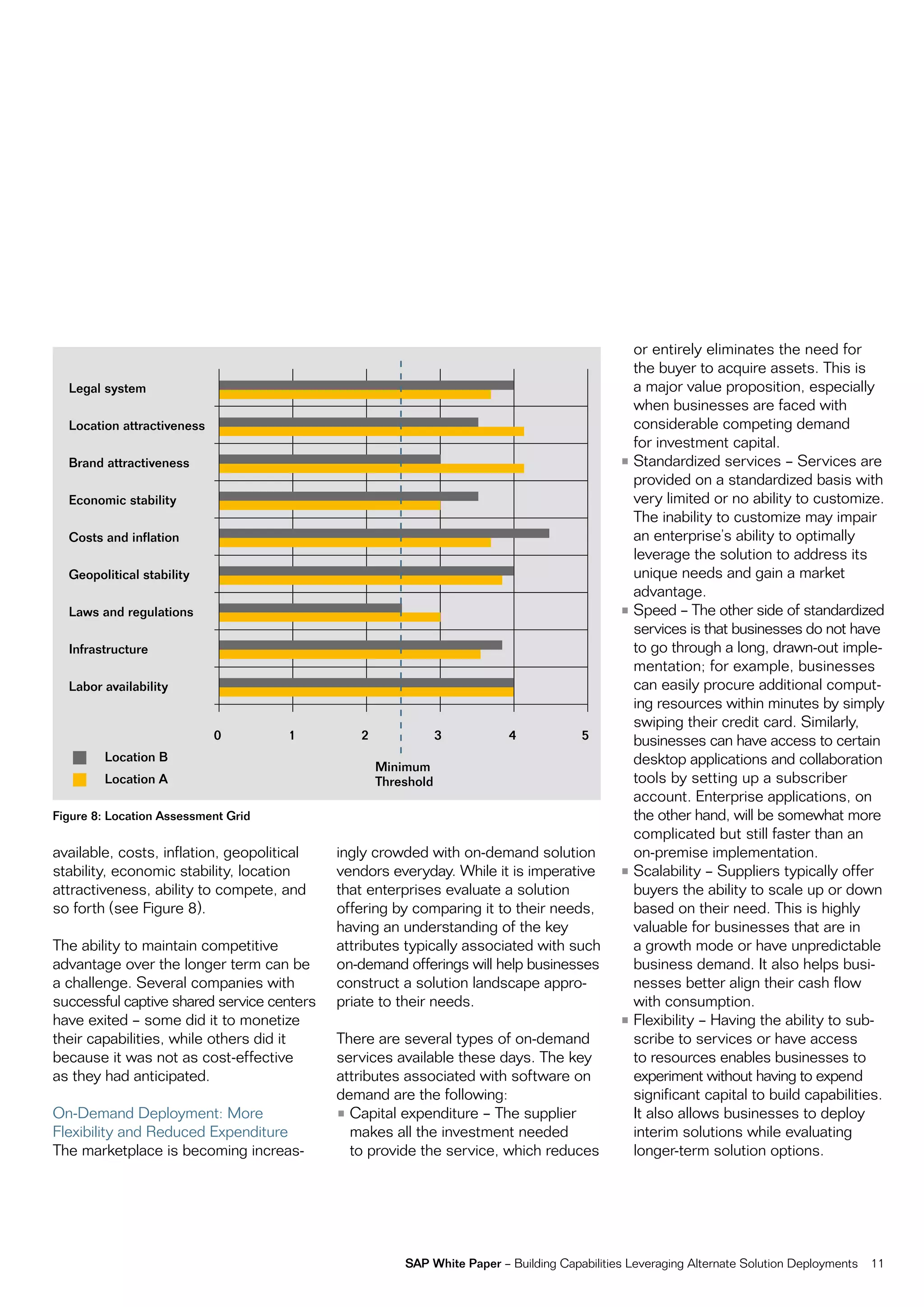
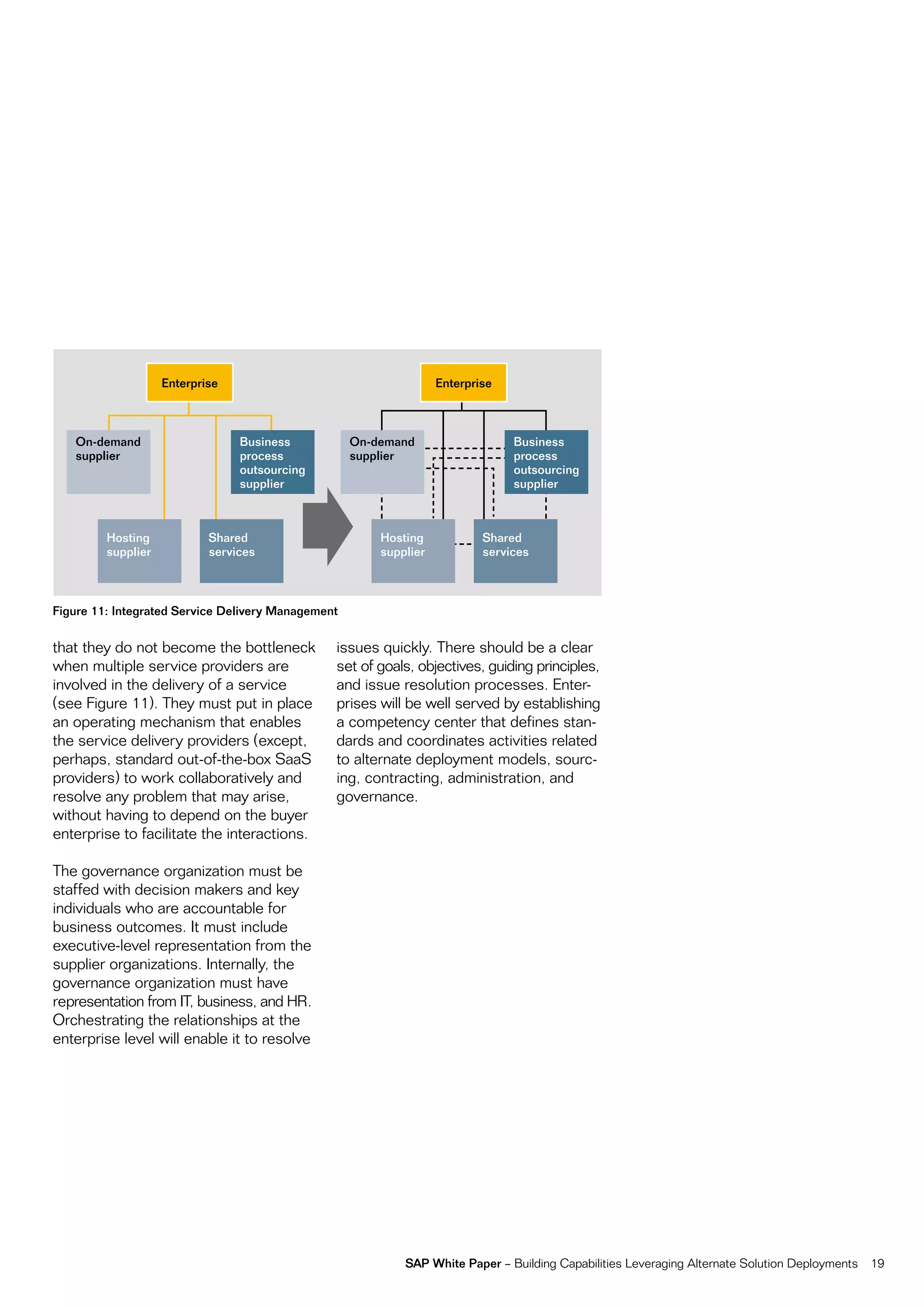
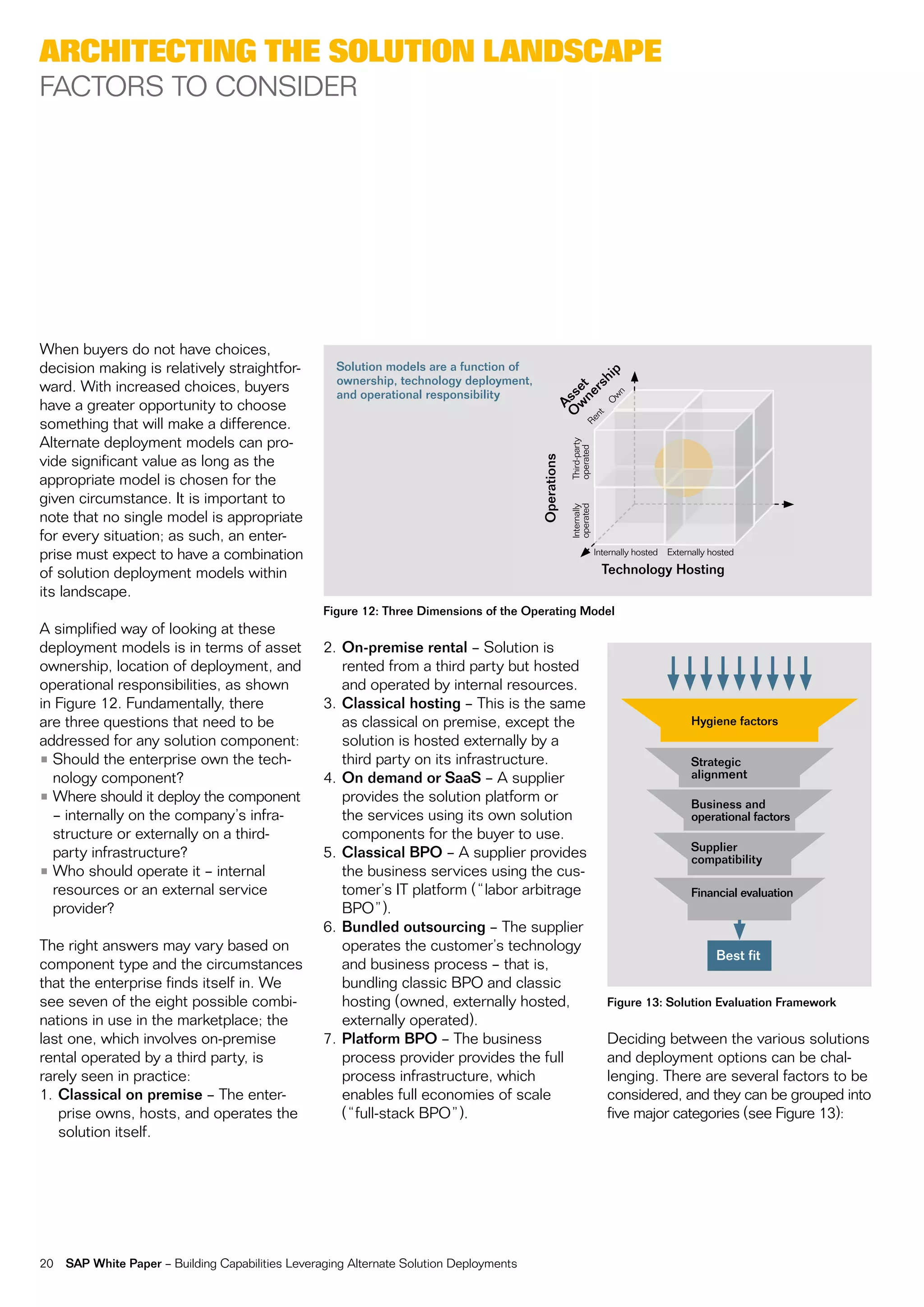
