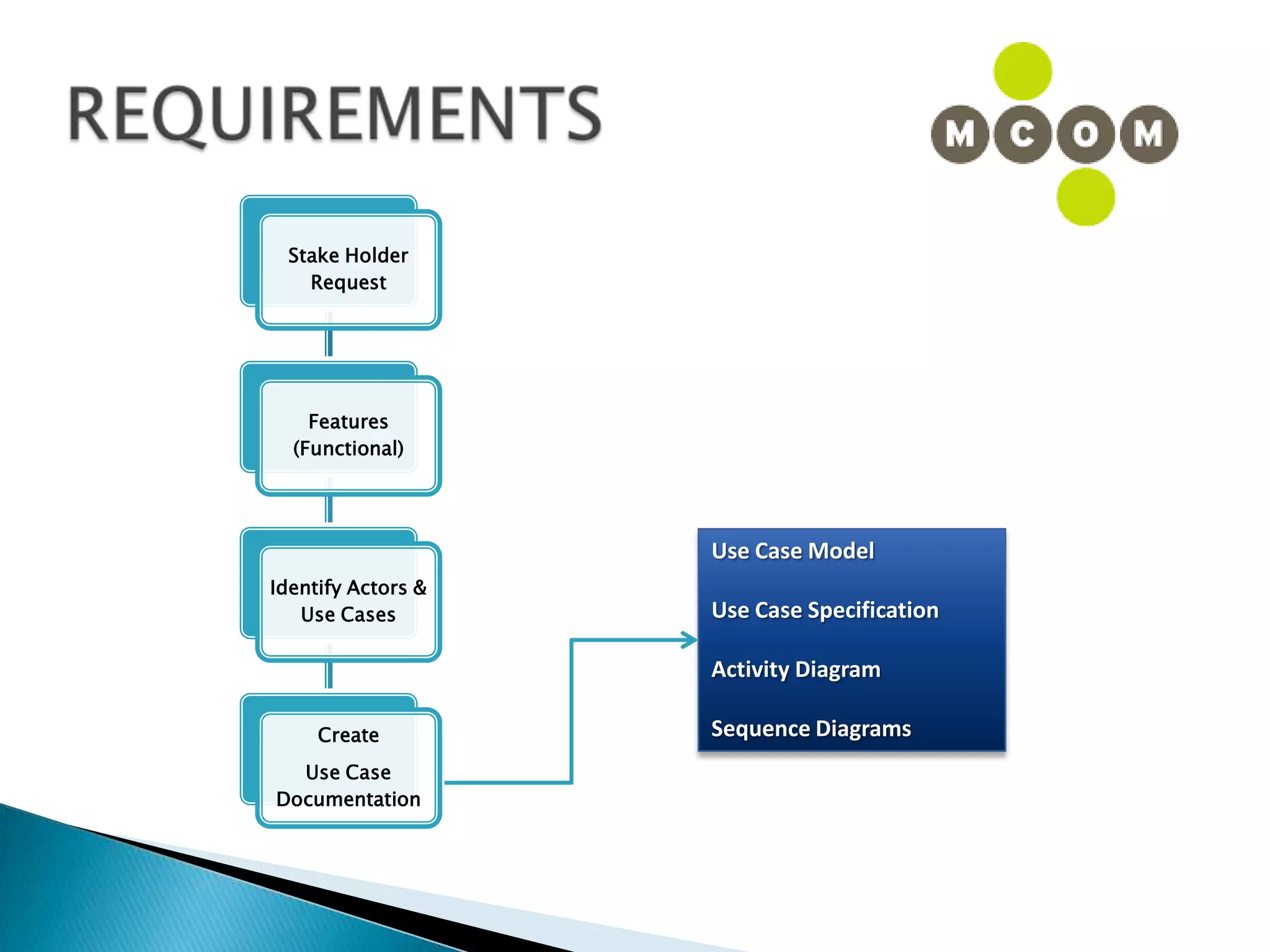
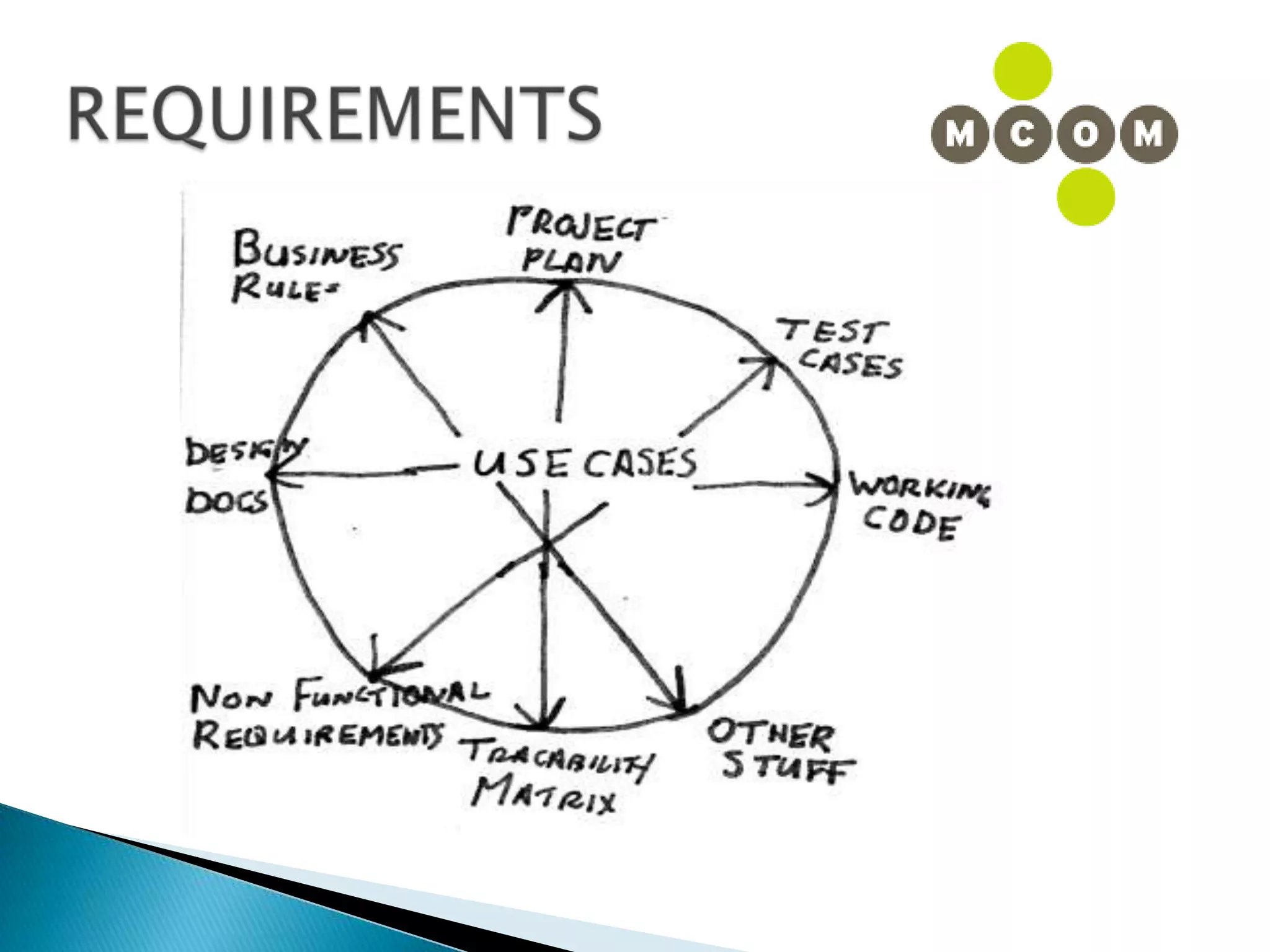
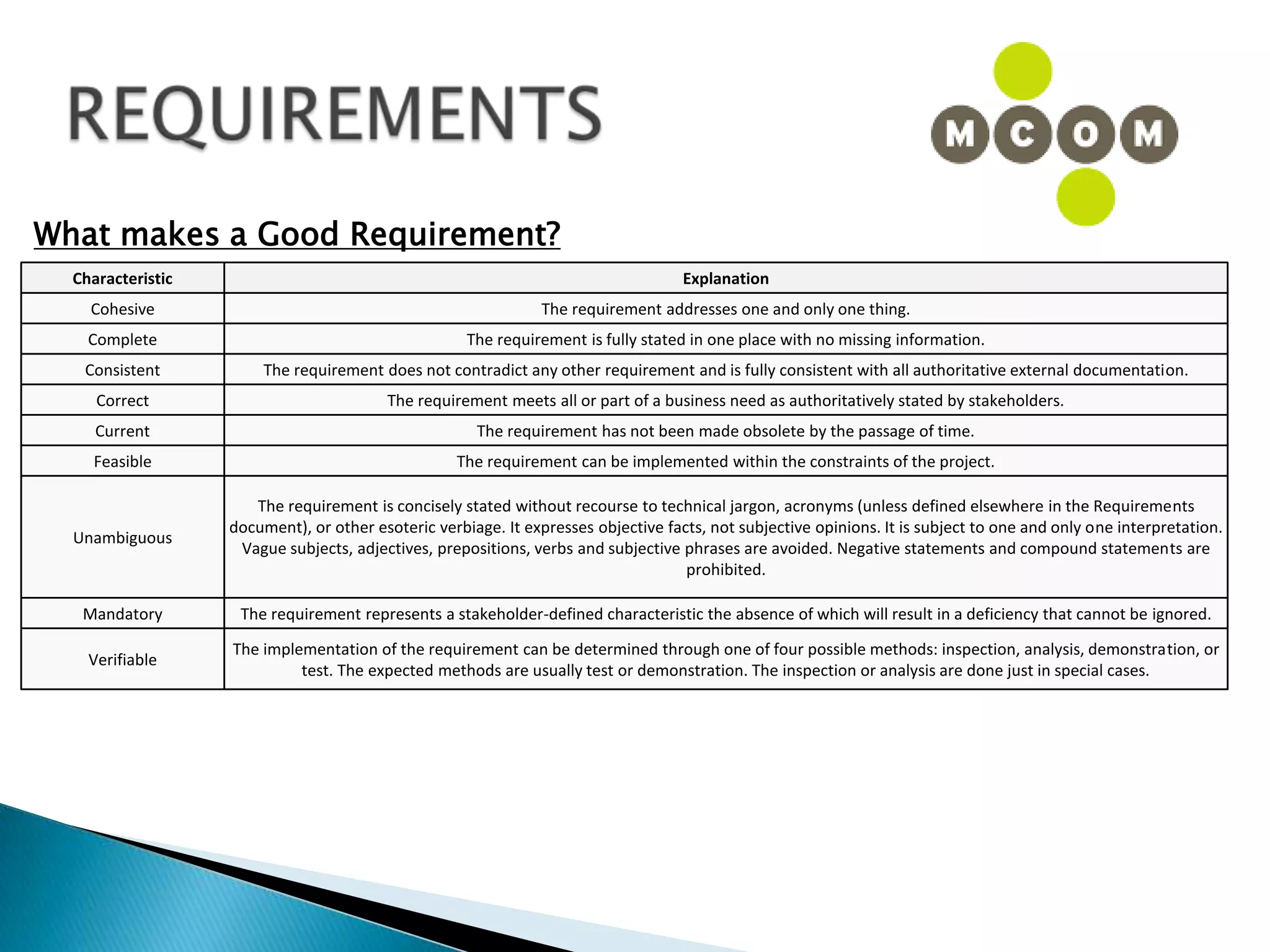
