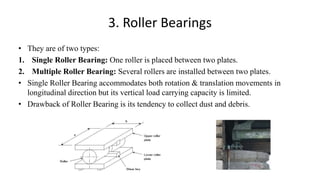
The document discusses bridge bearings, which are crucial for transferring forces from the superstructure to the substructure while managing movements due to temperature variations, deflection, and support sinking. It categorizes bearings into fixed and expansion types, detailing specific designs such as pin bearings, pot bearings, sliding plate bearings, and elastomeric bearings with their functionalities. A case study of the Audrain County steel bridge highlights the benefits of using elastomeric bearings for cost efficiency and ease of installation.