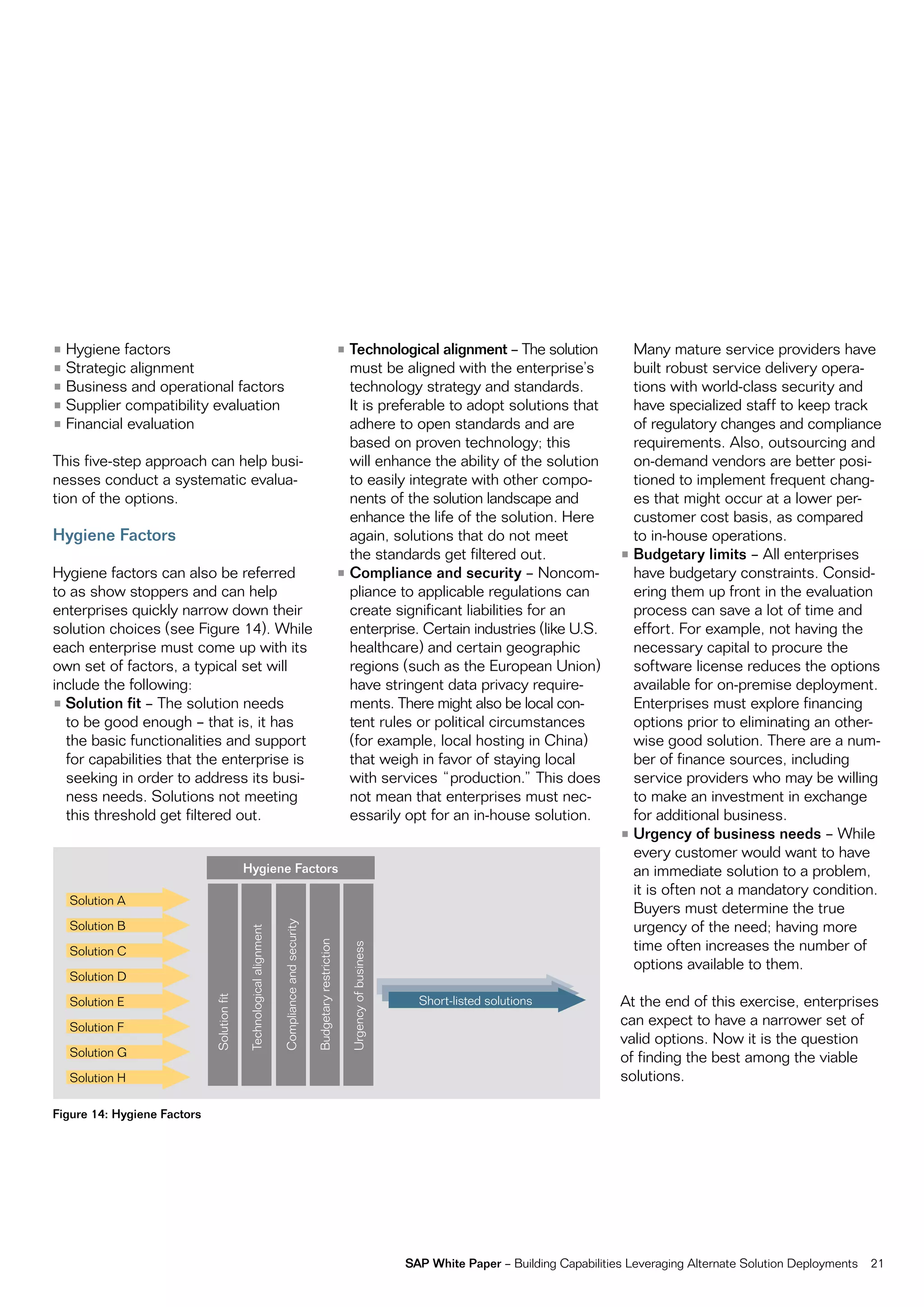
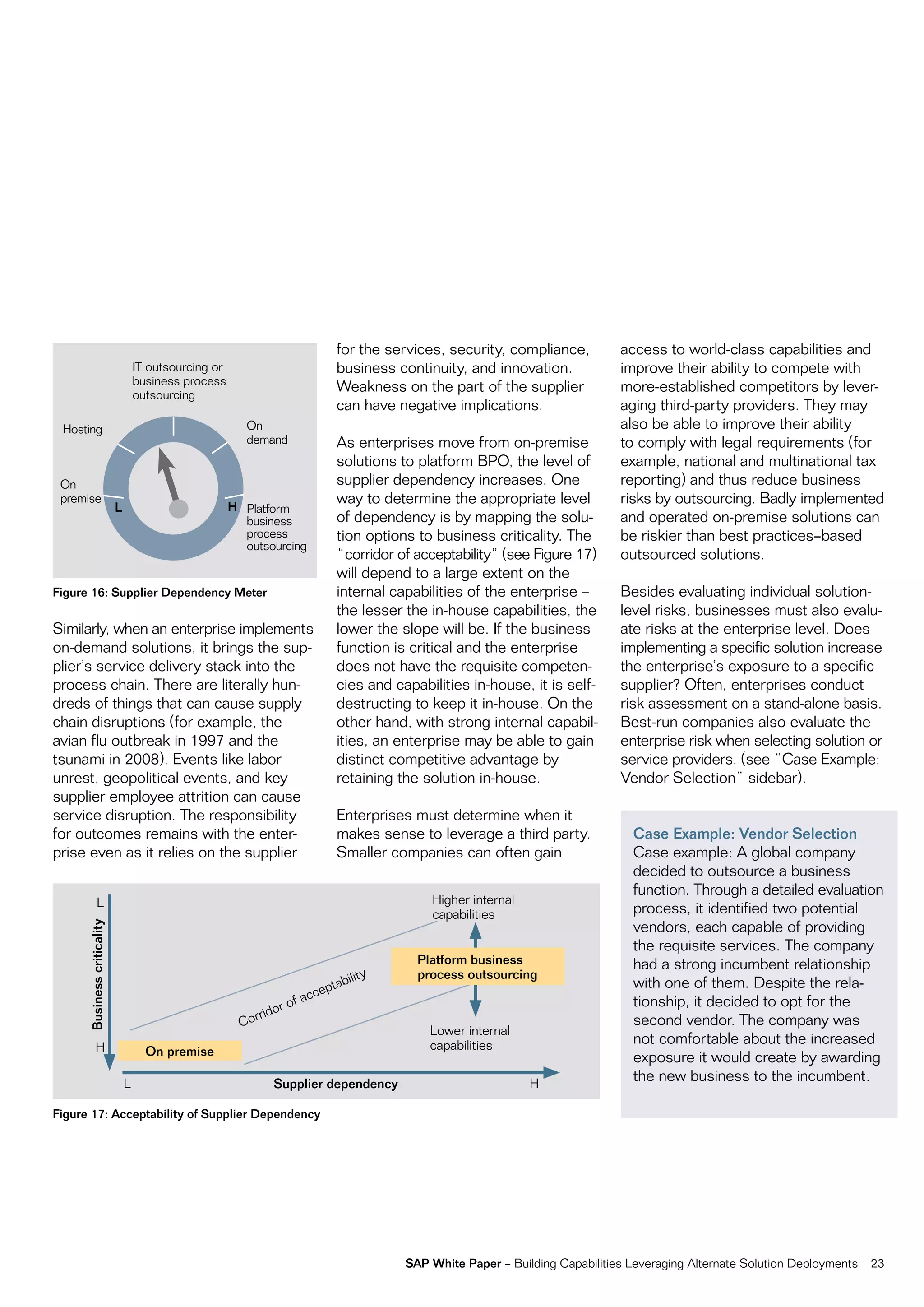
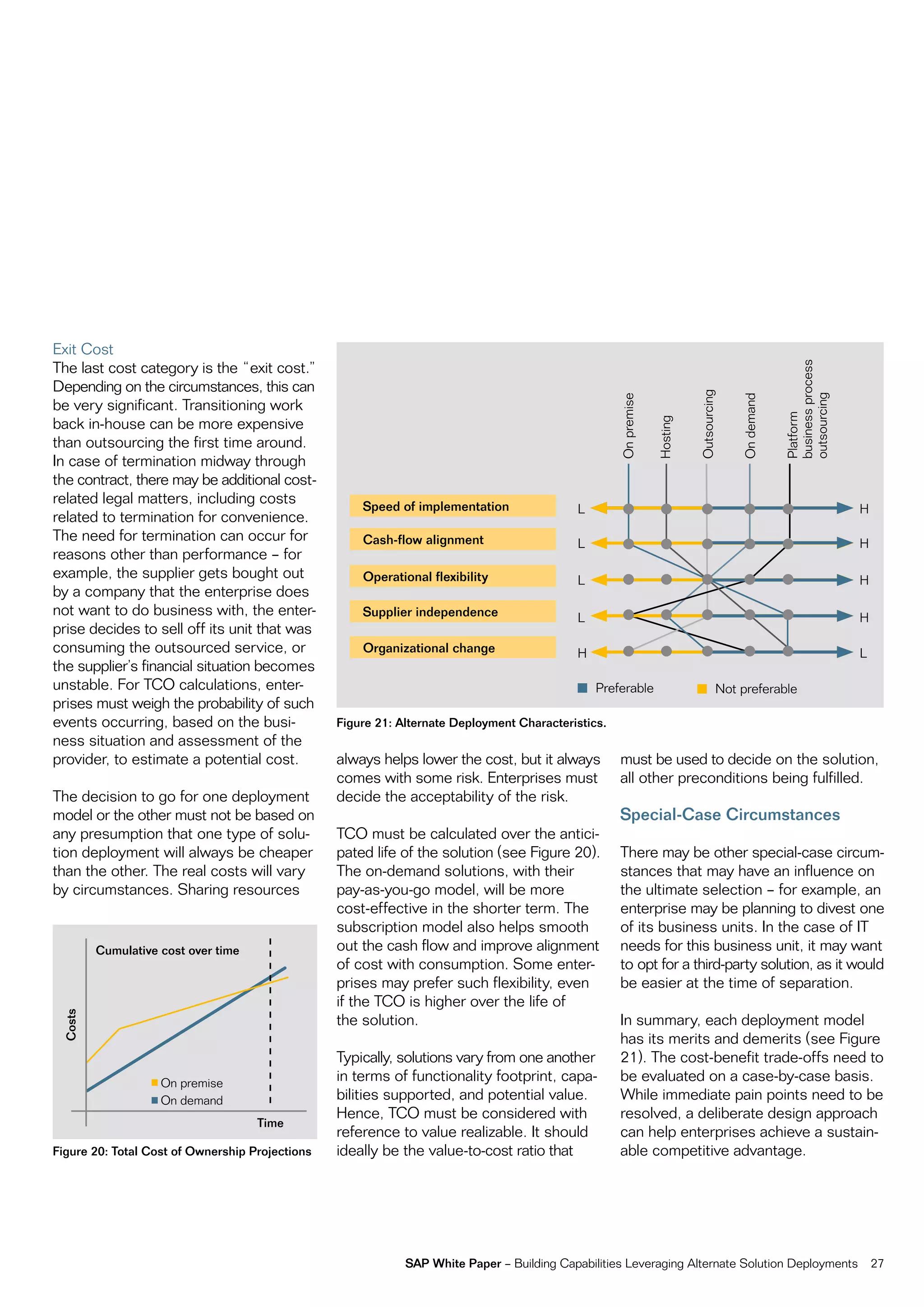
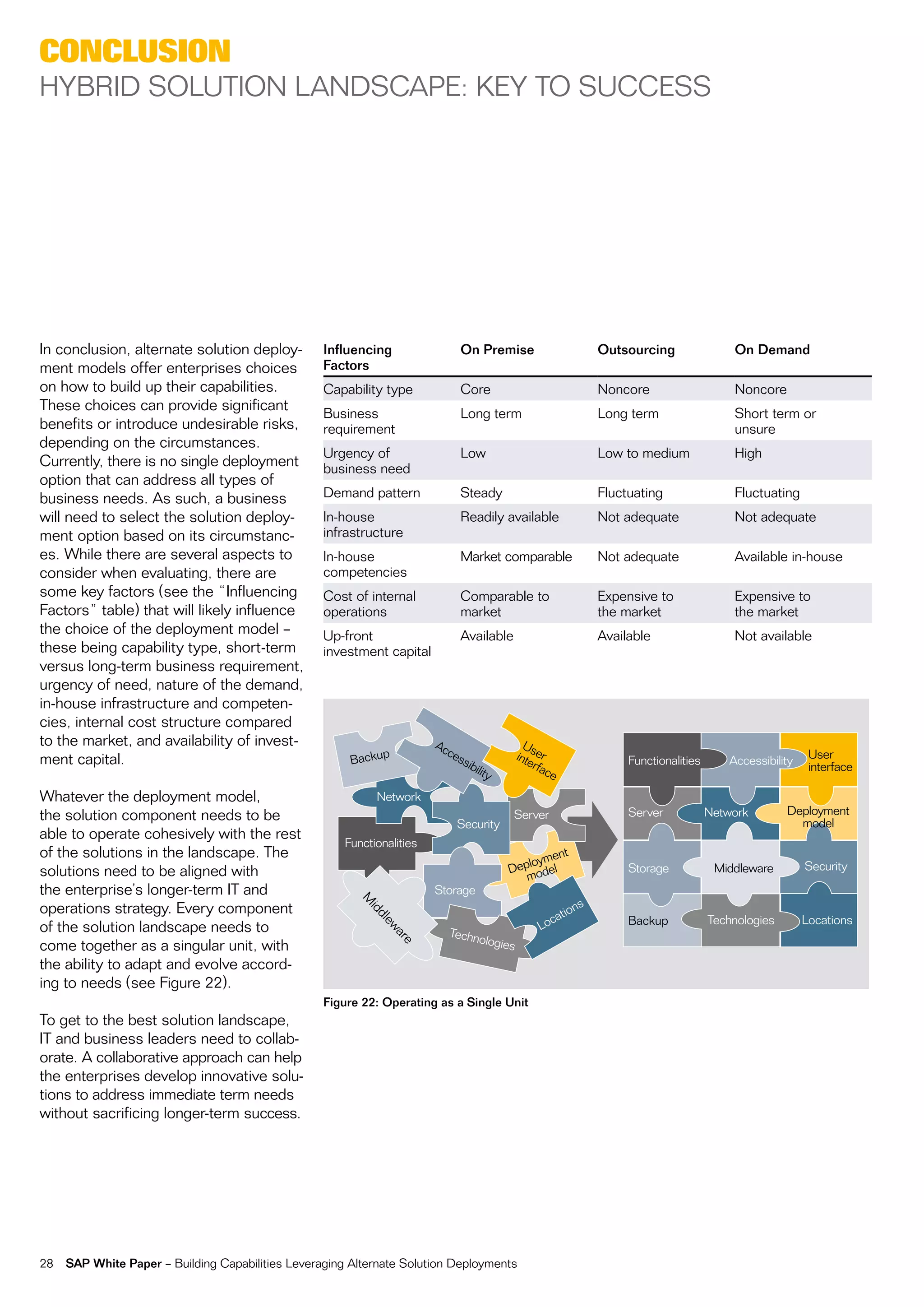
