The BRIS Report provides statistics and analysis on child contacts received by BRIS in 2005. Key findings include:
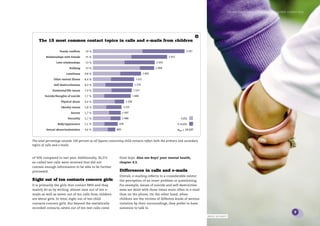
1) BRIS received a total of 19,237 calls and emails from children in 2005, with emails increasing and now comprising almost half of all contacts.
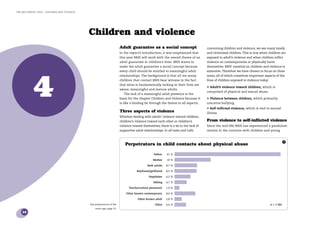
2) The most common topics in contacts were family conflicts, mental illness such as depression, bullying, violence and self-harm.
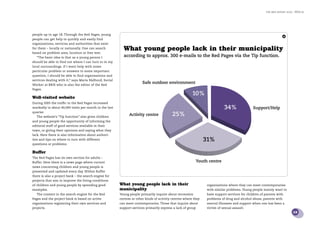
3) BRIS.se, the organization's website, saw 428,000 visits in 2005, a 24% increase over 2004. The site provides discussion forums, advice columns, and the ability for children to email BRIS for support.