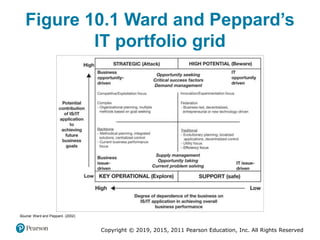
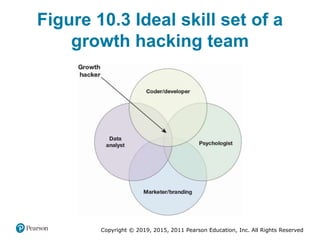
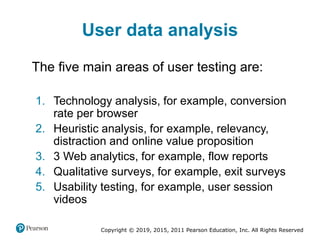
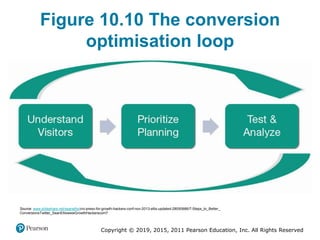
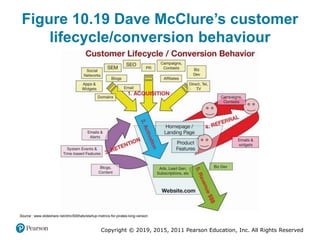
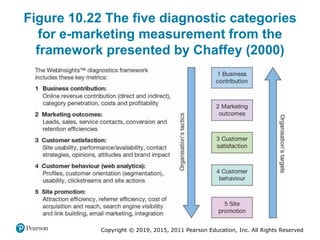
This document discusses managing digital business transformation and growth hacking. It provides learning outcomes on critically analyzing an organization's transformation journey, reviewing approaches for digital transformation, and producing growth hacking and analytics plans. The document also defines key terms, presents frameworks for digital transformation and growth hacking, and discusses measuring the effectiveness of digital businesses.