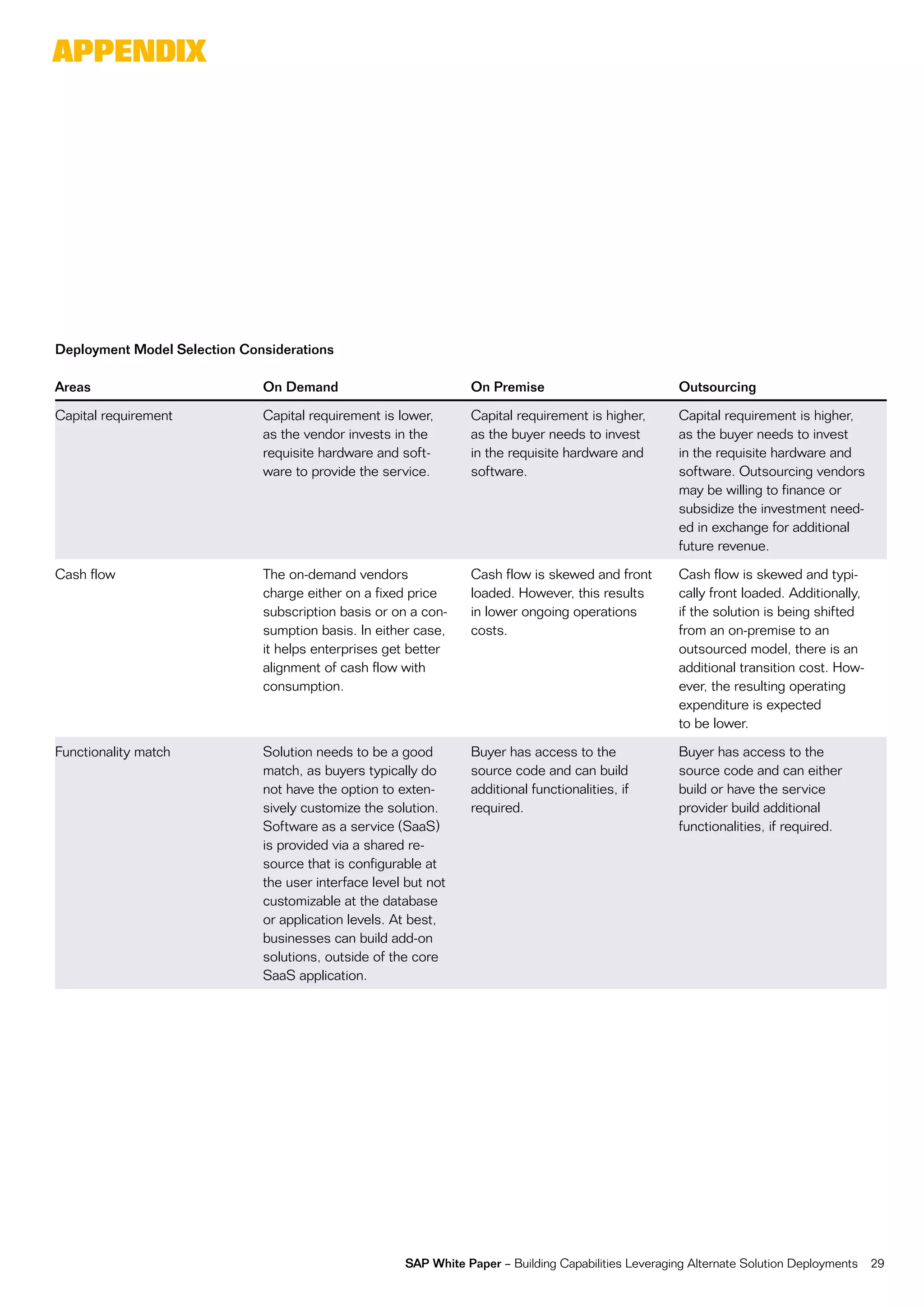
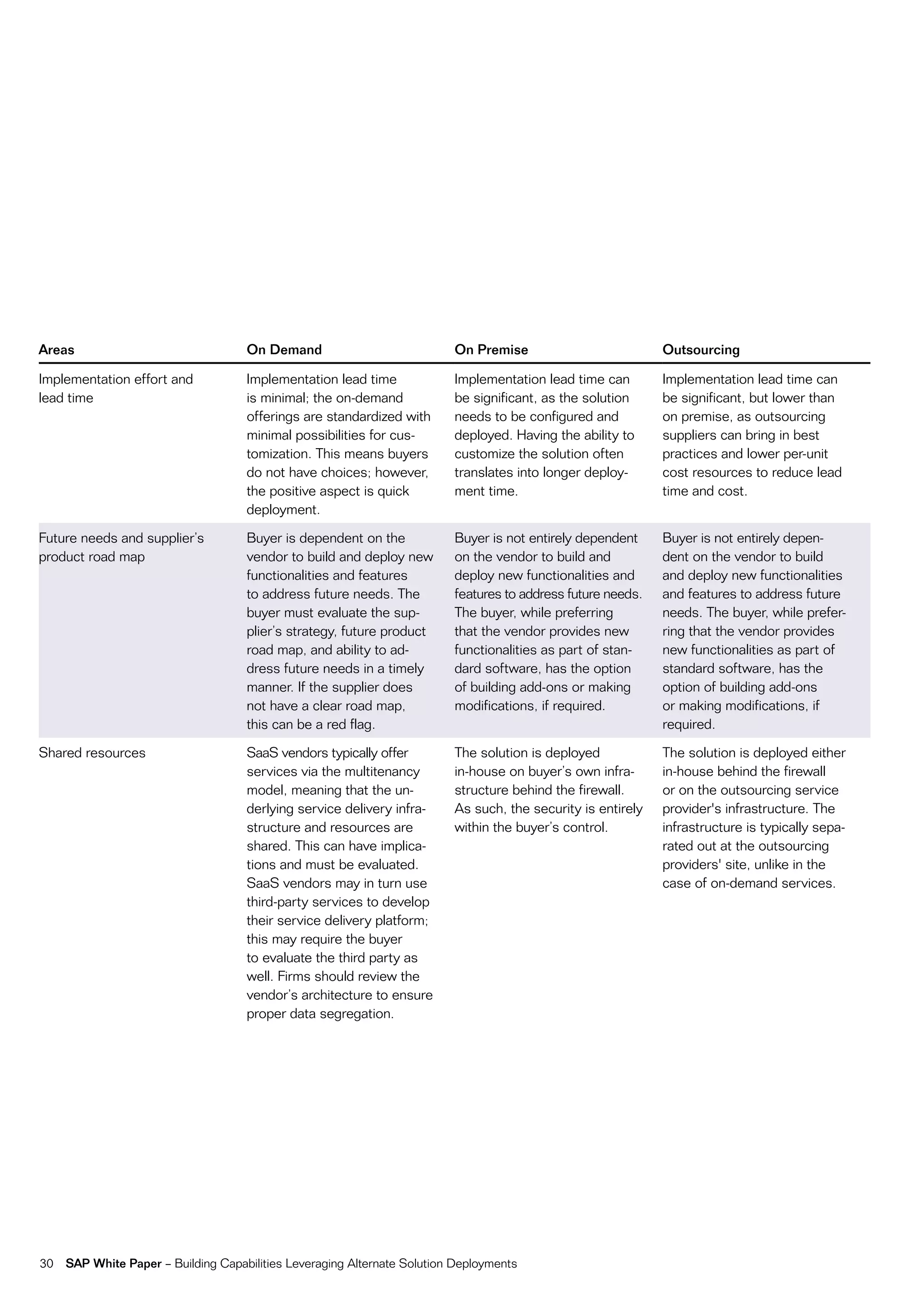
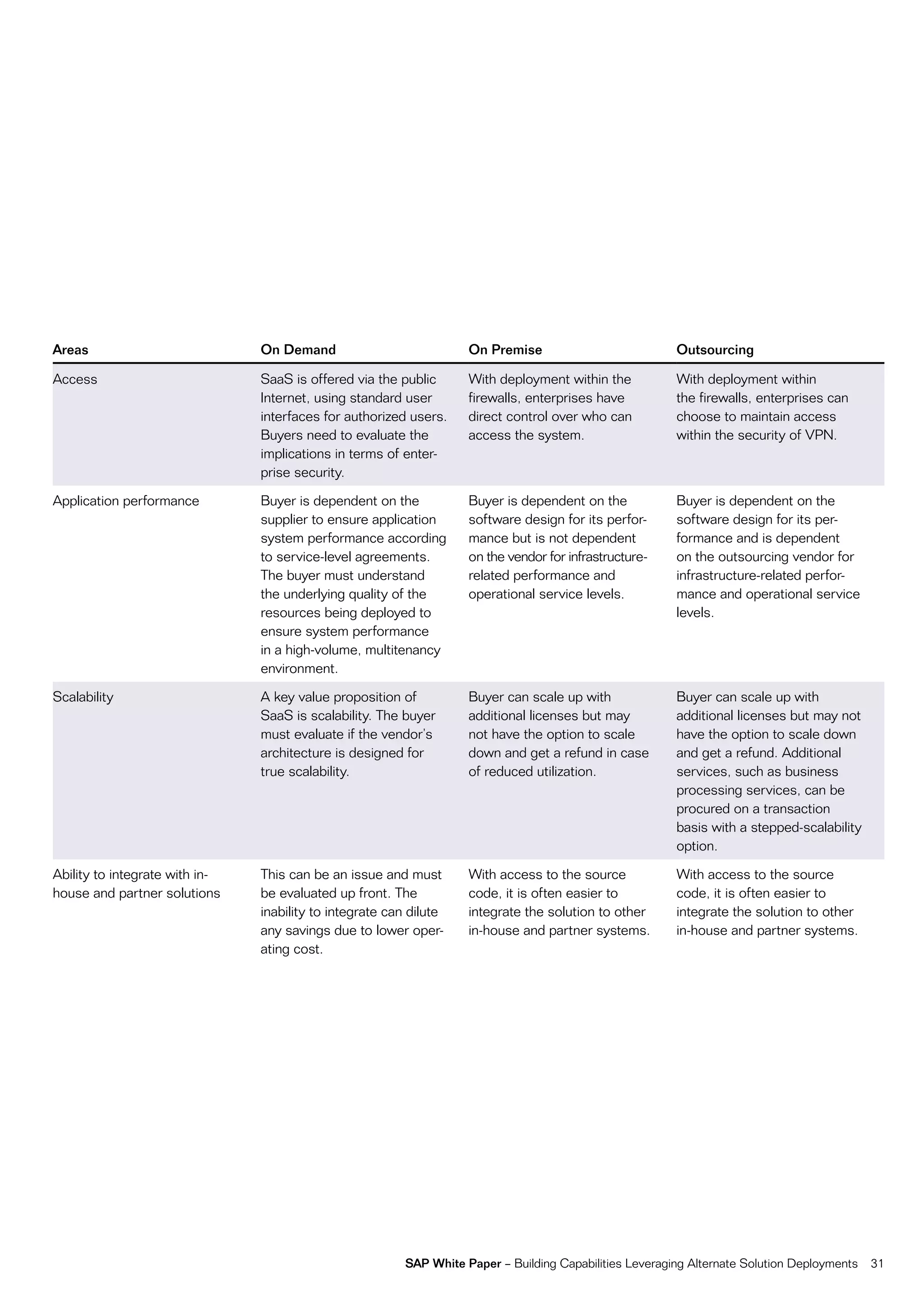