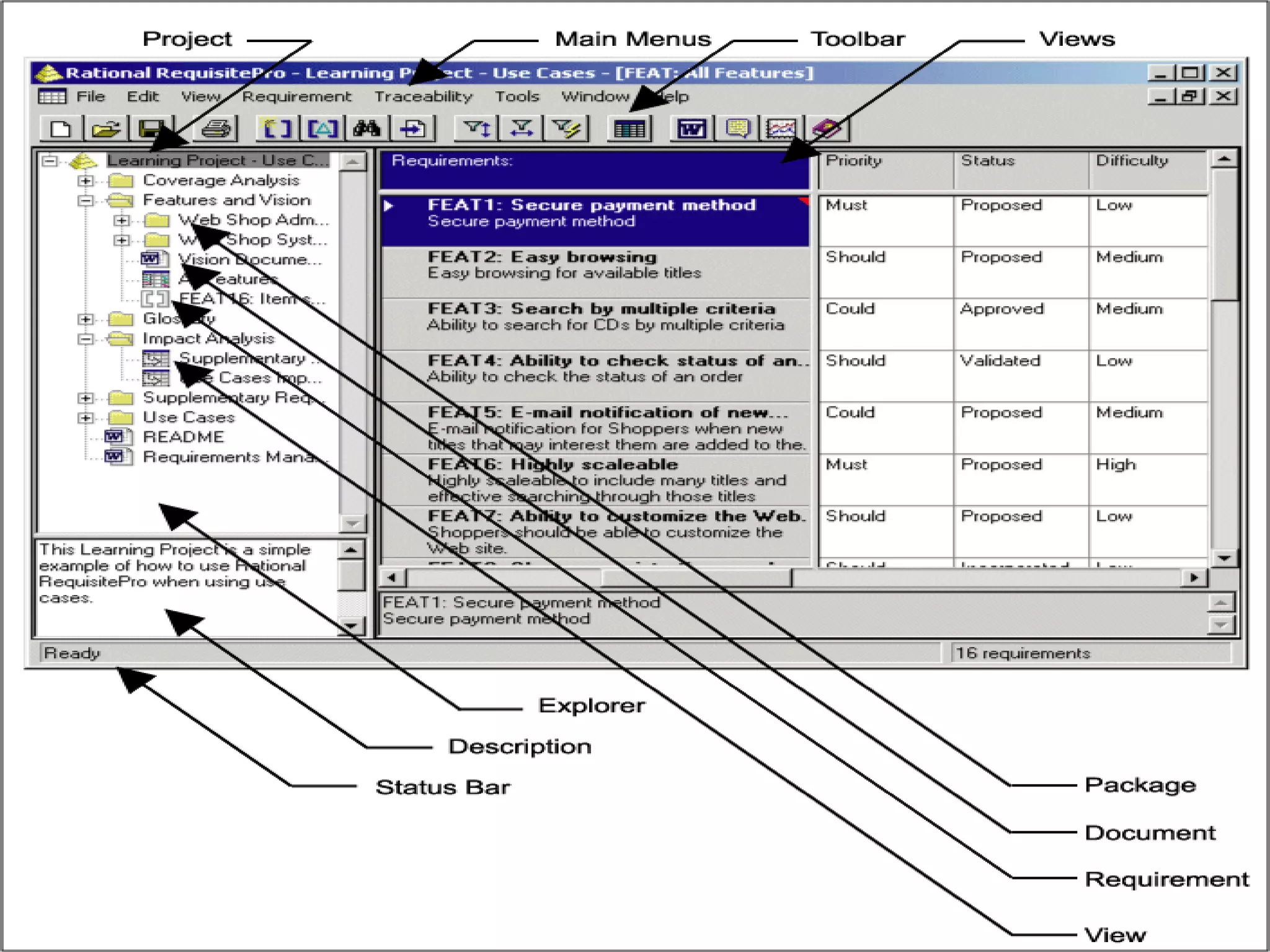
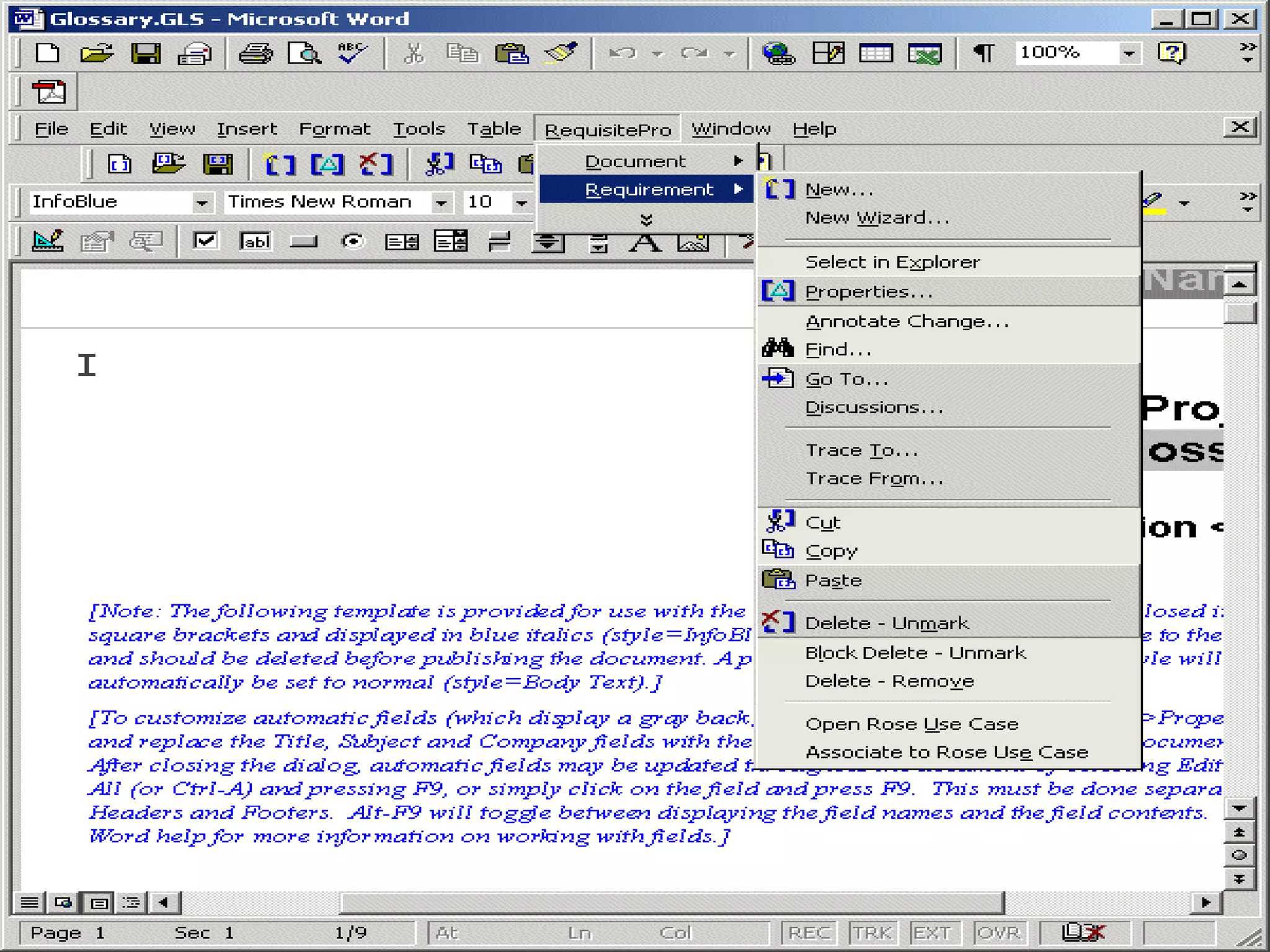
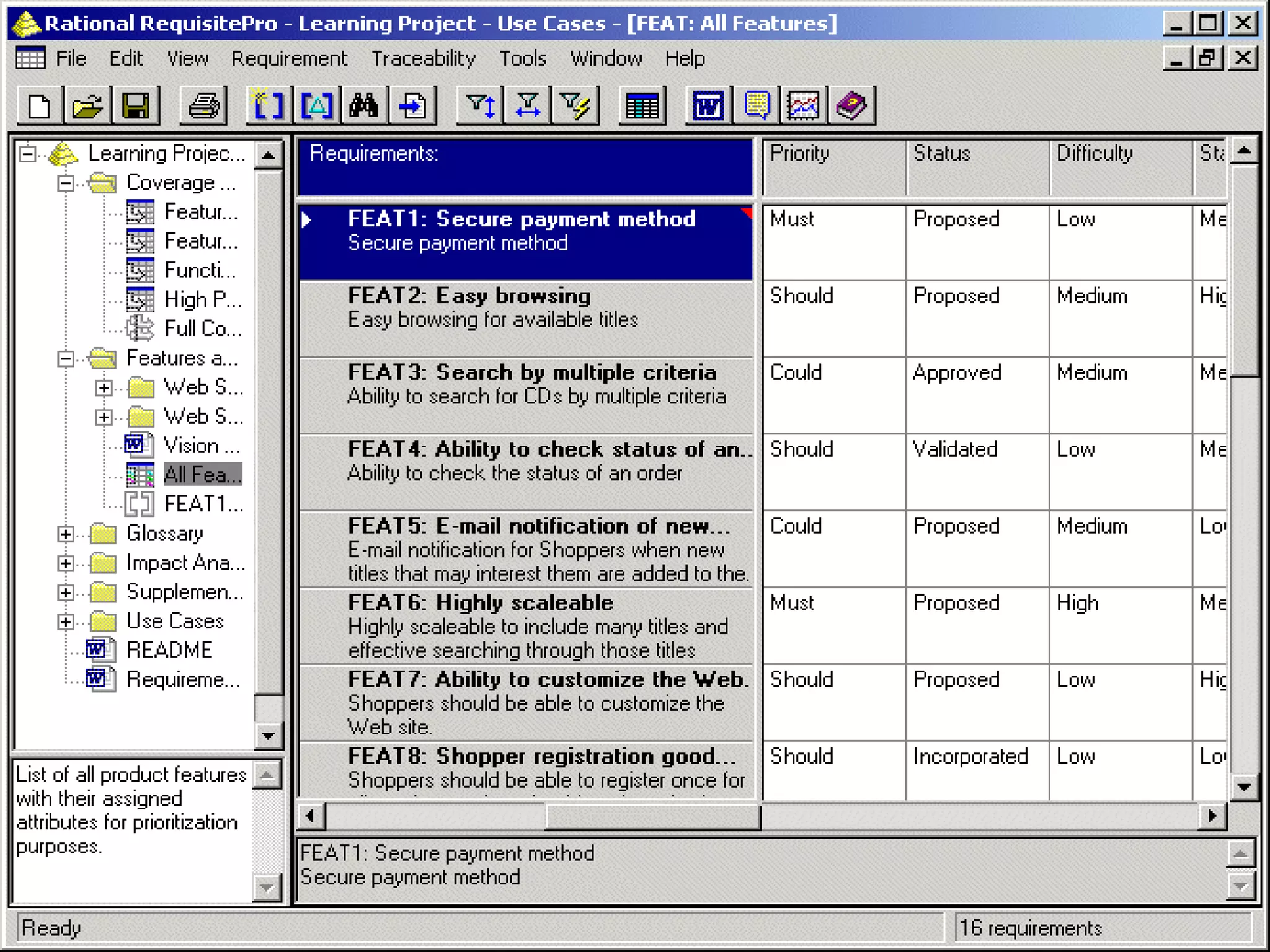
