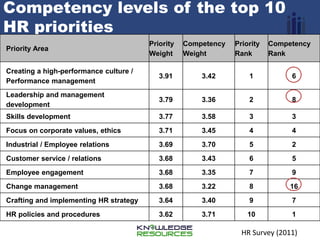
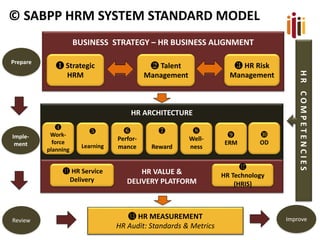
The document discusses the role of HR practitioners as change agents to improve HR practices and service delivery in local governments. It emphasizes that HR practitioners should drive the implementation of HR standards and audits to bring consistency and continuous improvement. The standards can act as a catalyst for change by providing a framework to assess current practices, identify gaps, and guide practitioners on strengthening areas like skills development, performance management, and employee relations. Regular audits against the standards will allow benchmarking progress and verifying the quality of HR practices. The document calls on HR practitioners to internalize the standards, educate others, conduct self-assessments, and work towards external audits to ultimately raise the bar on HR practices.