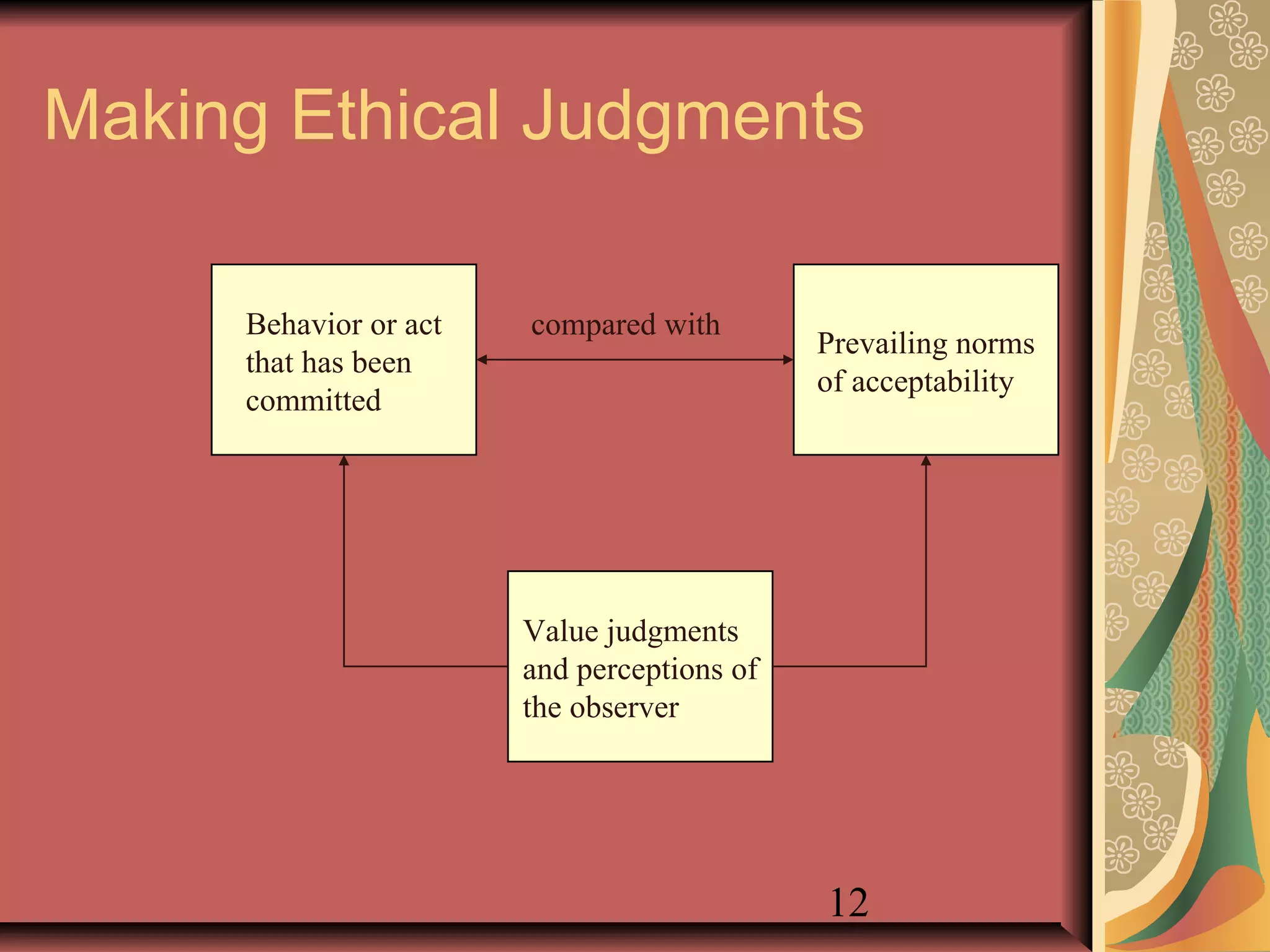
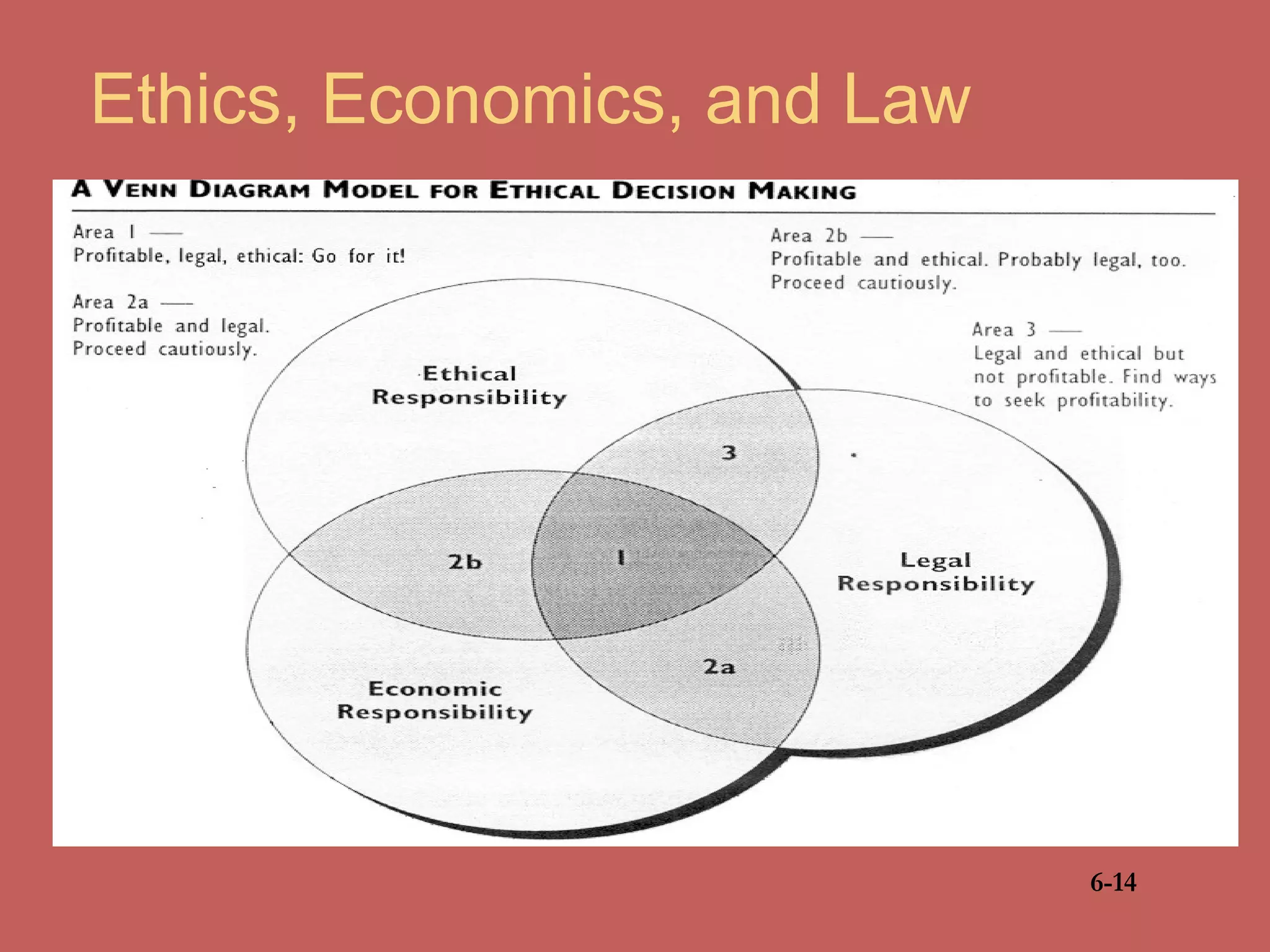
