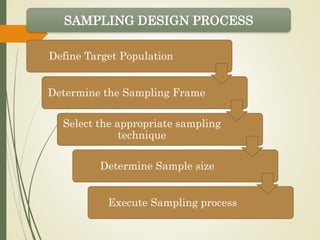
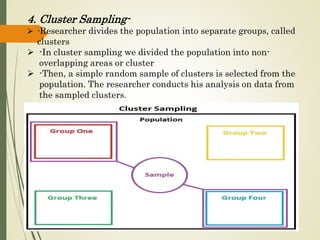
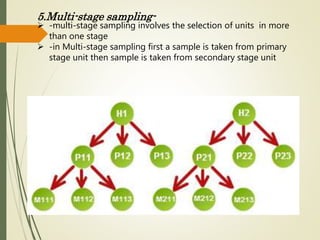
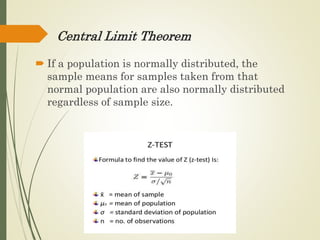
This document outlines the steps in the sampling design process:
1. Define the target population, which is the group to which conclusions will be generalized.
2. Determine the sampling frame, which is the list of all elements that can be sampled.
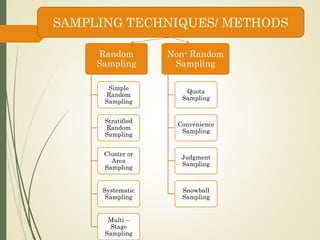
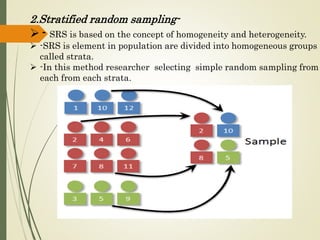
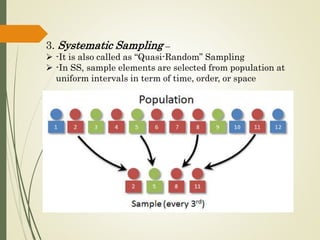
3. Select the appropriate sampling technique, either random or non-random, depending on the research needs.
4. Determine the sample size based on the nature of research and desired analysis.
5. Execute the sampling process by following the defined target population, sampling frame, technique, and size.