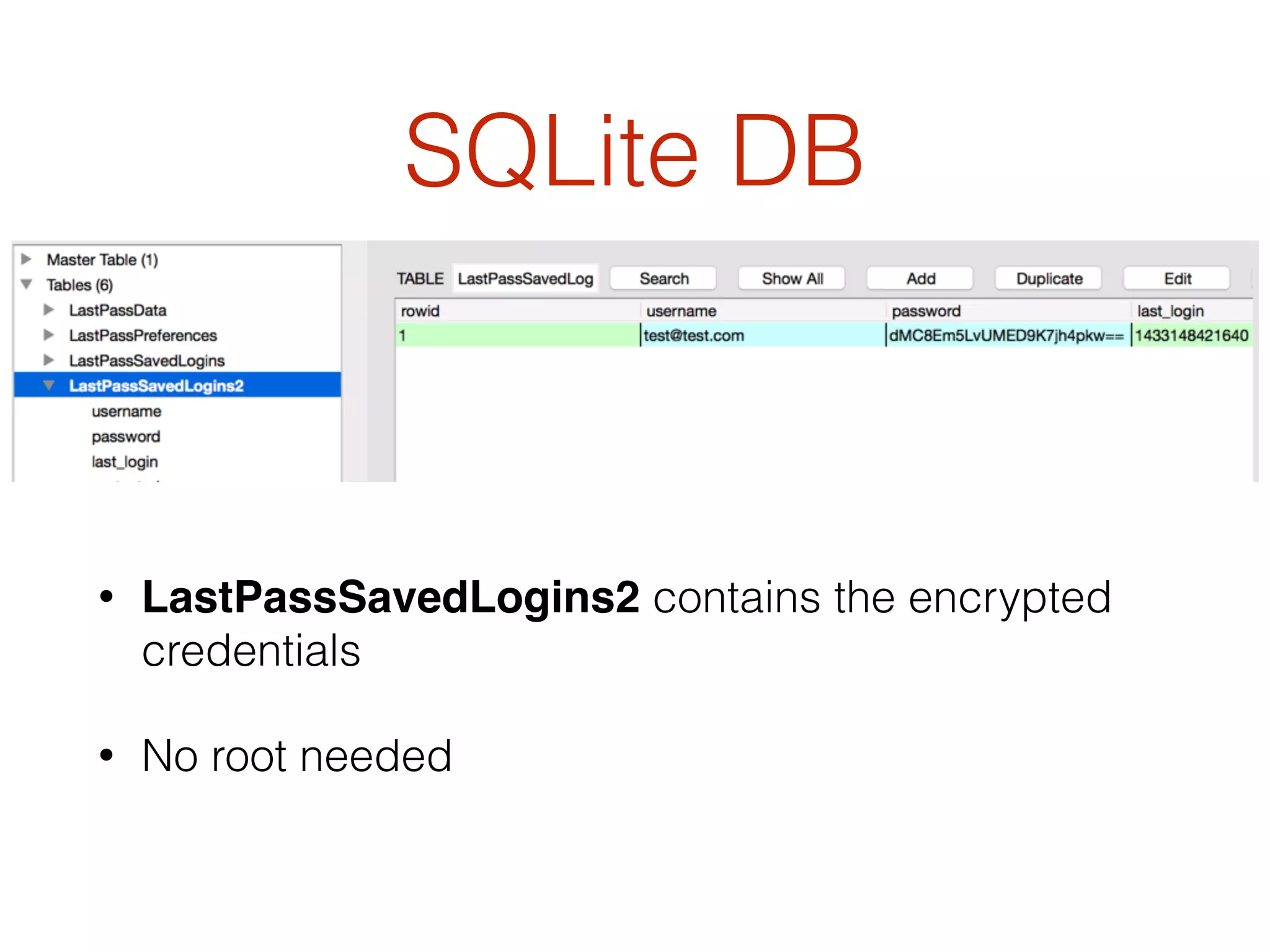
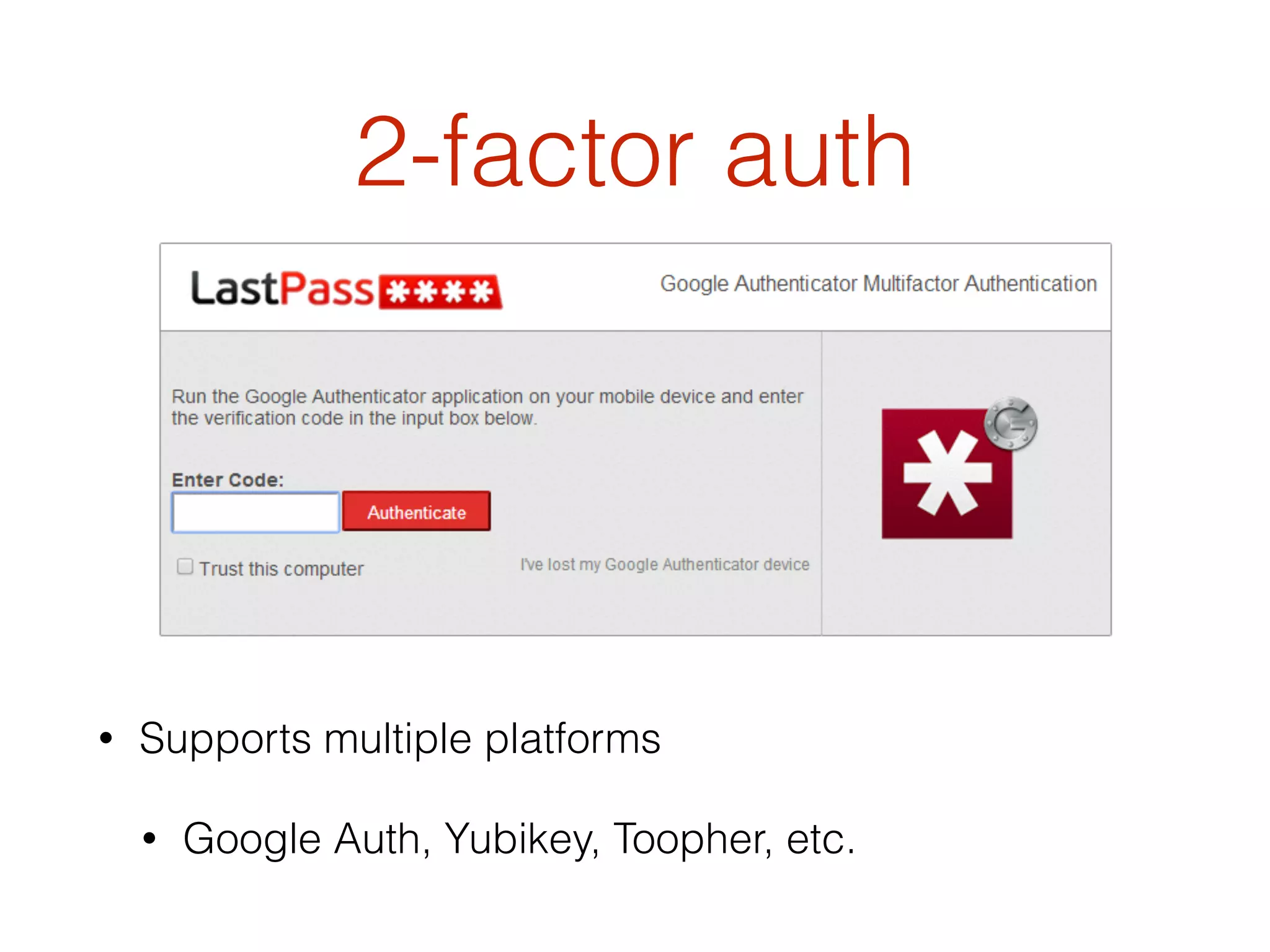
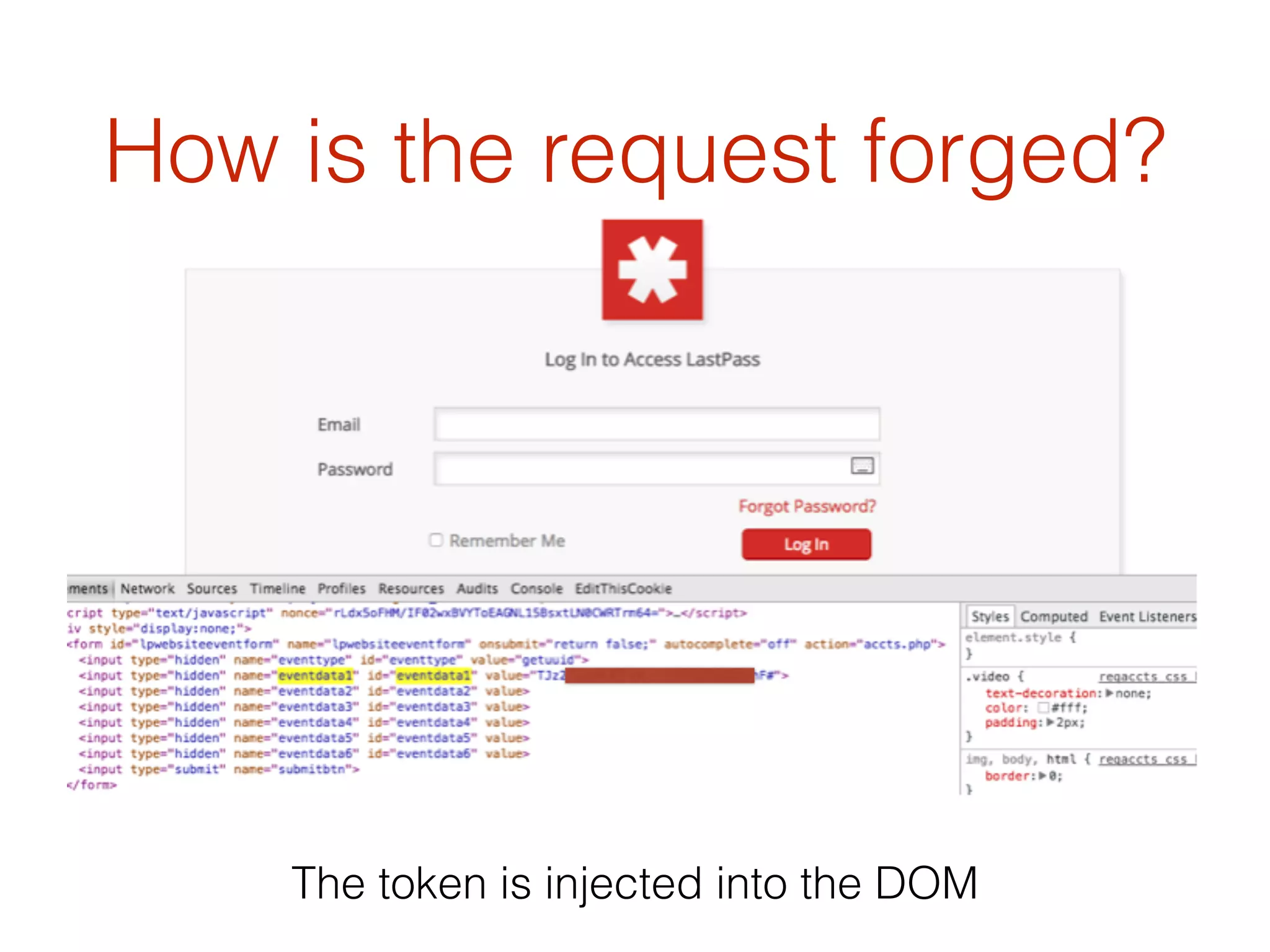
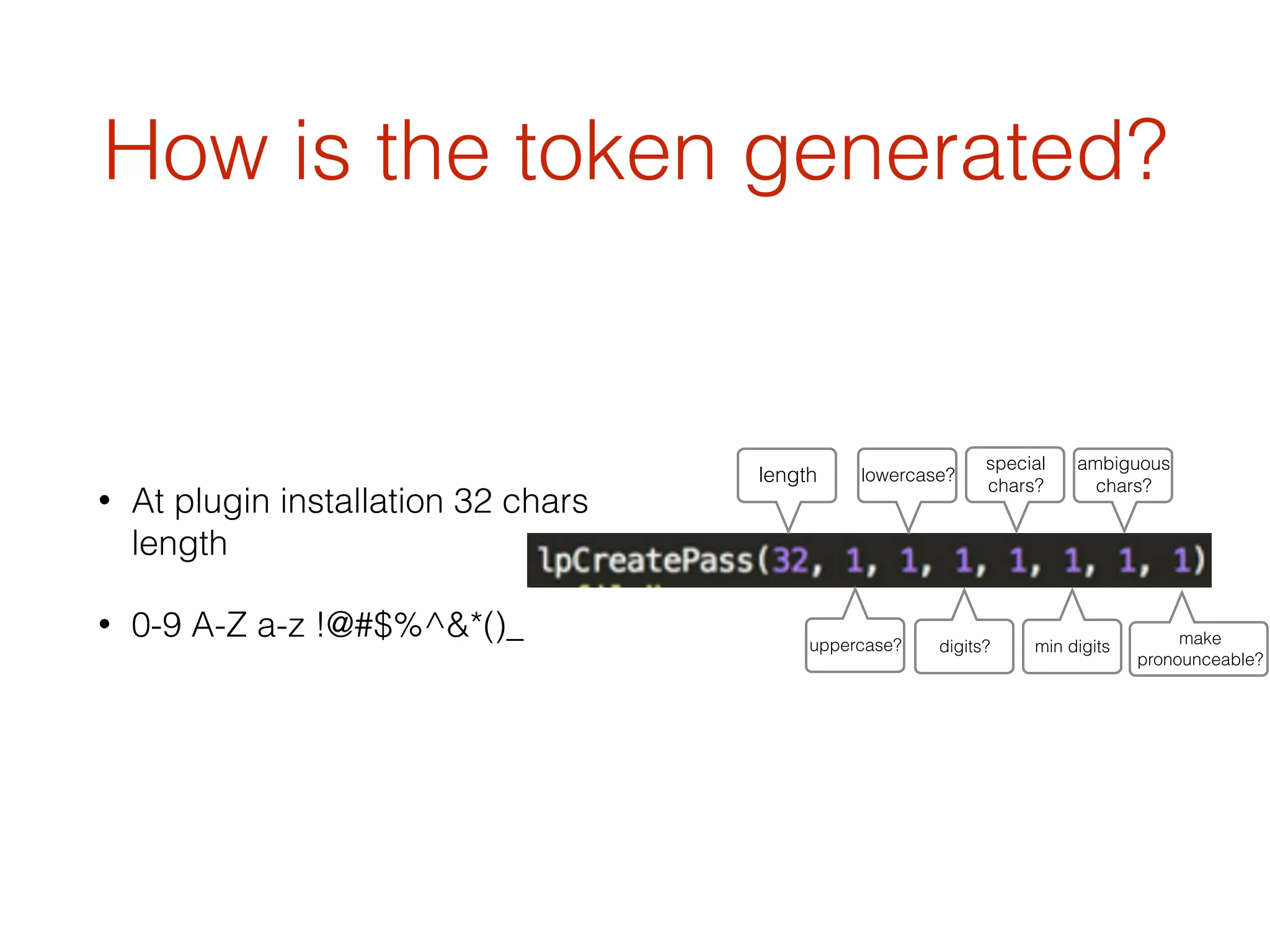