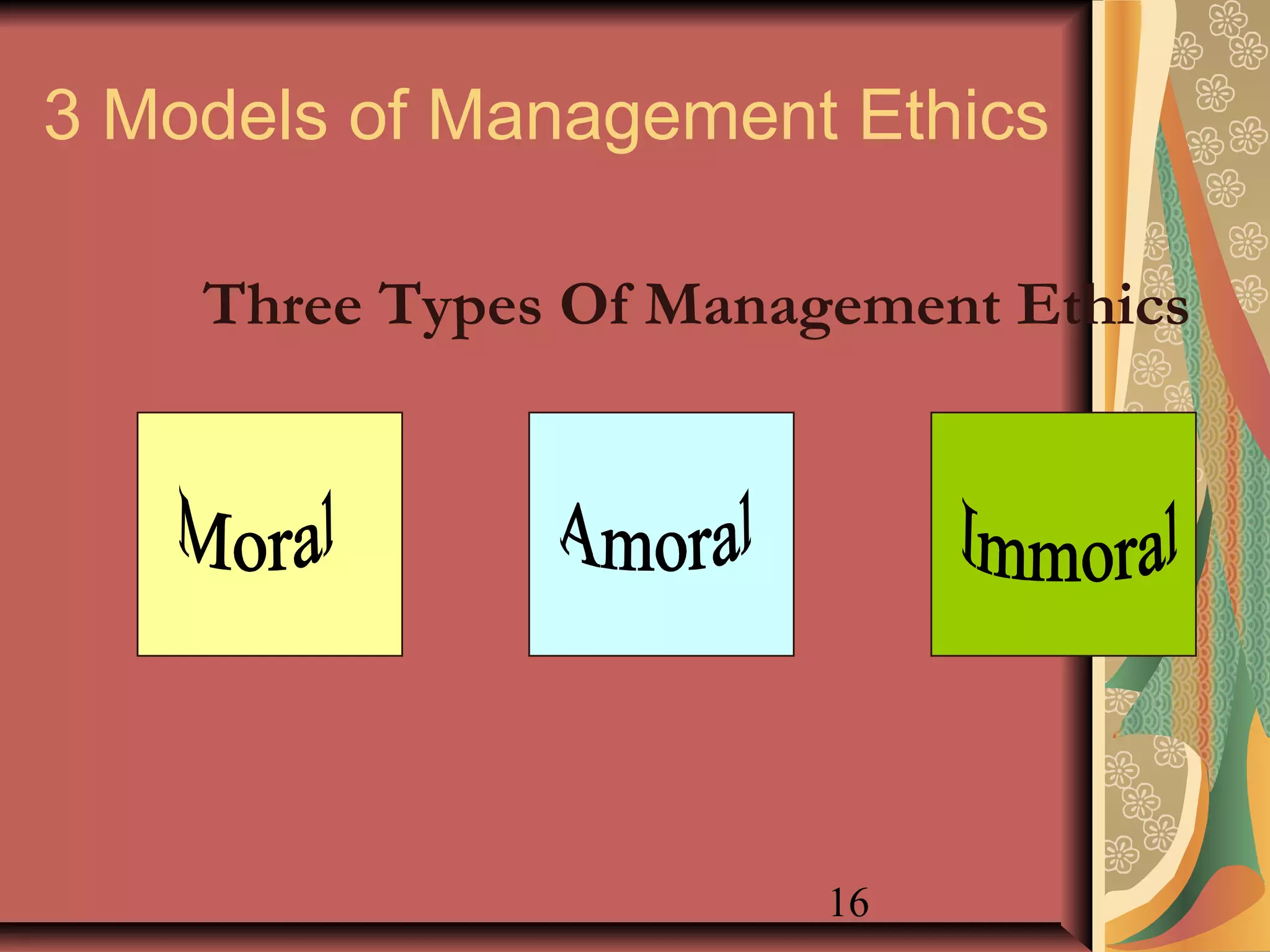
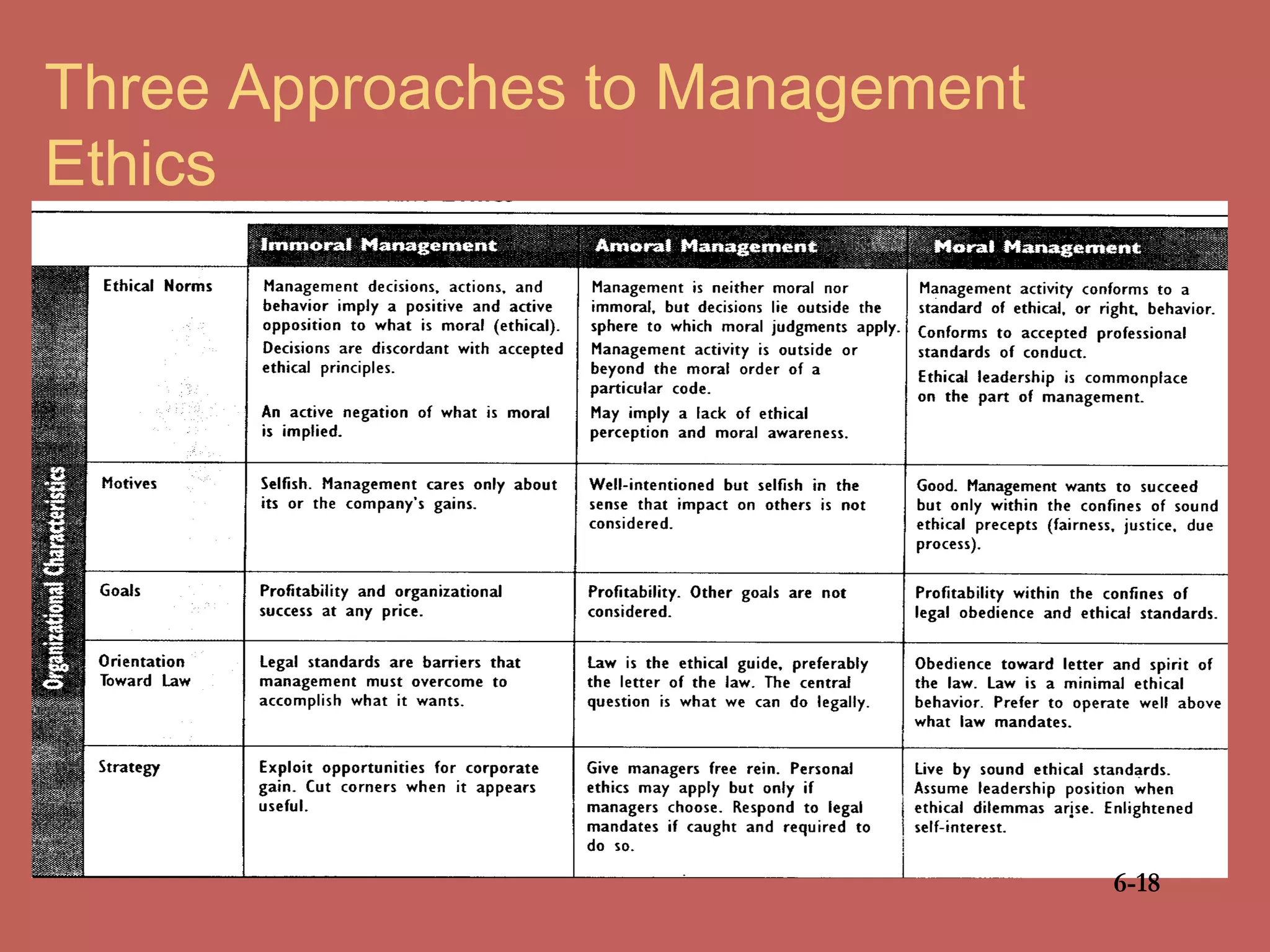
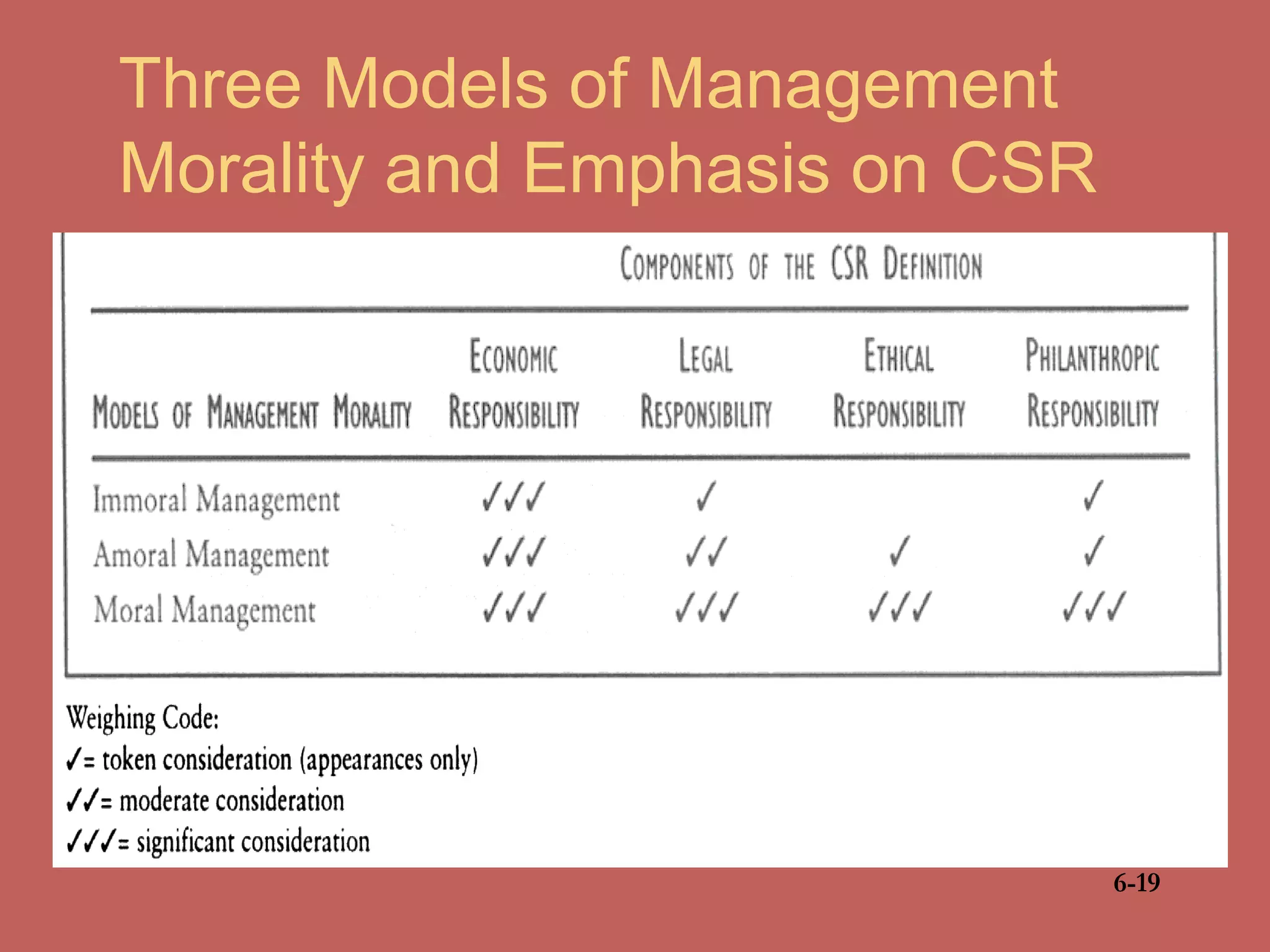
