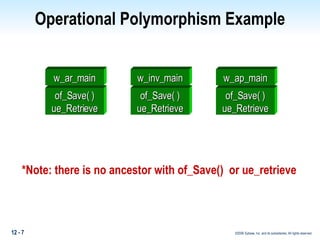
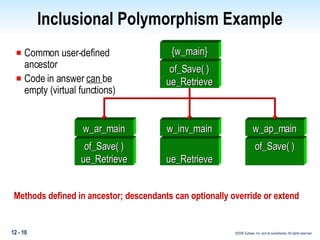
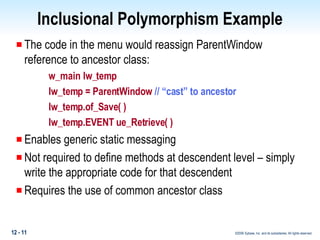
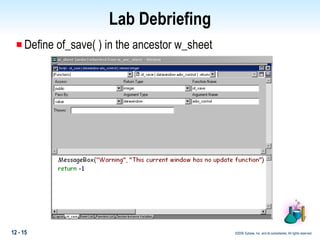
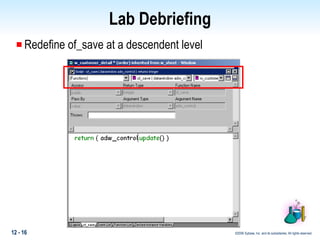
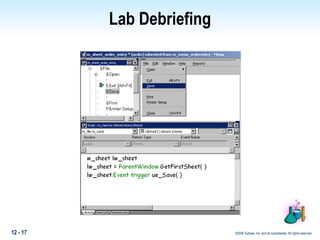
This document discusses polymorphism in PowerBuilder applications. Polymorphism allows the same method name to be used for different classes. Operational polymorphism uses the same method name for unrelated classes, while inclusional polymorphism uses inheritance and common ancestor classes. Inclusional polymorphism defines polymorphic methods in an ancestor class that descendant classes can optionally override or extend, allowing for generic messaging through the ancestor class. The document provides examples of implementing both operational and inclusional polymorphism using static and dynamic messaging.