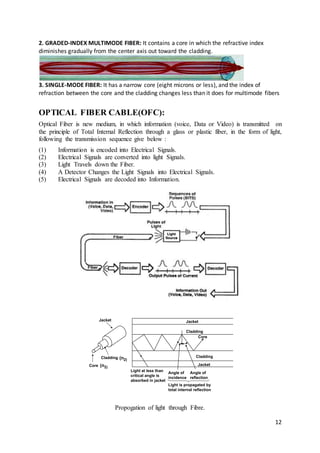
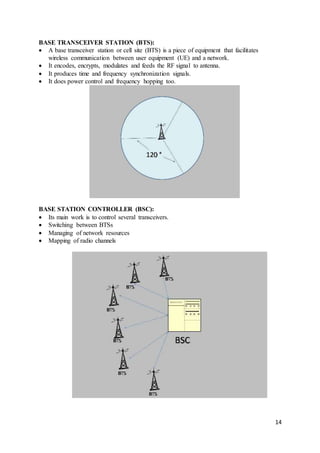
This 3 sentence summary provides the high level information about the document:
The document discusses Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL), India's state-owned telecommunications company. It covers the basic workings of a telecommunications network, components of BSNL exchanges like the main distribution frame, and mobile communication technologies used by BSNL like GSM, GPRS, CDMA. The document also discusses internet services provided by BSNL including broadband, WiMAX, FTTH and provides an overview of optical fiber transmission systems.