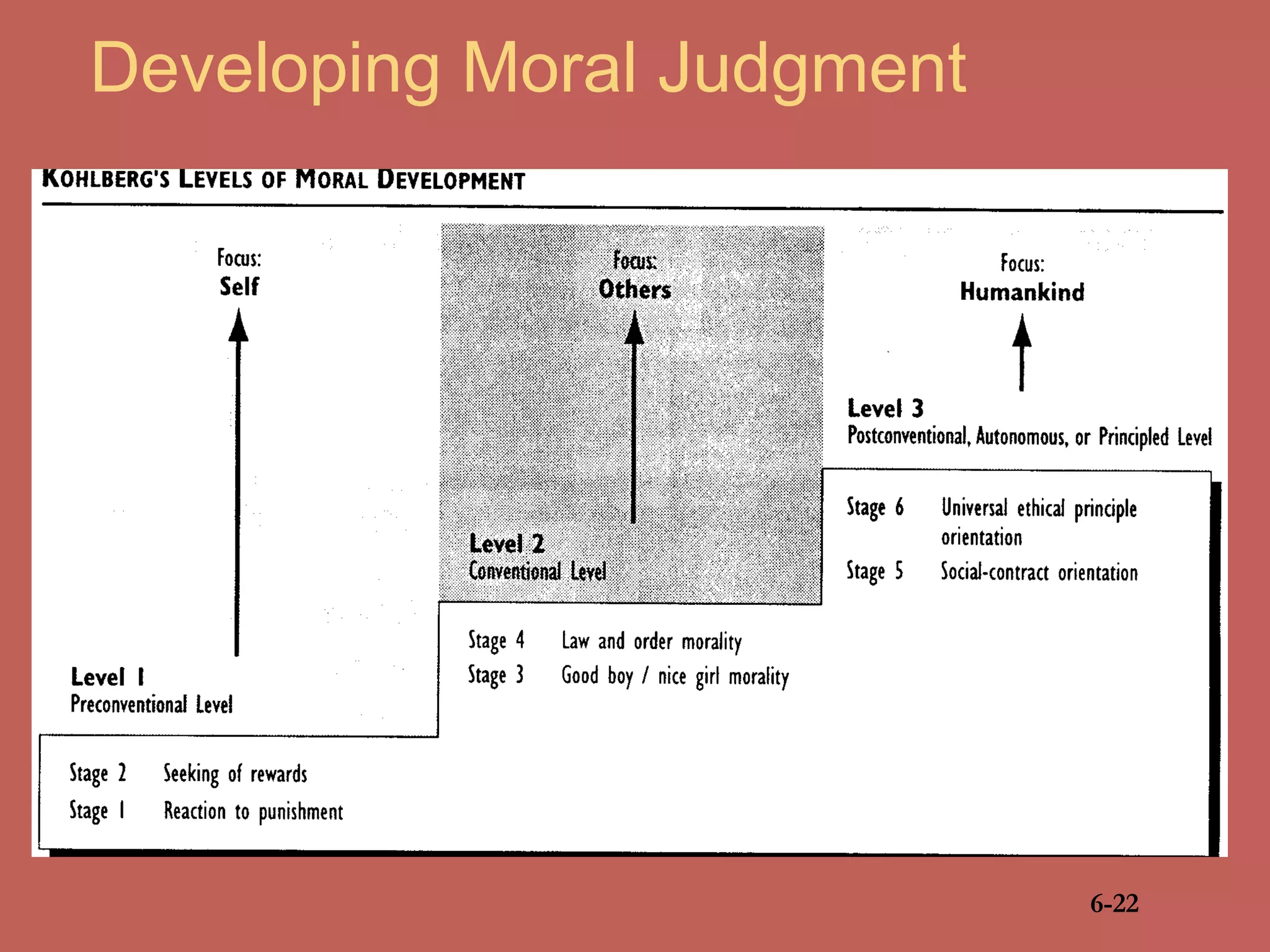
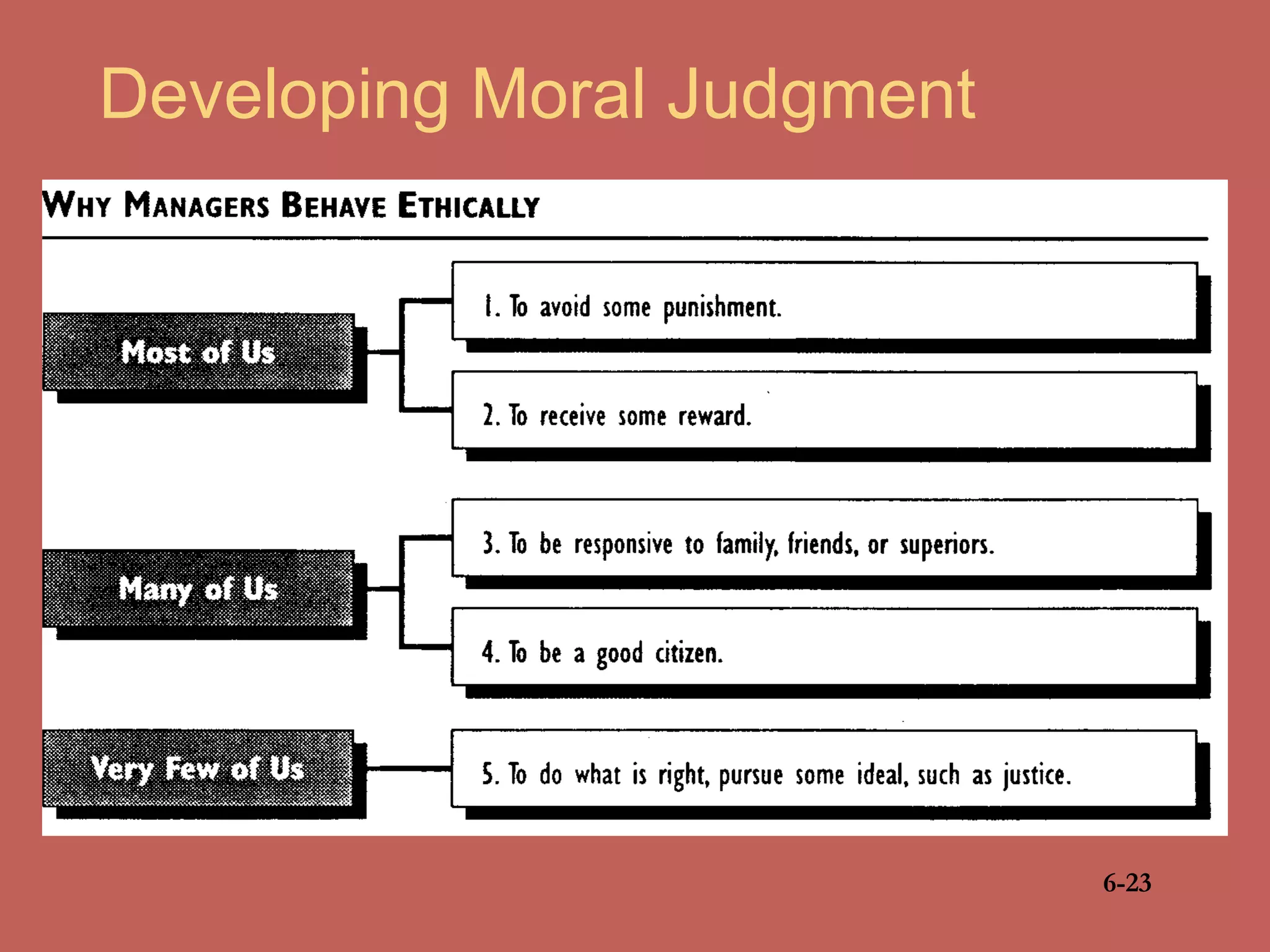
