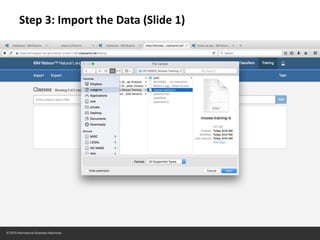
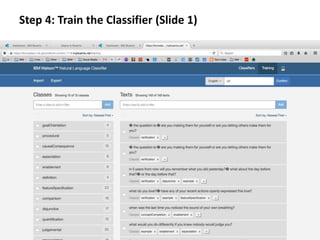
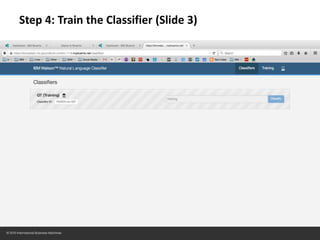
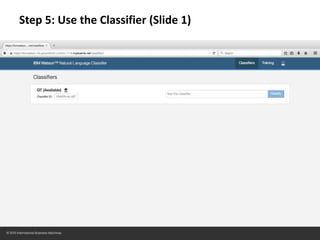
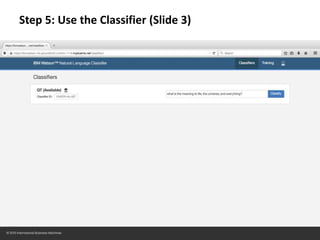
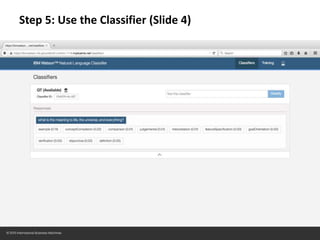
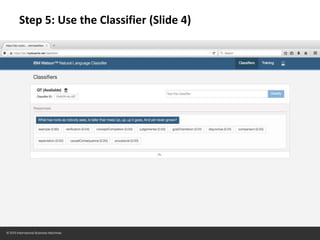
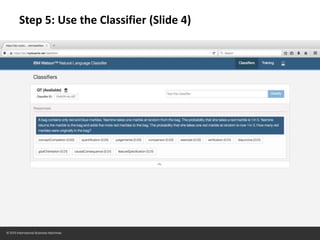
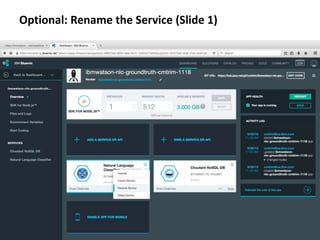
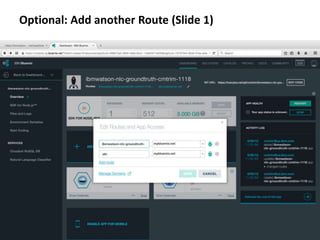
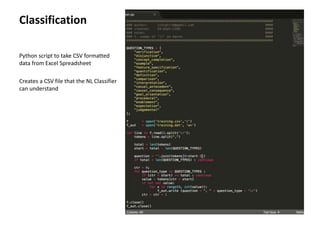
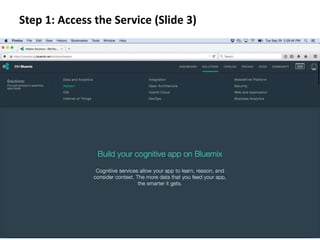
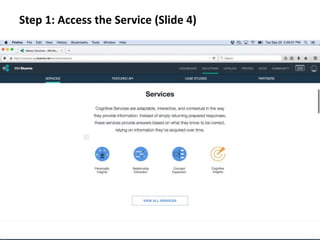
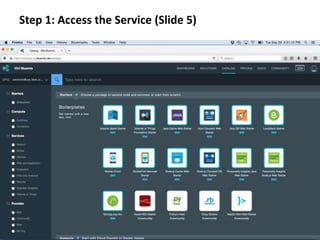
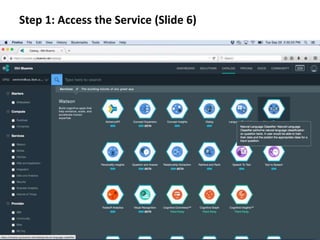
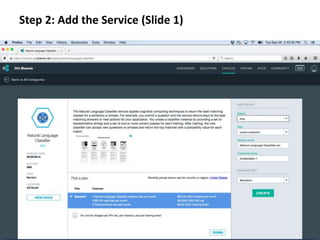
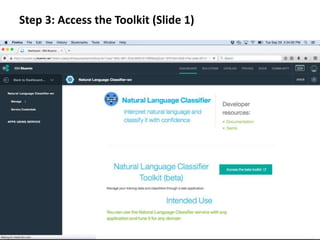
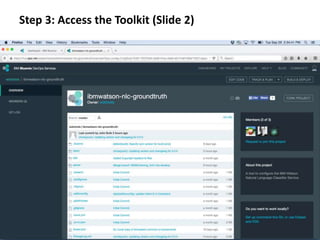
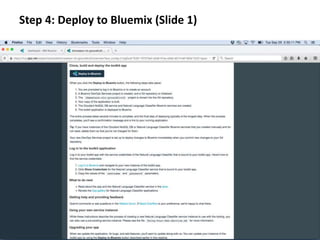
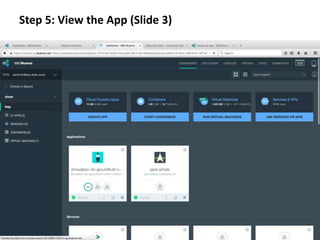
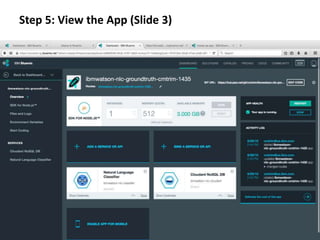
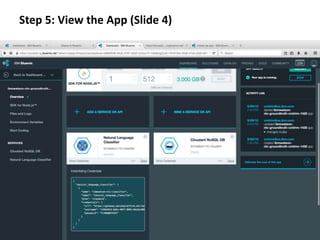
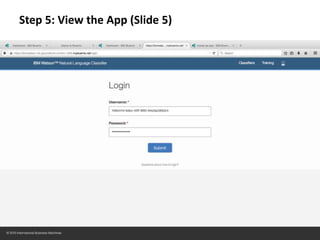
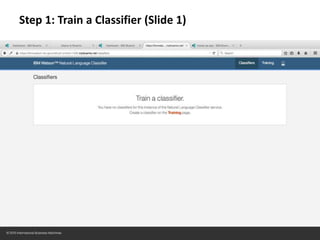
The document provides instructions for configuring a question type classifier on IBM Bluemix. It describes 15 common question types, how to prepare question data by formatting it as text-class pairs in a CSV file, and a 5-step process for deploying and training a classifier on Bluemix: 1) Access