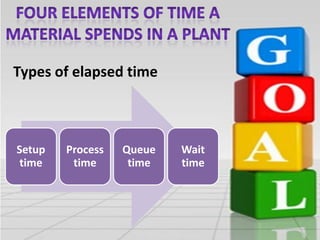
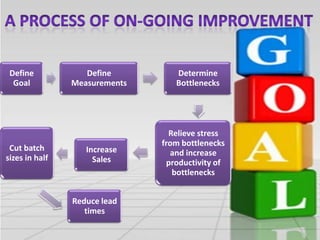
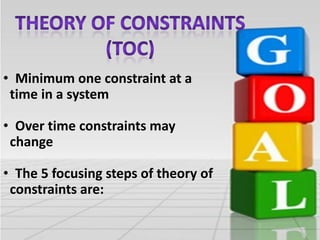
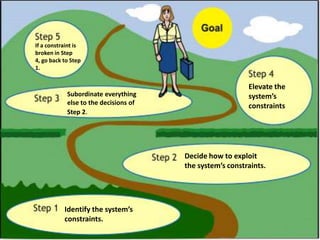
This document discusses the Theory of Constraints (TOC) developed by Eliyahu Goldratt. It introduces key concepts in TOC like bottlenecks, throughput, inventory, and operational expenses. It explains that bottlenecks limit the maximum speed of a process and must be identified and improved. The five focusing steps of TOC are identified as identifying the constraint, deciding how to exploit it, subordinating everything else to dealing with the constraint, elevating the system's constraints, and repeating the process if the constraint changes. Real-world examples are provided to illustrate how TOC can improve productivity and profitability.