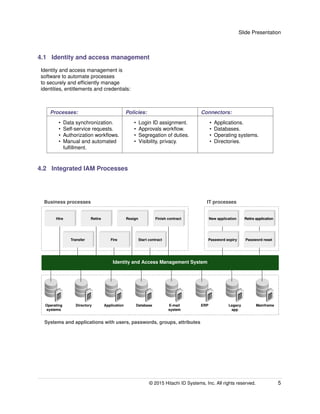
This slide presentation document discusses building a business case for identity and access management (IAM) automation. It outlines the business challenges of managing user identities, entitlements, and authentication across on-premises and cloud applications. The document discusses the IAM lifecycle and value proposition, providing metrics to measure cost savings, productivity improvements, and security enhancements. It emphasizes effective IAM project implementation by minimizing costs and addressing change management challenges.