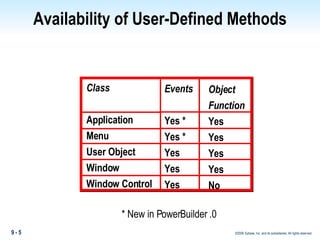
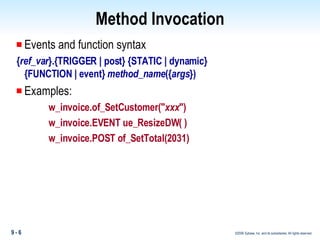
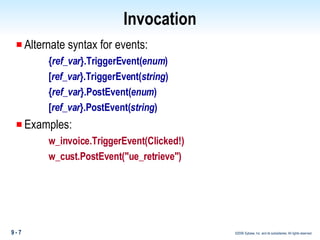
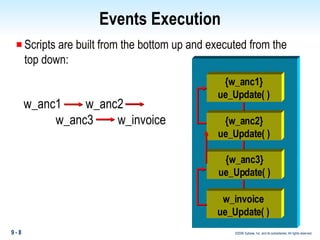
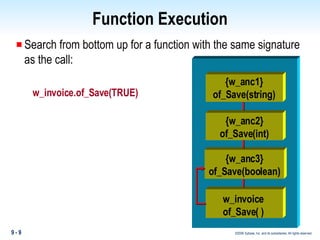
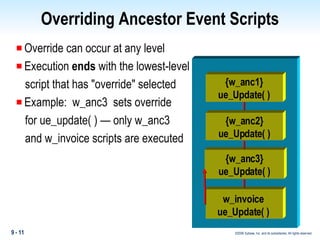
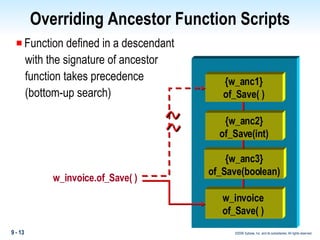
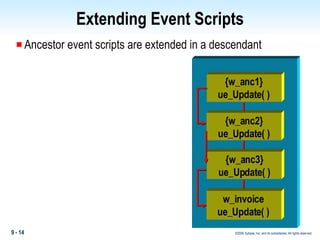
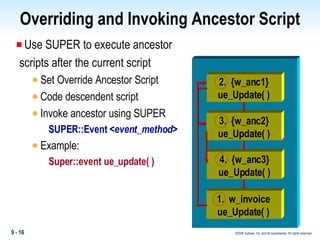
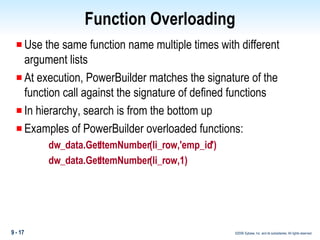
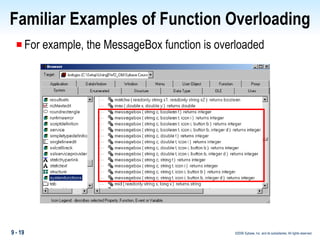
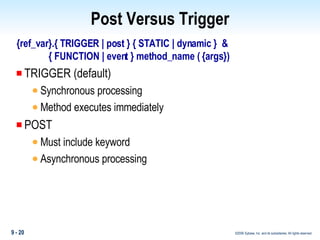
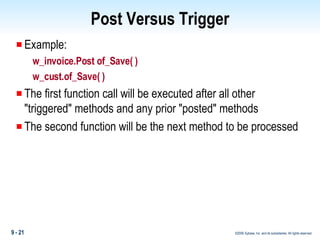
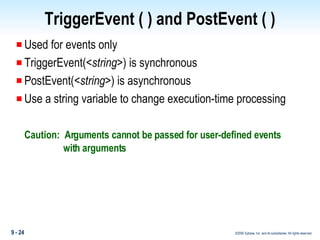
Methods in PowerBuilder include events and functions. Events are executed from the bottom-up while functions are searched for from the bottom-up based on signature. Descendent methods can override or extend ancestor methods. Functions can be overloaded with different argument lists to perform different tasks. Events and functions can be invoked synchronously with Trigger or asynchronously with Post.