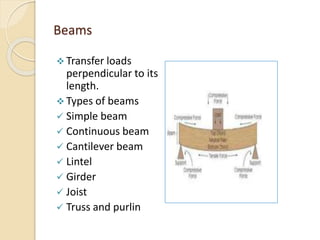
This document provides an overview of key aspects of building construction, including why buildings are needed, the construction process, design constraints, structural loads and elements. It discusses the main stages of construction including planning, design, tendering, and handover. It also identifies common construction materials like wood, steel, concrete, masonry and cement, outlining their structural properties and how they are impacted by factors like fire.