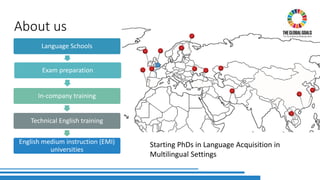
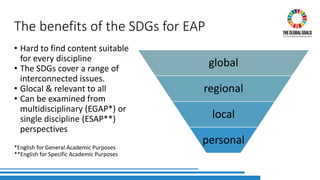
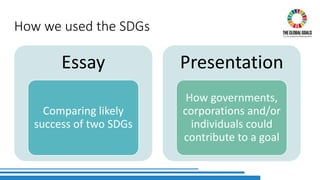
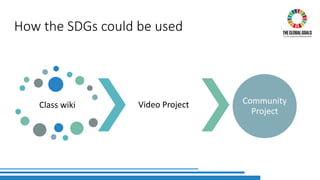
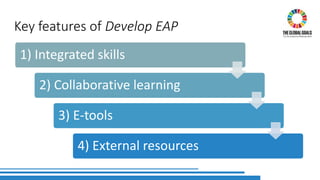
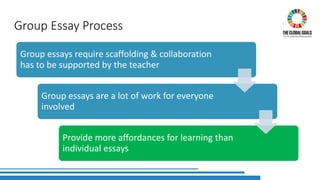
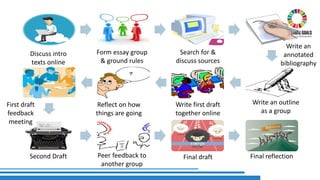
The document discusses the integration of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) into an English for Academic Purposes (EAP) course developed by Averil Bolster and Peter Levrai, with a focus on enhancing students' skills for success in English-medium higher education. It highlights key features of the course, such as integrated skills, collaborative learning, and the use of e-tools and external resources, as well as the adaptability and relevance of the SDGs to various academic disciplines. The authors emphasize the course's aim to prepare learners for addressing real-life problems and promoting sustainable educational practices.