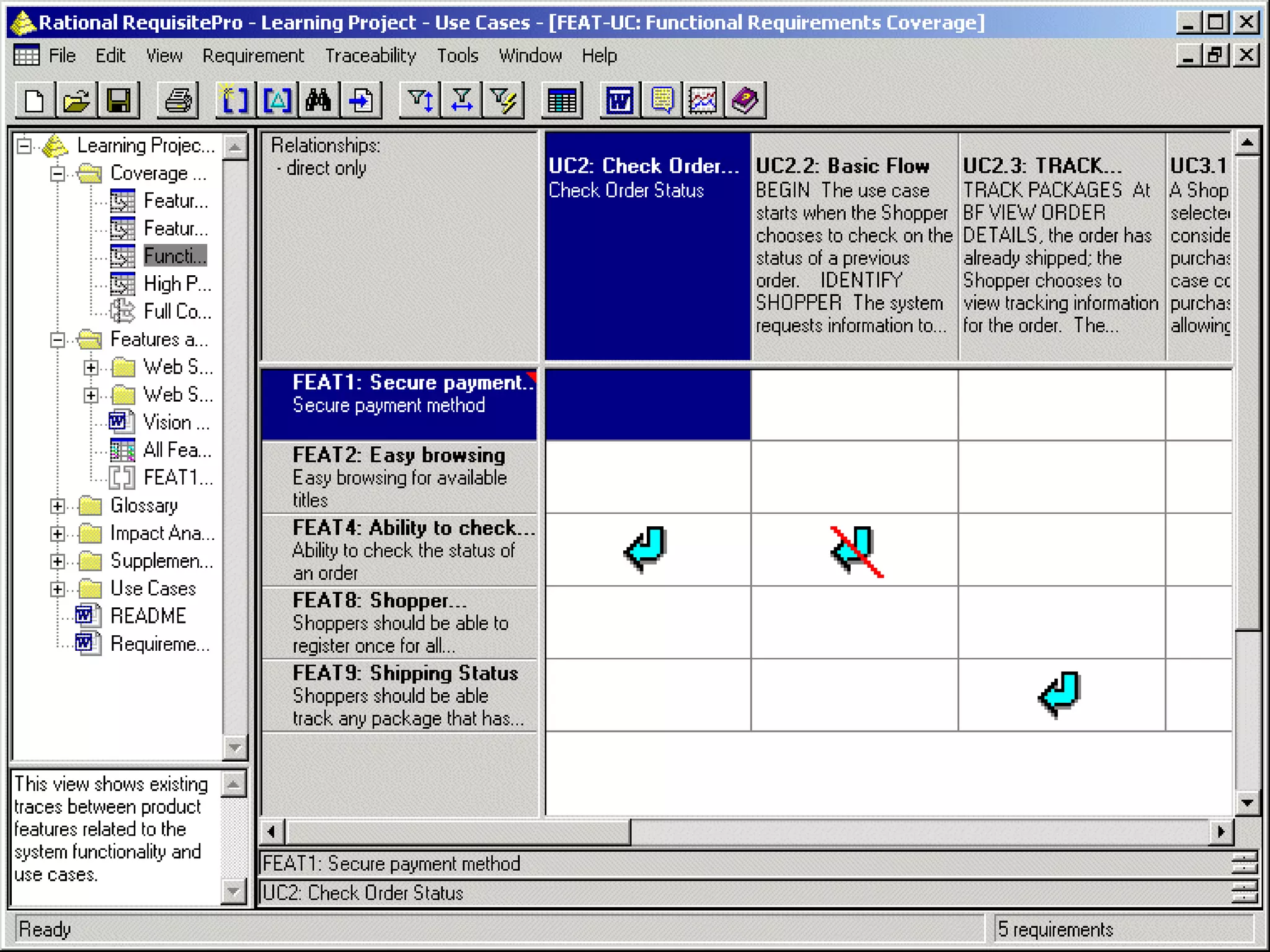
This document provides an overview of an IT business analyst career training module that covers topics such as: an introduction to business analysis and the IT business analyst role; the Rational Unified Process (RUP) methodology; requirements management; and the RequisitePro requirements management tool. The module includes sessions on requirements elicitation techniques like Joint Application Design (JAD) sessions. It also outlines an activity for a sample project to identify reporting requirements for an organization.