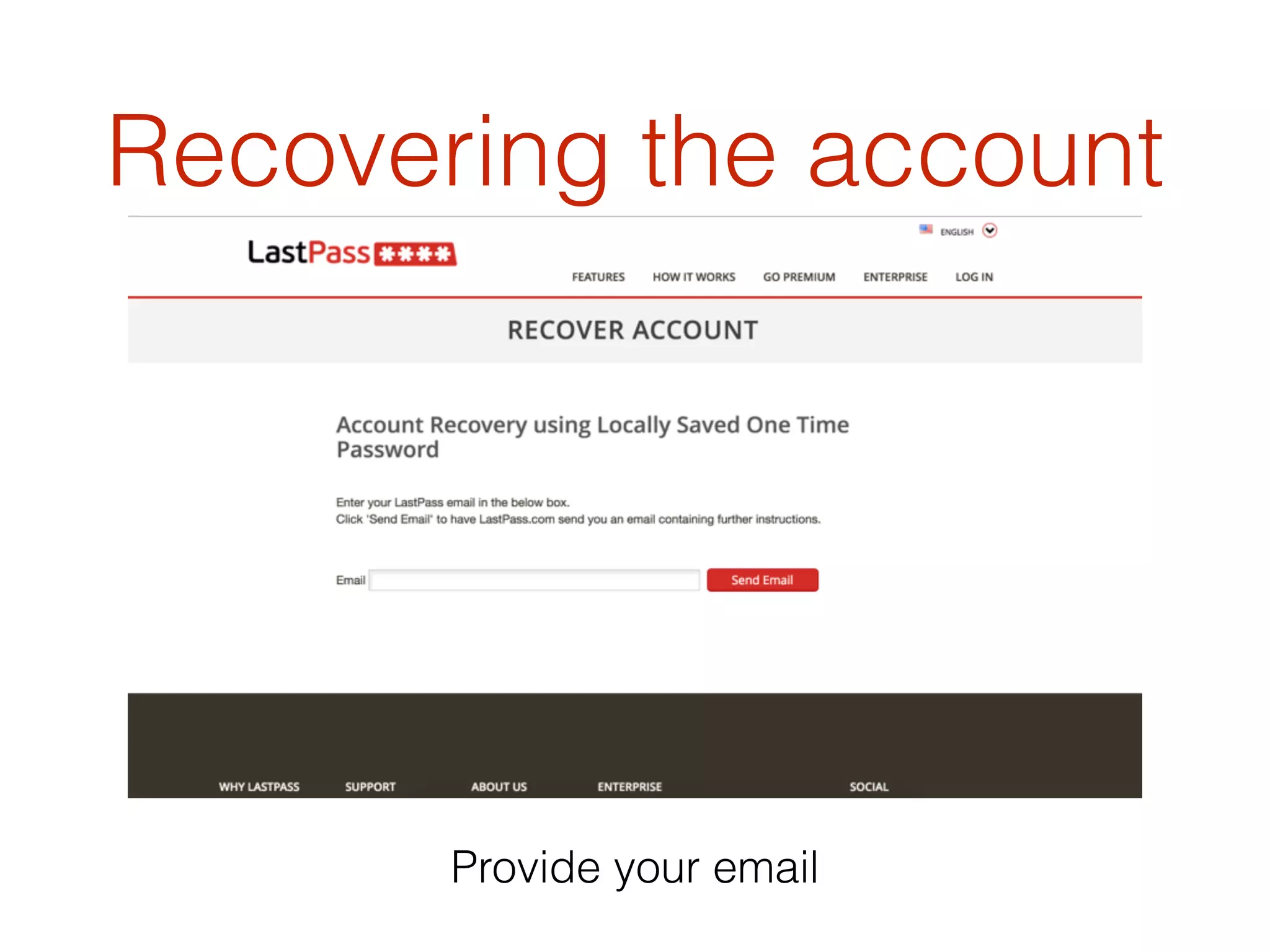
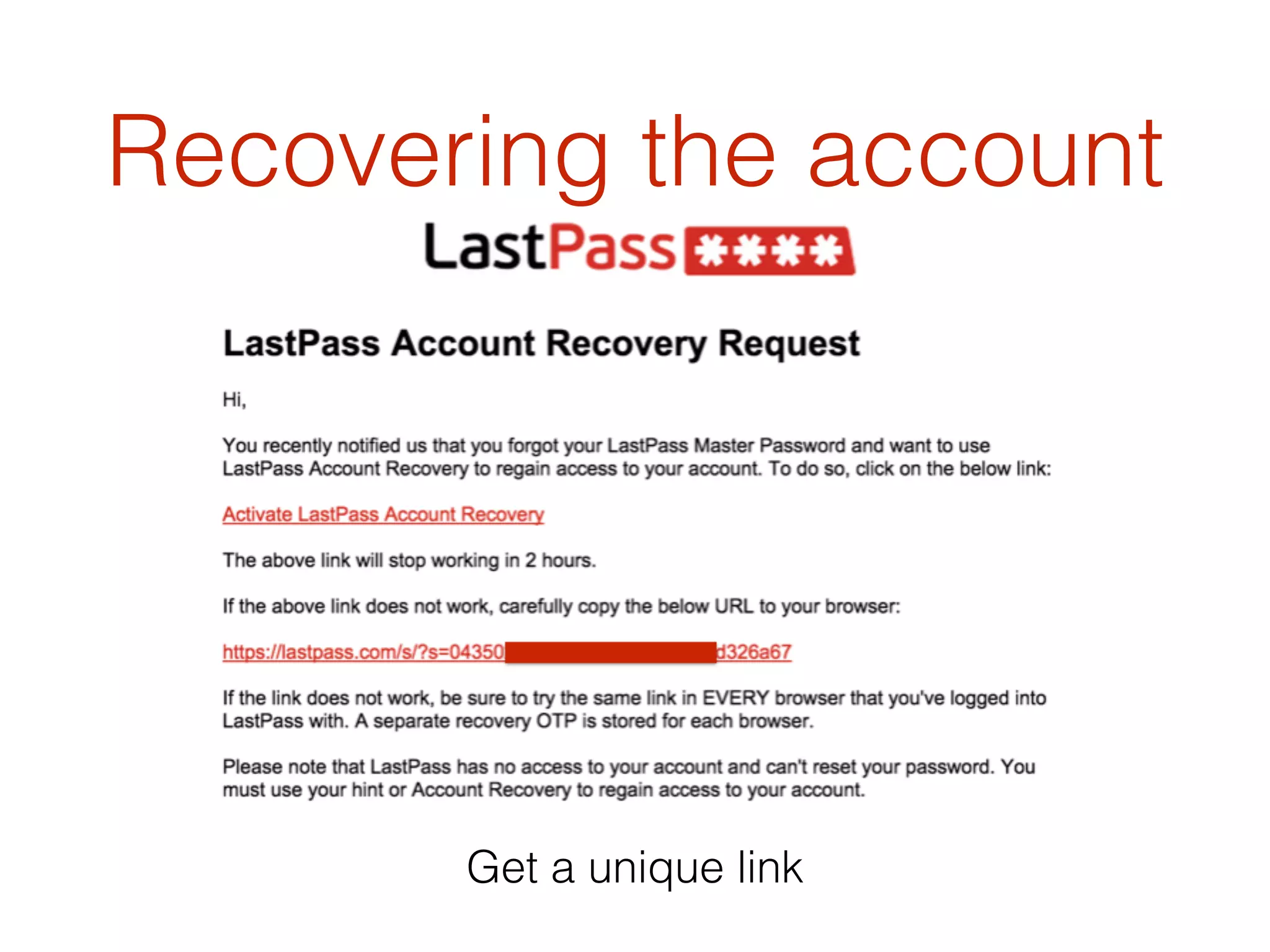
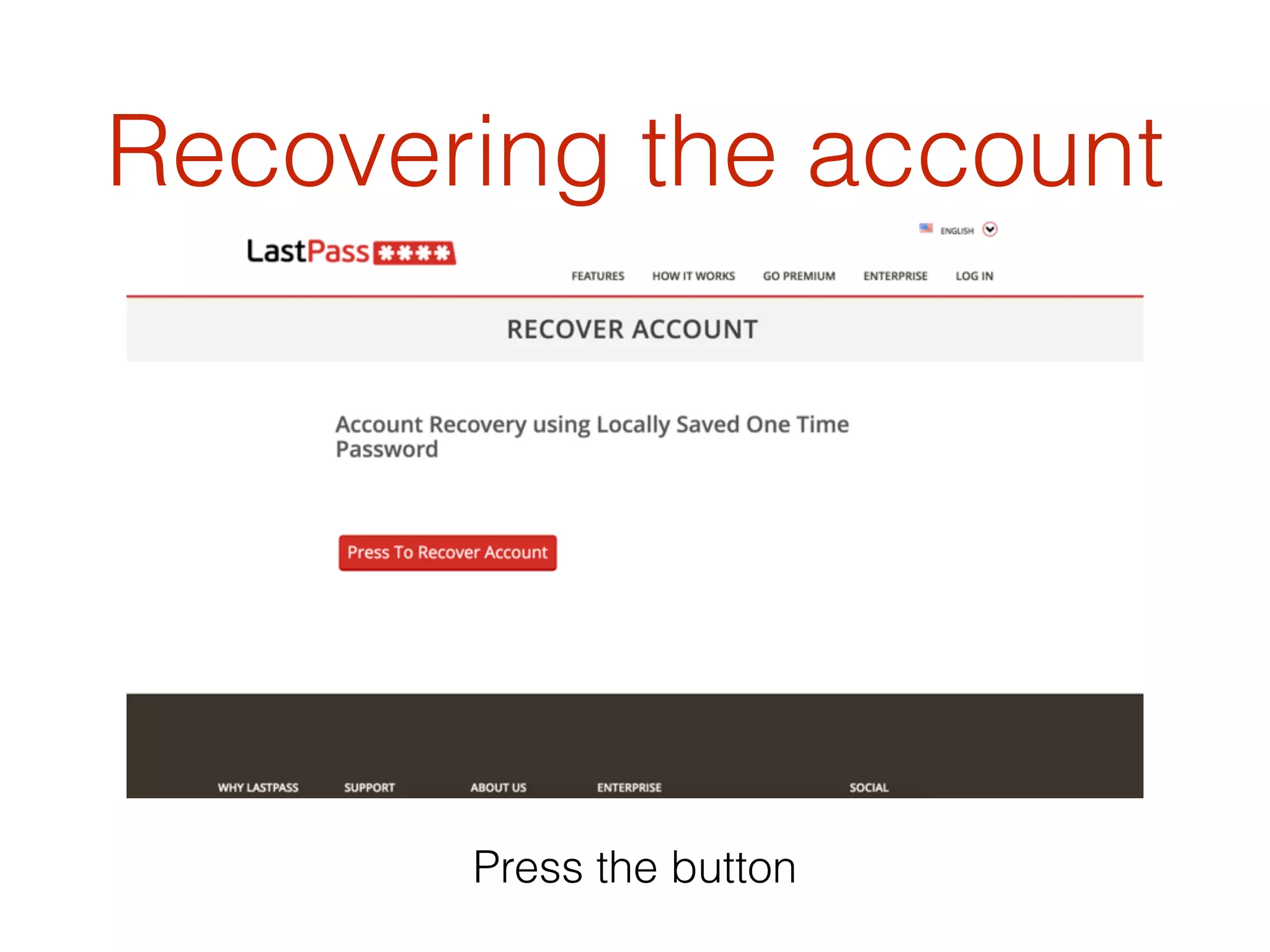
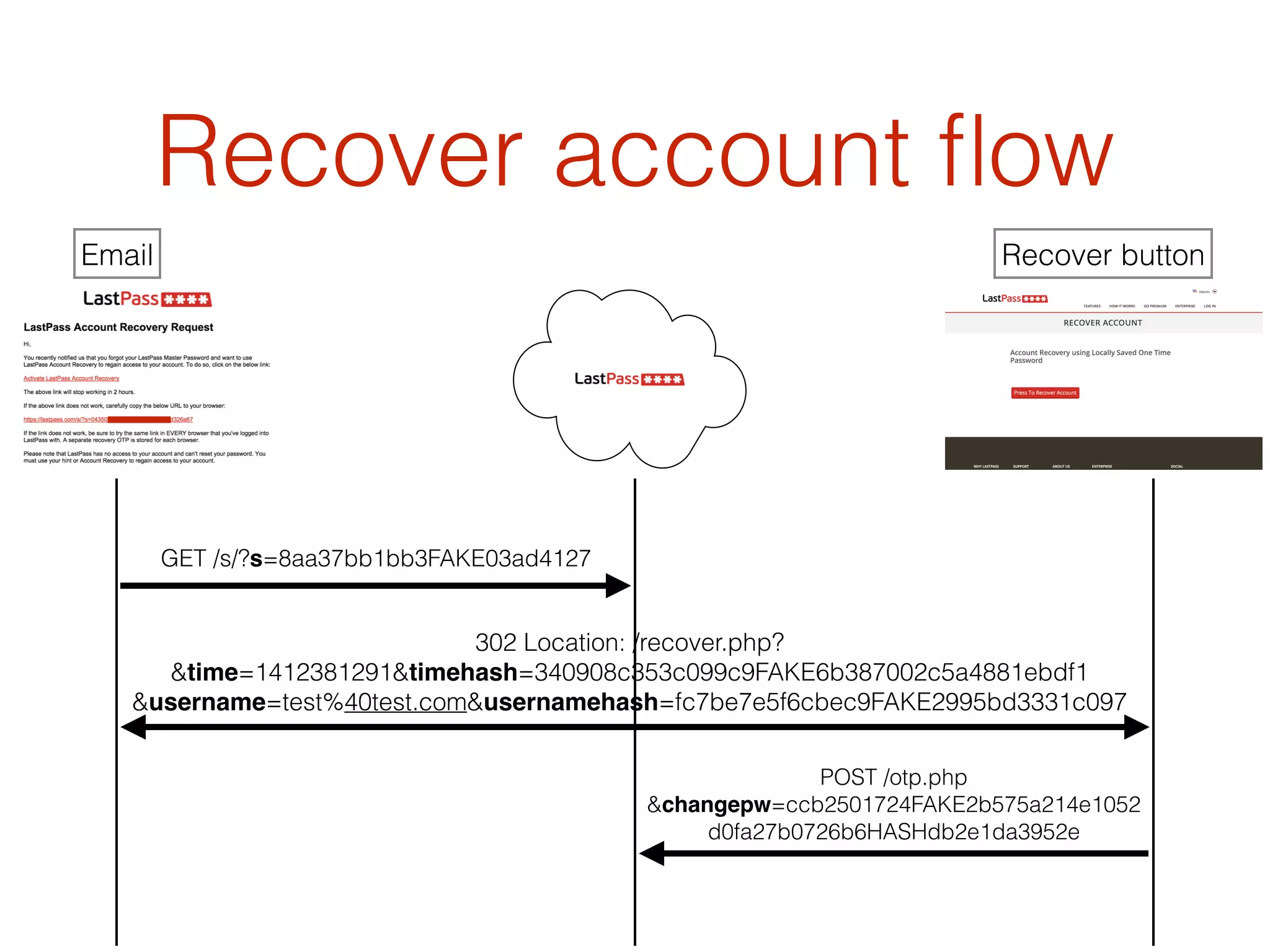