the service, 2) Add the service, 3) Access the toolkit, 4) Deploy the app, 5) View and use the trained classifier. Optional steps describe renaming the service, adding routes, and Java code for classification.





![Format
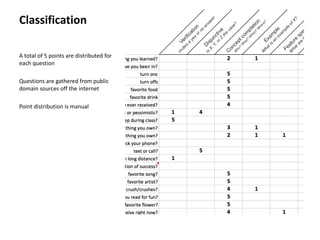
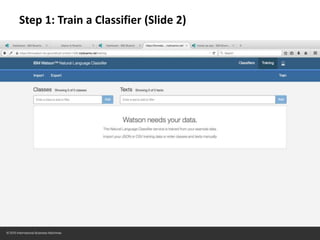
• The data format is:
text,class
• The text is the actual question
or user statement; some real
world example
• The class is the classification of
this real world example
– Only [A-Za-z0-9] are permitted
– Use “myClassName” rather than
“my_class_name”
• The text and the class are
comma separated, with the
text occurring first
Example
what is the difference between being
alive and truly living?,comparison
"when is it time to stop calculating
risk and rewards and just go ahead
and do what you know is
right?”,conceptCompletion
"when is it time to stop calculating
risk and rewards and just go ahead
and do what you know is
right?”,interpretation
"if we learn from our mistakes why
are we always so afraid to make a
mistake?”,enablement
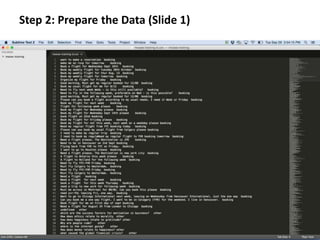
Step 2: Prepare the
Data (Slide 2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bluemixnlclassifiertutorial1-150930201058-lva1-app6892/85/Bluemix-NL-Classifier-Tutorial-29-320.jpg)