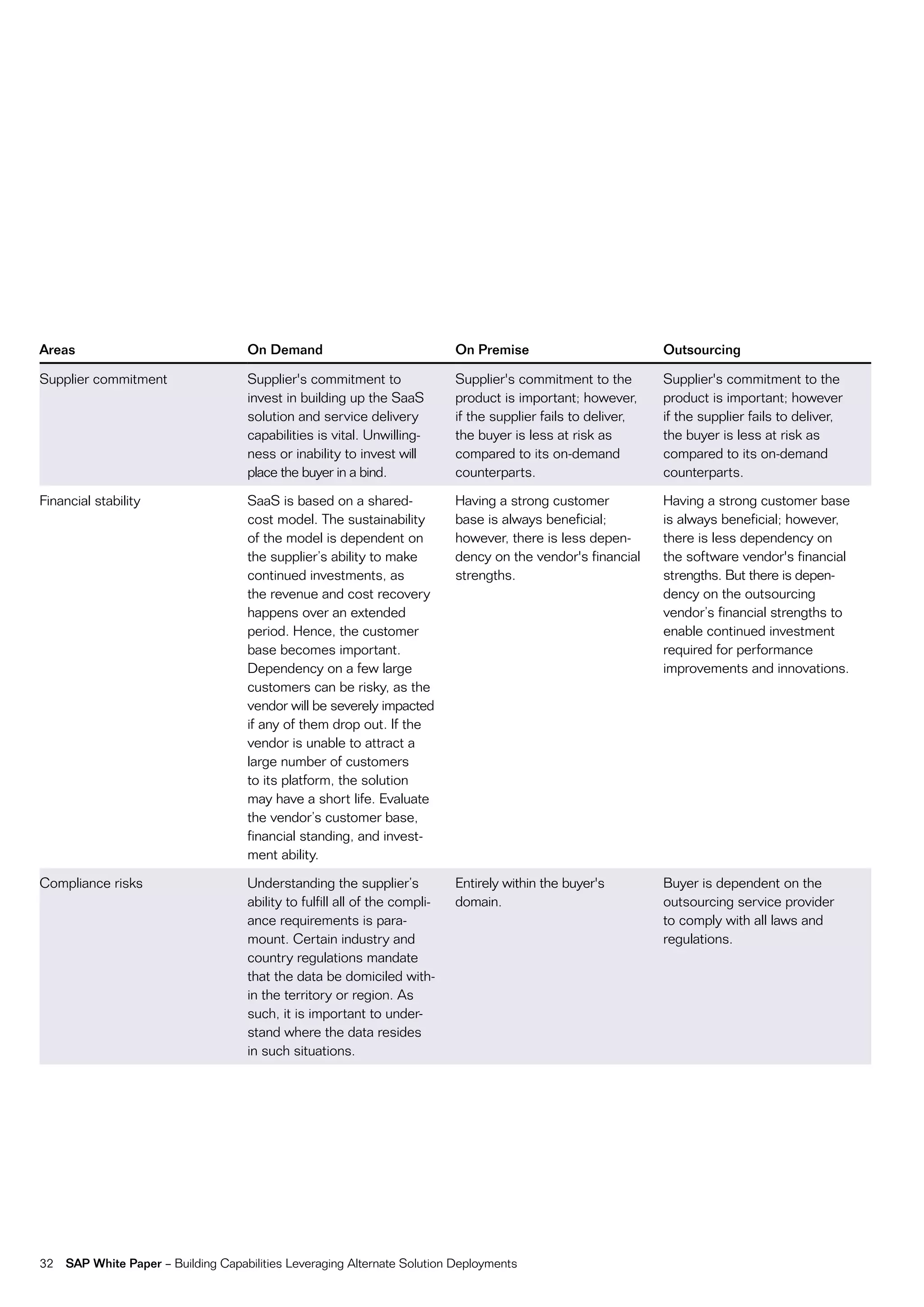
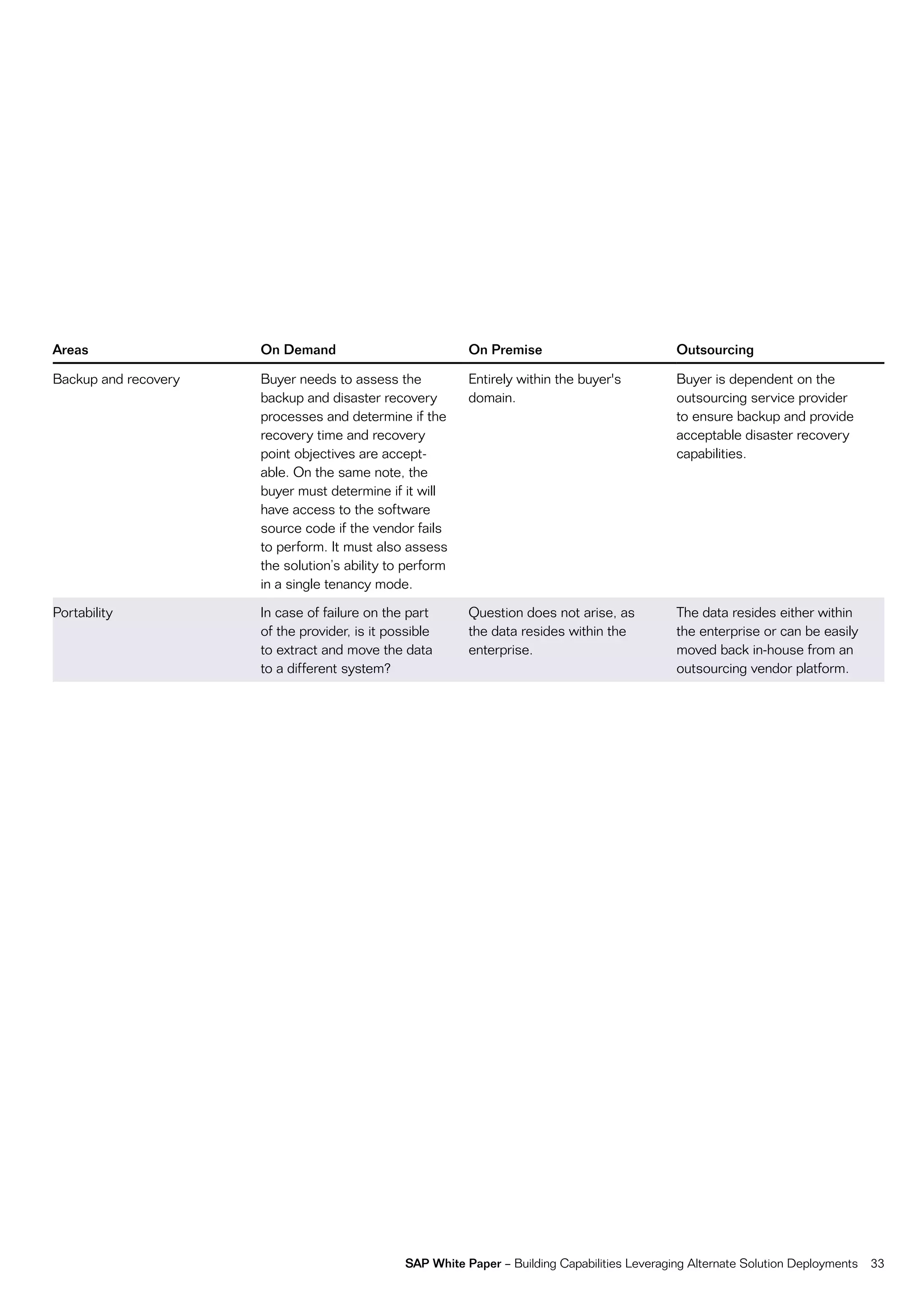
This document discusses strategies for building business capabilities using alternative solution deployment models beyond the traditional in-house approach. It recommends a deliberate design process to architect a best-in-class hybrid solution landscape and operating model. This involves clarity of vision, understanding existing capabilities and options, value-based decision making, and managing the transformation process through collaboration to drive efficiency and achieve strategic goals. Choosing the right combination of on-premise, outsourced, shared services, and on-demand deployment models is key to success.