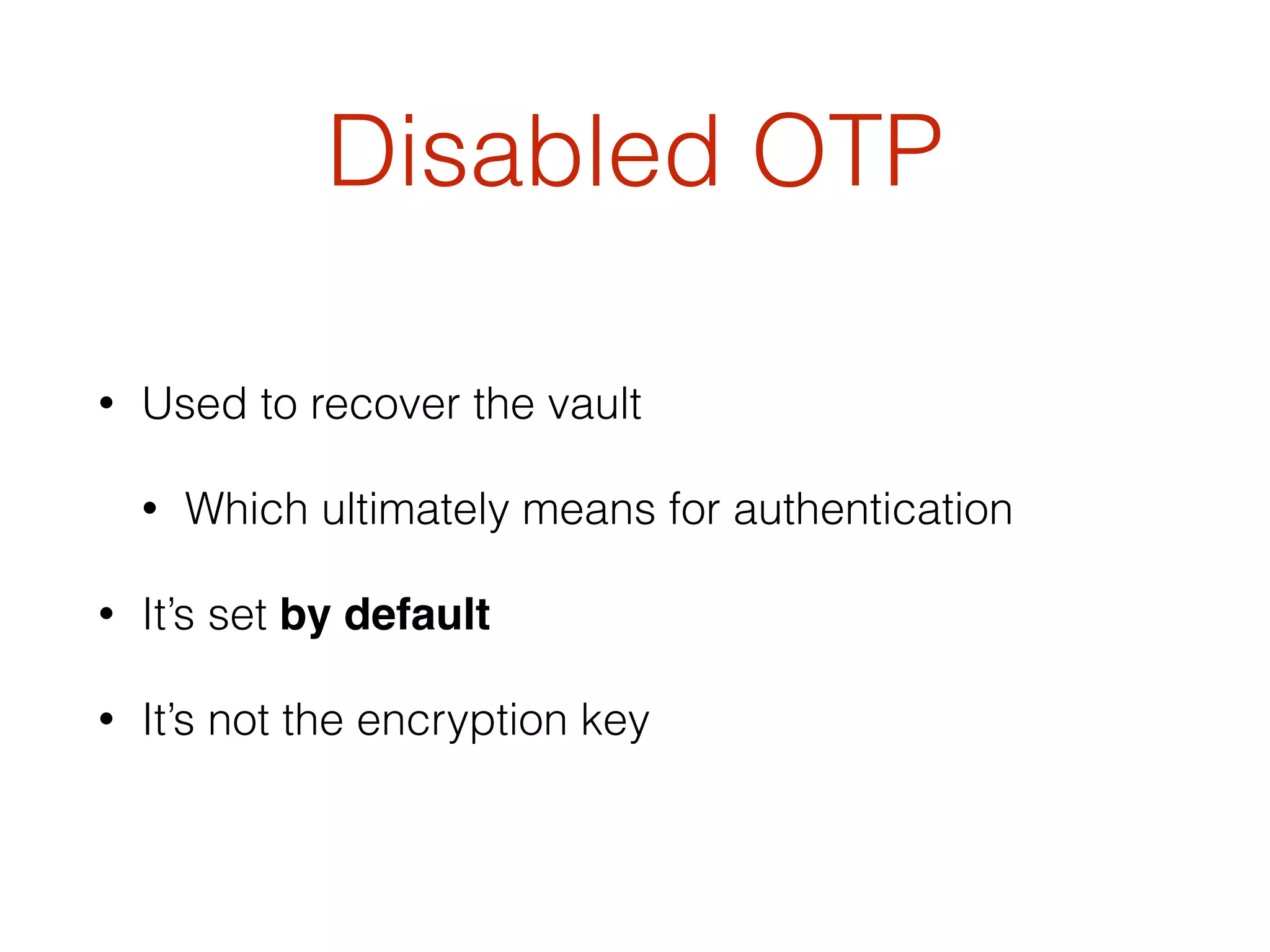
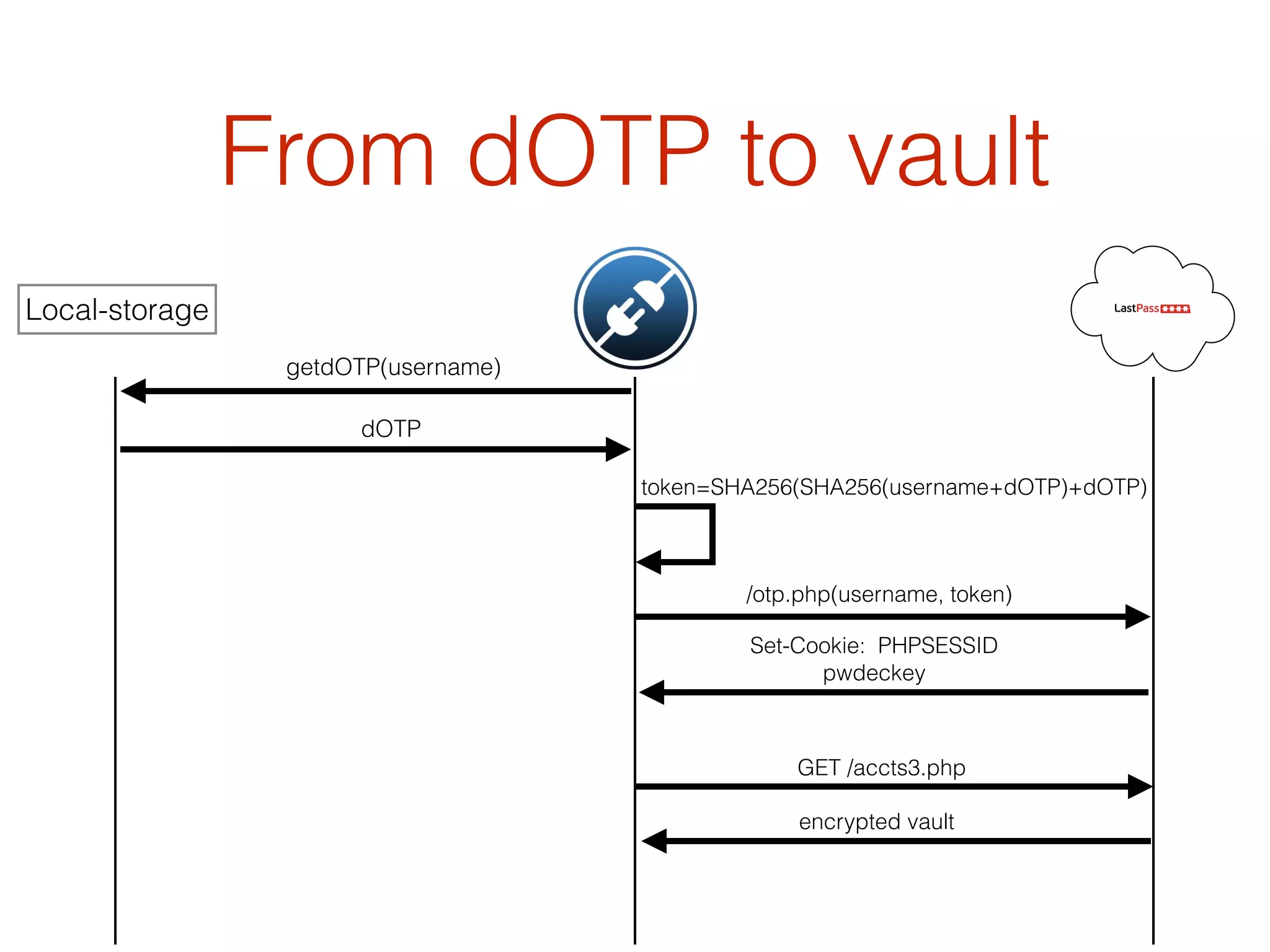
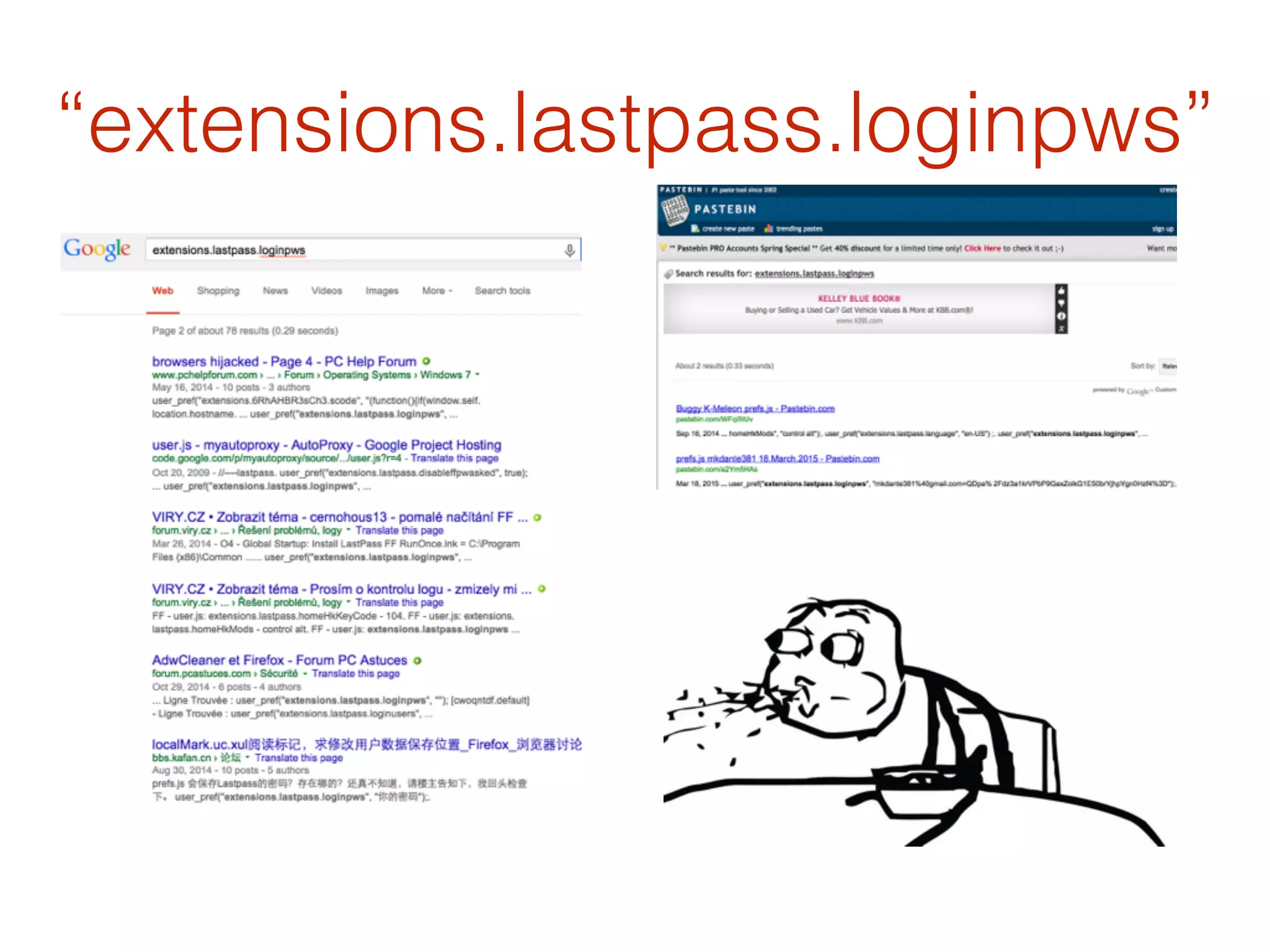
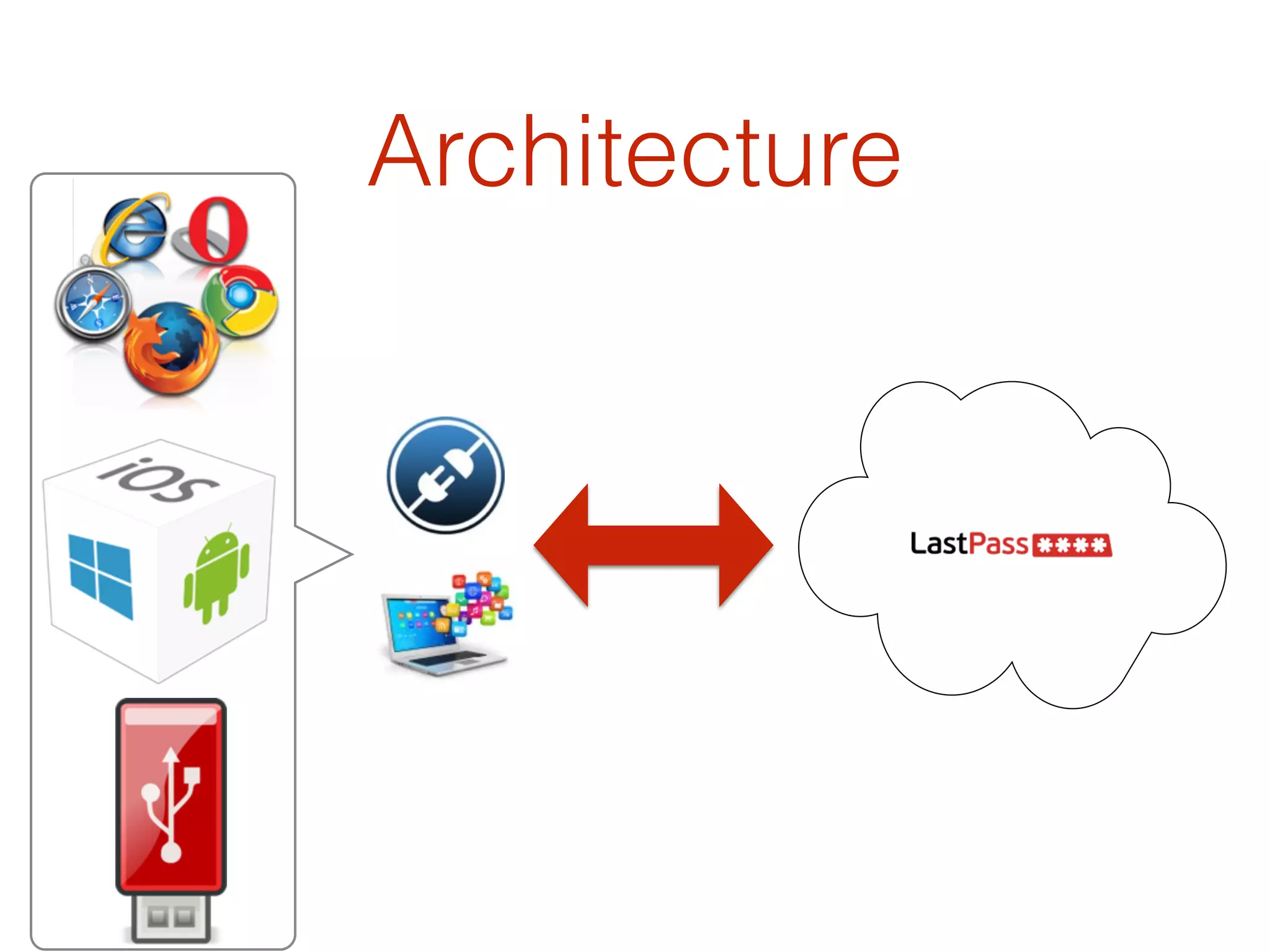
