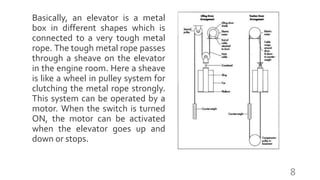
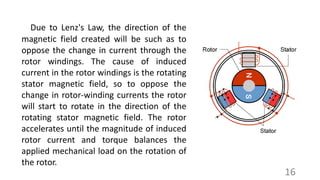
This document provides information about building elevators, including different types, working principles, and specifications. It discusses hydraulic elevators, geared and gearless traction elevators, and machine room-less elevators. The working principle is explained using an analogy to a pulley system. Key specifications covered include lift capacity, number of floors, travel height, speed, and controller type. Motor specifications like manufacturer, type, RPM, power, and gear ratio are also listed.