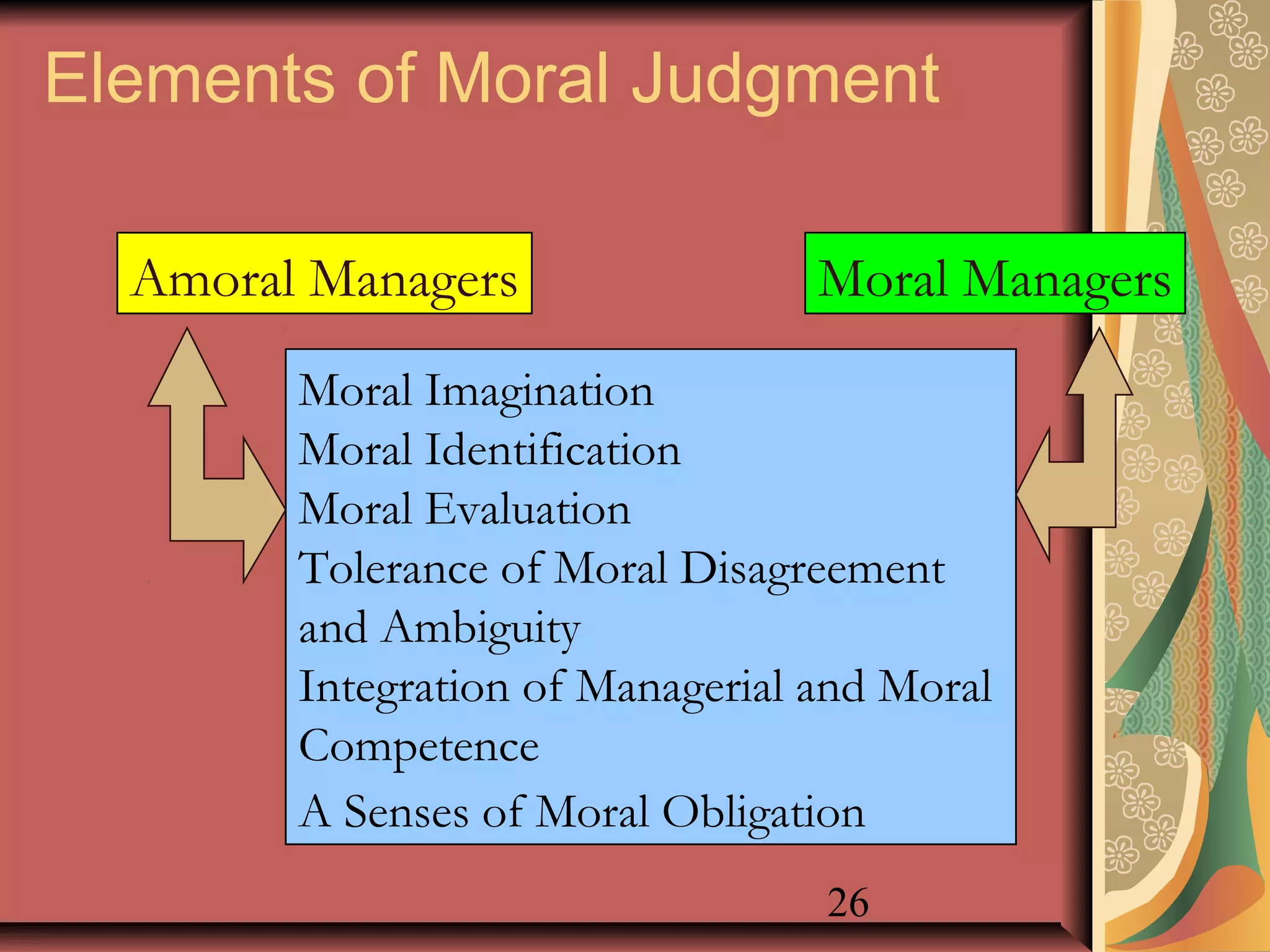
This document discusses business ethics fundamentals and models of management ethics. It begins by noting the increased public interest in business ethics over the last few decades. It then examines definitions of ethics, morality, and business ethics. It presents three models of management ethics: immoral management, moral management, and amoral management. It concludes by discussing elements of moral judgment and developing moral judgment in managers.