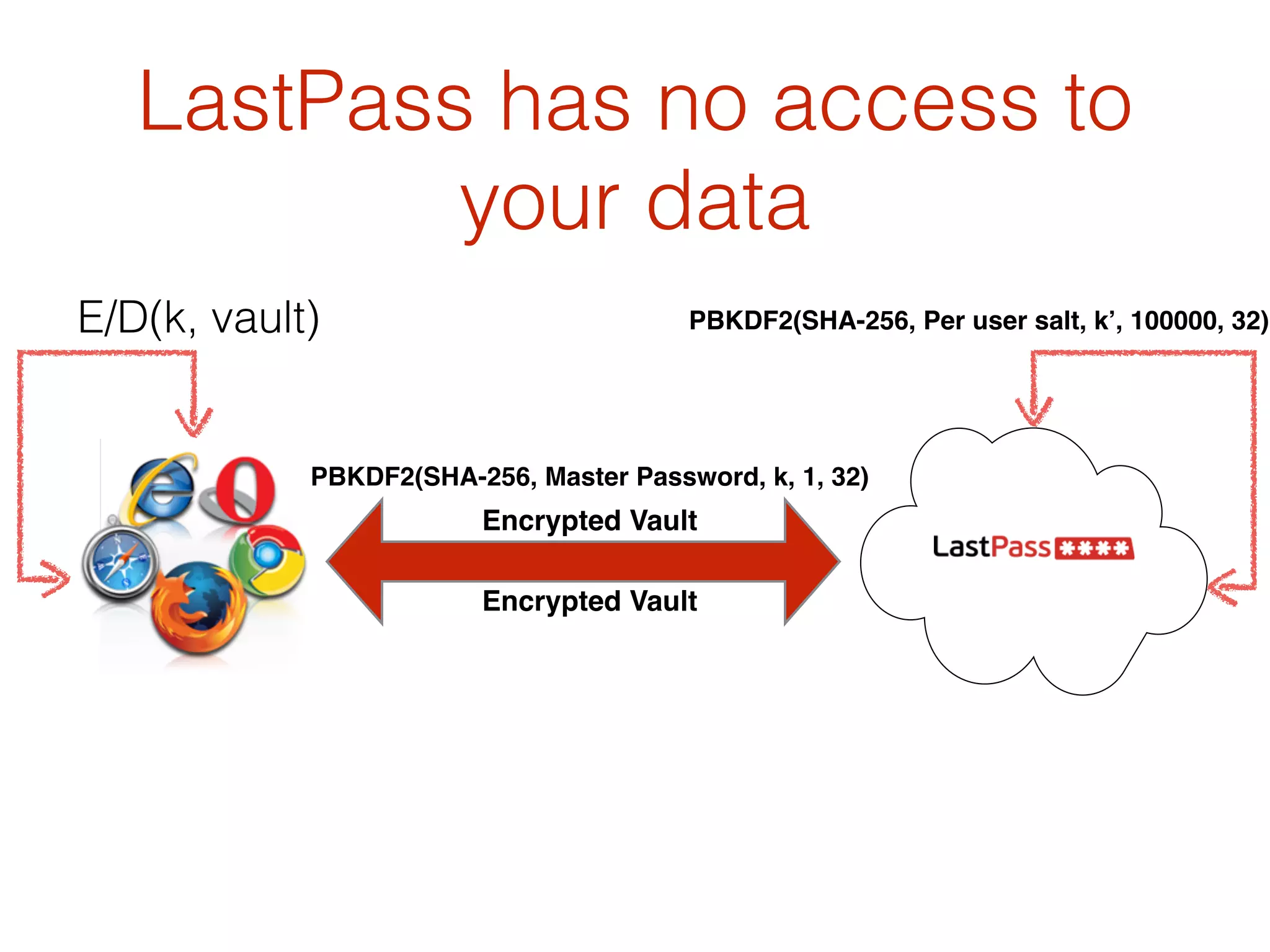
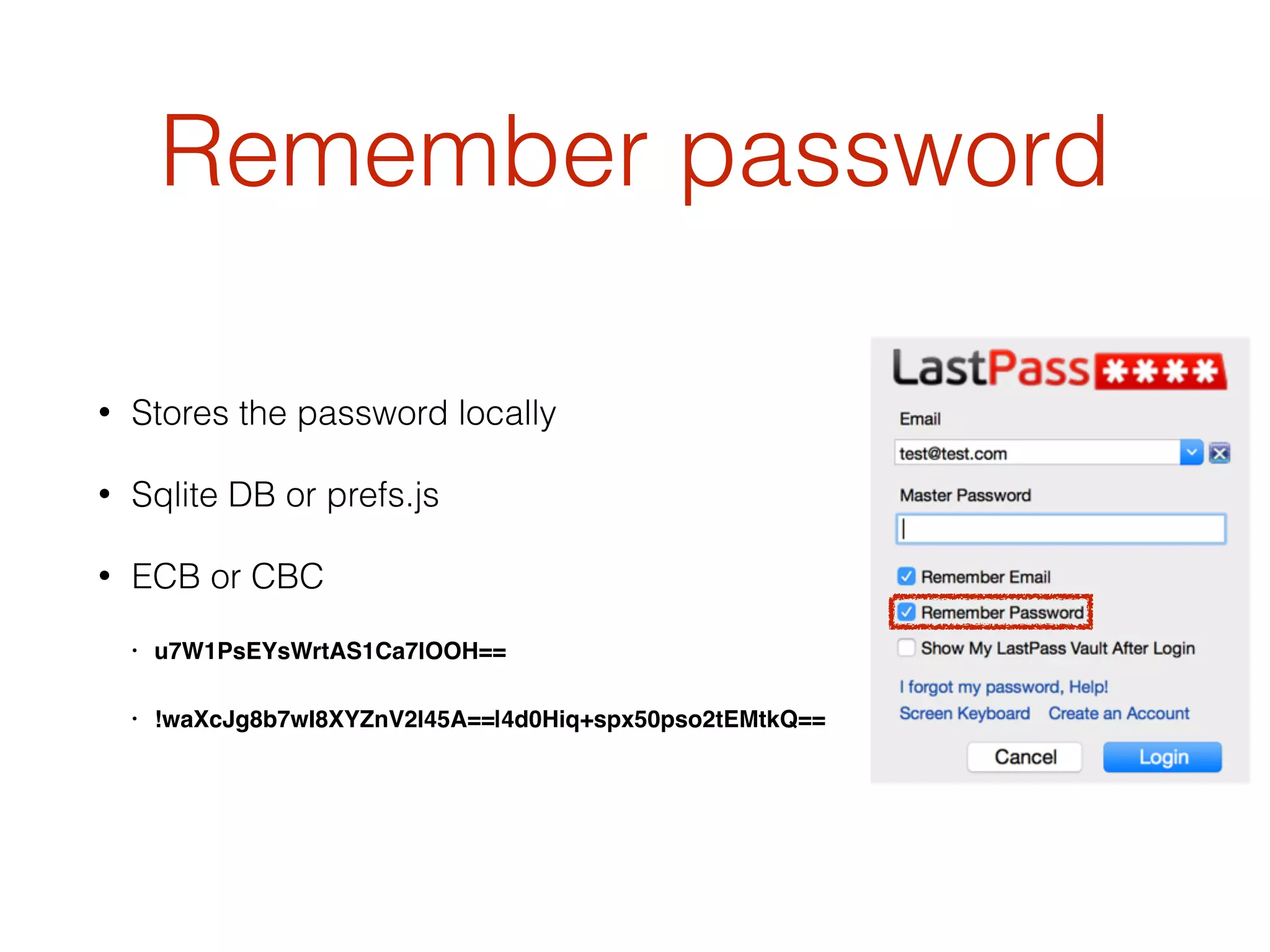
This document discusses the security vulnerabilities associated with LastPass, a popular password management service, highlighting how attackers can exploit various methods including DNS poisoning and XSS to gain access to users' sensitive information. It explains the architecture of LastPass, encryption mechanisms, and potential security failures, particularly focusing on the risks of stolen master passwords and bypassing two-factor authentication. The document concludes with recommendations for hardening LastPass security practices.










![siesta.py
• Beautifies every JS file
• Injects a payload to every function
• console.log([file] [function] [params])
• Credits to Alberto Garcia (@algillera)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/martinvigo-breakingvaults-stealinglastpassprotectedsecrets-150722215357-lva1-app6891/75/Breaking-Vaults-Stealing-Lastpass-Protected-Secrets-by-Martin-Vigo-14-2048.jpg)





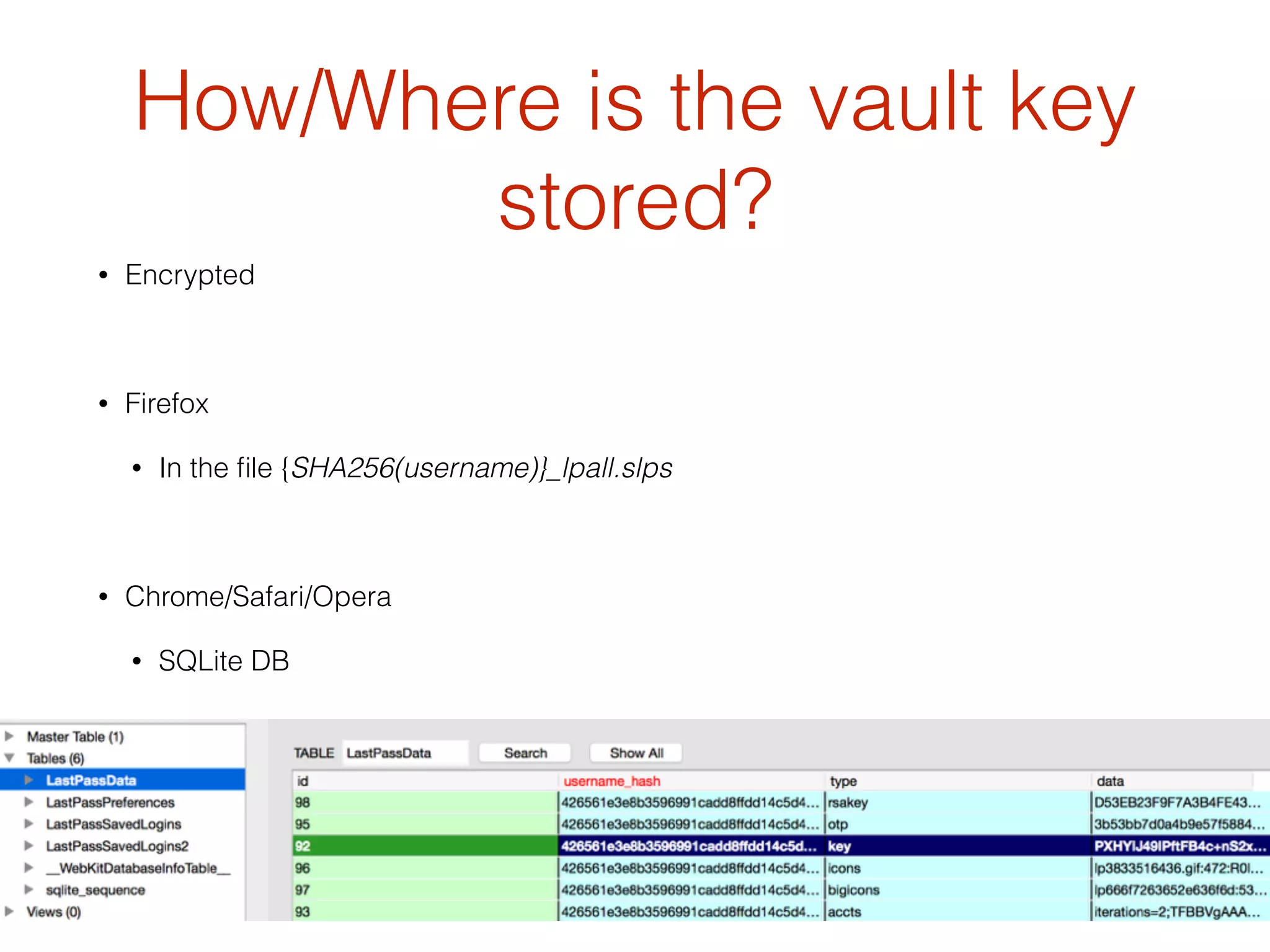
![Storage
Chrome Firefox Safari Opera
Windows
#{user_profile['LocalApp
Data']}/Google/Chrome/
User Data/Default/
databases/chrome-
extension_hdokiejnpimak
edhajhdlcegeplioahd_0
#{user_profile[
'AppData']}/
Mozilla/
Firefox/Profiles
#{user_profile['LocalAppData
']}/Apple Computer/Safari/
Databases/safari-
extension_com.lastpass.lpsaf
ariextension-n24rep3bmn_0
#{user_profile['AppData']}/
Opera Software/Opera
Stable/databases/chrome-
extension_hnjalnkldgigidg
gphhmacmimbdlafdo_0
Mac
#{user_profile['LocalApp
Data']}/Google/Chrome/
Default/databases/
chrome-
extension_hdokiejnpimak
edhajhdlcegeplioahd_0
#{user_profile['
LocalAppData']
}/Firefox/
Profiles
#{user_profile['AppData']}/
Safari/Databases/safari-
extension_com.lastpass.lpsaf
ariextension-n24rep3bmn_0
#{user_profile['LocalAppData']
}/com.operasoftware.Opera/
databases/chrome-
extension_hnjalnkldgigidggph
hmacmimbdlafdo_0
Unix
#{user_profile['LocalApp
Data']}/.config/google-
chrome/Default/
databases/chrome-
extension_hdokiejnpimak
edhajhdlcegeplioahd_0
#{user_profile['
LocalAppData']
}/.mozilla/firefox
#{user_profile[‘LocalApp
Data’]}/.opera/widgets/
wuid-*/pstorage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/martinvigo-breakingvaults-stealinglastpassprotectedsecrets-150722215357-lva1-app6891/75/Breaking-Vaults-Stealing-Lastpass-Protected-Secrets-by-Martin-Vigo-22-2048.jpg)